




|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
Jaspal S. Sandhu PhD

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/jaspal-sandhu/
Mandatory notification allergy forecast charlotte prednisolone 5mg free shipping, annual testing allergy medicine phenylephrine trusted 20mg prednisolone, the identification of carrier stallions and control of transmission from these animals allergy symptoms fall order 40 mg prednisolone amex, and selective vaccination are being used in New Zealand to eradicate equine viral arteritis allergy medicine rite aid buy prednisolone 20 mg online. Recommended actions if equine viral arteritis is suspected Last Updated: August 2009 © 2009 page 3 of 4 Equine Viral Arteritis Public Health There is no indication that equine arteritis virus can infect humans. Equine viral arteritis control scheme: a brief review with emphasis on laboratory aspects of the scheme in New Zealand. N Engl J Med 2003;349:160-169 Vasculitis 10 Giant Cell Arteritis Pathogenesis Weyand, C. N Engl J Med 2003;349:160-169 Vasculitis 11 Giant Cell Arteritis Pathogenesis Weyand, C. N Engl J Med 1997;337:1512-1523 Pulmonary Arteriolar Vasculitis Vasculitis 34 Necrotizing Glomerulonephritis* * "Pauci-immune" Glomerulonephritis Palpable Purpura Vasculitis 35 Palpable Purpura Necrotizing Arteritis in a Small Epineural Artery Jennette J and Falk R. No part of this publication may be reproduced, storedinaretrievalsystem, ortransmittedinanyformorbyanymeans (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise) without the prior written permission of the publisher. The treatment techniques produce a concentrated dose in the lesion with steep dose gradients external to the treatment volume. The rapid dose falloff from the edge of the treatment volume provides dramatic sparing of normal brain tissues. Heavy charged panicles, gamma rays, and megavoltage x rays have been used in the intervening decades to irradiate arteriovenous malformations as well as benign and malignant tumors. The first three-dimensional treatment of a brain lesion with a megavoltage unit took place in April 1948 (Kerst, 1975). The first combined use of an x-ray unit and stereotactic frame occurred in 1950 (Leksell, 1951, 1983). Safety precautions include the implementation of interlocks on the patient support assembly (couch) motion and the gantry motion, which limit the arc or rotation of the equipment and prevent patient injury. The quality assurance requirements demand that every step be checked by a physicist and independently rechecked by a 1 B. Introduction second expert (clinical medical physicist or a board-eligible medical physicist). A joint statement has been issued on this subject by the American Association of Neurological Surgeons and the American Society for Therapeufic Radiology and Oocology (Lunsford el al. The statement defines radiosurgery, but also recommends that training be received by the radiation oncologist and physicists. The location and geometry of the target is then transferred to a treatment planning system that calculates dose distributions in three dimensions. The treatment planning system must be capable of computing dose distributions from either the combination of noncoplauararcs or the intersection of the °Co beams, For linac-besed radiosurgery, the arc geometry can be varied to provide a concentrated dose to the selected target while minimizing the dose to critical structures surrounding the target. Acceptance testing requirements for the pedestal-mounted and couch-mounted frames are contained in Section V. For Administrators Table I contains time estimates for various tasks that are involved with commissioning a linac-based radiosurgery procedure. These time estimates deal solely with the time requirements for collecting the physical data and testing the hardware and software of a radiosurgery installation. For example, it is estimated that it would take approximately 10 weeks for a department with a scanning film densitometer and the appropriate ionization chambers to commission a commercial radiosurgery package. To fabricate the treatment hardware (the tertiary collimation system) for the stand or the couch mount systems would take approximately 0. To install a prefabricated hardware system and write a treatment planning software package for radiosurgery would take 2. To design the entire system in-house and install the hardware and software would require almost 3 yr. These time estimates do not include the background efforts regarding the coordination of the disciplines of radiation ontology, neurosargory, and neuroradiology. Finally, there are time estimates for planning and treating a typical radiosurgery patient. This begins with acquiring imaging data early in the day, entering the data sets into the computer, establishing the appropriate contours and surfaces of the tumor and normal tissue structures developing a plan, and reviewing the plan with the radiation oncologists, the neurosurgeons, and finally treating the patient. The time requirements for treating a typical patient per week amounts to 20% of a typical weekly patient load. This procedure represents a significant increase in the staffing requirements of the physics section of the department of radiation oncology, We recommend an additional 0. Radiosurgery is a very time-consuming procedure requiring a high degree of attention to detail, the consequences of understaffing and misadministration are a significant "" and grave risk to the patient. Nonmalignant Lesions Stereotactic radiosurgery has been used for nonmalignant lesions such as arteriovenous malformations and acoustic neuromas. Arteriovenous malformations are congenital anomalies that develop from aberrant connections within the primitive arterial and venous plexus overlying the developing cortical mantle. During embryological maturation, this region of abnormal vasculature is incorporated into the brain parenchyma. Kihlstrom reported 1311 gamma knife unit radiosurgical procedures performed at Karolinska Hospital between 1968 and 1986 (Kihlstrom, 1986). The natural history of inoperable arteriovenous malformations may be favorably influenced by radiosurgery as discussed below. The role of radiosurgery in radiation oncology may be analogous to that of interstitial brain implants as a high-dose boost following the standard course of exterhal beam therapy (Halperin et al. Their preliminary findings were that no significant toxicities were encountered and the necrosis rate was 10% at a follow-up of 13. The mechanical position uncertainty in any orthogonal axis of a stcreotactic frame is 0. The gantry rotation axis, collimator rotation axis, and table rotation axis should coincide within a sphere of 1 mm radius. The l-ram limit derives from the radiologists ability to identify a unique poim from two views. However, the extent of the nidus cannot be determined frmn the orthogonal radiographs, preventing the optimum plan of irradiating the target while sparing normal tissue. Similar uncertainties exist for certain brain tumors, but it is caused by the invasive nature of the malignancies. In nine cases, autopsies indicated that the tumor extended beyond a I-cm margin around the contrast-enhancing areas. Furthermore, the differences between survival rates for whole brain irradiation versus partial brain irradiation are not statistically signifi- Accuracy limits not only reflect the technical limitations of the frames and treatment units, but also reflect the current knowledge of the neurological abnormality and its radiation response. Although the techniques differ in accuracy, it is unclear whether the difference is clinically significant. The uncertainty in dose delivery is a result of two processes: (I) target definition and (2) the machine tolerances of the dose delivery apparatus (including the frame). The accuracyof patient setup in conventionalexternal beam therapy has been investigated by several groups, including that of. The variation in setup was determined from the differences between simulation and port films. However, the average discrepancy between the simulation films and port films was 5 mm when the brain was the treatment site. Hence, the benefit of stereotactic 1ocalization and treatment is the ability to plan and treat a target with reduced position uncertainty. This lack of difference between treatments is a resultof the failure of externalbeam therapy to control bulky disease. The accuracy in dose delivery to the target of linac-based radiosurgery is a significant improvement over conventional techniques and approaches that of the heavy-charged:particle facilities. Until technology affords accurate target localization, the differences in position accuracy wig have minimal impact on treatment delivery. However, the impact of the net positionaccuracyon the planning processshould be foremostin the mindsof the oncologistand physicist. Two basic approaches have been taken in the tertiary collimation and stereotactic frame system or (2) the use of a dedicated a Co unit. Linac-based radiosurgery delivers a narrowly collimated xray beam while rotating about the target. The process is repeated for a number of treatment couch angles, Thus, the target is caught in a cross fire of x-ray beams which past: (1)modification deliver a lethal dose toof standardand a sublethal dose to the surrounding the target linear acceleratorswith the addition of normal tissues. The gamma knife unit delivers a comparable dose by means of the simultaneous irradiation from 201 cobalt beams. The dose distribufrom up to 201 Co sources (gamma knife unit shown in Figure 1) or of the multiple arcs from a linear accelerator. Figure 2 illustrates the beam entry patterns for (I) the gamma knife unit; tion a single 360 ° arc a in the transverse plane by the intersection (3) a four (2) is concentrated in localized small volume of the patient; of beams ) noncoplanar arc geometry; and (4) the dynamic radiosurgery approach (b, a, e, and g, respectively in Figure 2).
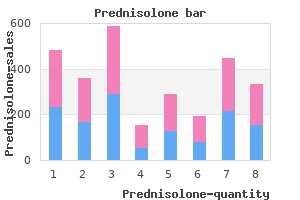
Emerging adults in European societies make the most of these advantages allergy medicine brands names 40mg prednisolone with amex, gradually making their way to adulthood during their twenties while enjoying travel and leisure with friends allergy throat treatment buy prednisolone 5 mg. Like European emerging adults allergy treatment to cats cheap prednisolone 40 mg amex, Asian emerging adults tend to enter marriage and parenthood around age 30 (Arnett allergy kvue generic prednisolone 5mg, 2011). Like European emerging adults, Asian emerging adults in Japan and South Korea enjoy the benefits of living in affluent societies with generous social welfare systems that provide support for them in making the transition to adulthood, including free university education and substantial unemployment benefits. In contrast, Asian cultures have a shared cultural history emphasizing collectivism and family obligations. Although Asian cultures have become more individualistic in recent decades, as a consequence of globalization, the legacy of collectivism persists in the lives of emerging adults. They pursue identity explorations and self-development during emerging adulthood, like their American and European counterparts, but within narrower boundaries set by their sense of obligations to others, especially their parents (Phinney & Baldelomar, 2011). For example, in their views of the most important criteria for becoming an adult, emerging adults Is your culture one that promotes romantic relationships for in the United States and Europe consistently emerging adults? According to Rankin and Kenyon (2008), historically the process of becoming an adult was more clearly marked by rites of passage. However, these role transitions are no longer considered the important markers of adulthood (Arnett, 2001). Economic and social changes have resulted in more young adults attending college (Rankin & Kenyon, 2008) and a delay in marriage and having children (Arnett & Taber, 1994; Laursen & Jensen-Campbell, 1999) Consequently, current research has found financial independence and accepting responsibility for oneself to be the most important markers of adulthood in Western culture across age (Arnett, 2001) and ethnic groups (Arnett, 2004). College students who had placed more importance on role transition markers, such as parenthood and marriage, belonged to a fraternity/sorority, were traditionally aged (1825), belonged to an ethnic minority, were of a traditional marital status; i. These findings supported the view that people holding collectivist or more traditional values place more importance on role transitions as markers of adulthood. In contrast, older college students and those cohabitating did not value role transitions as markers of adulthood as strongly. The current trend is that young Americans are not choosing to settle down romantically before age 35. Since 1880, living with a romantic partner was the most common living arrangement among young adults. Another 14% of early adults lived alone, were a single parent, or lived with one or more roommates. The remaining 22% lived in the home of another family member (such as a grandparent, in-law, or sibling), a non-relative, or in group quarters. Comparing ethnic groups, 36% of black and Hispanic early adults lived at home, while 30% of white young adults lived at home. In 2014, 35% of young me were residing with their parents, while 28% were living with a spouse or partner in their own household. Young women were more likely to be living with a spouse or partner (35%) than living with their parents (29%). Additionally, more young women (16%) than young men (13%) were heading up a household without a spouse or partner, primarily because 250 women are more likely to be single parents living with their children. Lastly, young men (25%) were more likely than young women (19%) to be living in the home of another family member, a non-relative, or in some type of group quarters (Fry, 2016). First, early adults are postponing marriage or choosing not to marry or cohabitate. Lack of employment and lower wages have especially contributed to males residing with their parents. Wages for young men (adjusting for inflation) have been falling since 1970 and correlate with the rise in young men living with their parents. The recent recession and recovery (2007-present) has also contributed to the increase in early adults living at home. College enrollments increased during the recession, which further increased early adults living at home. However, once early adults possess a college degree, they are more likely to establish their own households (Fry, 2016). Learning Objectives: Physical Development in Emerging and Early Adulthood · · · · · · · · · · · Summarize the overall physical growth in early adulthood Describe statistics, possible causes, and consequences of obesity Explain how early adulthood is a healthy, yet risky time of life Identify the risk factors for substance use Describe the changes in brain maturation Describe gender in adulthood, including gender minorities and stress Define sexuality and explain the female and male reproductive systems Describe the brain areas and hormones responsible for sexual behavior Identify sexually transmitted infections Describe cultural views related to sexuality Describe research on sexual orientation the Physiological Peak People in their mid-twenties to mid-forties are considered to be in early adulthood. By the time we reach early adulthood, our physical maturation is complete, although our height and weight may increase slightly. Those in their early twenties are probably at the peak of their physiological development, including muscle strength, reaction time, sensory abilities, and cardiac functioning. The reproductive system, motor skills, strength, and lung capacity are all operating at their best. Most professional athletes are at the top of their game during this stage, and many women have children in the early-adulthood years (Boundless, 2016). For example, the lens of the eye starts to stiffen and thicken, resulting in changes in vision (usually affecting the ability to focus on close objects). Hair can start to thin and become gray around the age of 35, although this may happen earlier for some individuals and later for others. The skin becomes drier and wrinkles start to appear by the end of early adulthood. This includes a decline in response time and the ability to recover quickly from physical exertion. The immune system also becomes less adept at fighting off illness, and reproductive capacity starts to decline (Boundless, 2016). Obesity Although at the peak of physical health, a concern for early adults is the current rate of obesity. Results from the National Center for Health Statistics indicated that an estimated 70. The current statistics are an increase from the 2013-2014 statistics that indicated that an estimated 35. The average man in his 20s weighs around 185 pounds and by his 30s weighs approximately 200 pounds. The average American woman weighs 162 pounds in her 20s and 170 pounds in her 30s. This translates to 266 million obese men and 375 million obese women in the world, and more people were identified as obese than underweight. Societal factors include culture, education, food marketing and promotion, the quality of food, and the physical activity environment available. Behaviors leading to obesity include diet, the amount of physical activity, and medication use. Rather, research has identified variants in several genes that may contribute to obesity by increasing hunger and food intake. The genes that helped our ancestors survive occasional famines are now being challenged by environments in which food is plentiful all the time. Overall, obesity most likely results from complex interactions among the environment and multiple genes. Additionally, the medical care costs of obesity in the United States were estimated to be $147 billion in 2008. However, the top five causes of death in emerging and early adulthood are non-intentional injury (including motor vehicle accidents), homicide, and suicide with cancer and heart disease completing the list (Heron, & Smith, 2007). Rates of violent death (homicide, suicide, and accidents) are highest among young adult males, and vary by race and ethnicity. Rates of violent death are higher in the United States than in Canada, Mexico, Japan, and other selected countries. Males are 3 times more likely to die in auto accidents than are females (Frieden, 2011). Heavy drinking is defined as drinking five or more drinks on the same occasion on each of five or more days in the past 30 days. Nearly 88,000 people (approximately 62,000 men and 26,000 women) die from alcohol-related causes annually, making it the fourth leading preventable cause of death in the United States. In 2014, alcohol-impaired driving fatalities accounted for 9,967 deaths (31% of overall driving fatalities). This typically occurs after four drinks for women and five drinks for men in approximately two hours. In 2014, 25% of people ages 18 or older reported that they engaged in binge drinking in the past month.
Neurotoxic ptosis results from a venom reaction from cobras or kraits and Pseudo ptosis results from lack of lid support or a higher lid position from external measures allergy shots pet dander 5mg prednisolone mastercard. Trauma to the 3rd cranial nerve or muscles of the eyelid in-utero or during the birth process allergy testing on child buy prednisolone 20mg visa, along with an underlying brain tumor allergy testing hives effective 10mg prednisolone, diabetes mellitus or other myasthenia conditions are rare allergy testing greenville sc buy generic prednisolone 20 mg on-line. Patient visits for Ptosis ate and appropriately determine listings and chiropractic techniques to administer for the purpose of normalizing neural input for proper eye mechanics. Following surgery, patients are monitored every 2-4 weeks for correction issues, infection, granuloma formation or keratopathy. Neonatal history included breastfeeding and steady weight gain with regular bowel movements. A familial history of a sibling with mild ptosis that did not require medical intervention was noted. The diagnosis of congenital ptosis was recorded by the pediatrician 20 days post birth. The pediatrician also recorded that he observed "symmetrical facies", with the exception of the left eyelid ptosis, and a referral was made to an ophthalmologist. A diagnosis of severe ptosis affecting the left upper eyelid was confirmed by the opthalmologist. Upon examination the infant was unable to open the left eyelid without assistance. When the eyelid was opened manually, the eye was unable to focus on any presented object and did not move towards external stimuli such as Case Report A one-month-old female with a Caucasian father and Asian mother presented with a chief complaint of congenital ptosis of the left eye. The mother and hospital staff noted the left eye opened on the first day of life, but after that initial day, the eye required external force be applied to lift the lid. There was no record of trauma reported or an explanation given as to why the left eyelid no longer functioned properly. A left head tilt was noted along with an eccentric head shape, oblong with the mandible perpendicular to the right eye. Adjustments were performed on the right atlas which was fixed in rotation and adjusted posterior to anterior (P-A) contacting the posterior arch with a single digit contact and on the left axis which was fixed in rotation and adjusted posterior to anterior contacting the posterior arch with a single digit contact. Cranio-sacral technique (sphenofrontal release at the lesser wing)10 was performed along with a parietal lift. The opinion of the second opthalmologist was that surgical intervention was prudent. The ophthalmologist performed a frontalis sling blepharoptosis repair with a Seiff silicone rod to the left upper eyelid. The surgeon considered the procedure successful and the patient was released to her original ophthalmologist for follow up as she was considered at risk for amblyopia which is a disorder of the visual system that is characterized by a vision deficiency in an eye that is otherwise physically normal. Also, sensory nerves from the suboccipital muscles, the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the longus capitus muscle, each directly influenced by the cervical adjustment, project to the nucleus intermedius through the upper cervical dorsal root ganglion creating chemical and electrical stimulation releasing excitatory and inhibitory post-synaptic potentials in the solitary tract. This theory could be applied to involvement of the levator palebrae superious muscle and its innervations from the oculomotor nerve. These include the occiput, temporal, parietals, ethmoid, palatines, frontal, and vomer. The chiropractic physician and second ophthalmologist concluded that complete loss of vision in one eye for an extended period of time had the potential for long term disability and recommended the surgery be performed as soon as possible. Loss of visual input has been very difficult to assess, but a study by Wiesel and Hubel on visual deprivation in kittens demonstrated that significant monocular or binocular deprivation leads to virtual blindness due to loss of neural connections between the eyes, optic nerves and cortical connections. Behavioral changes, including loss of self assurance and self esteem were noted, although some behavioral recovery did occur after the blindness was resolved. There is very little published research regarding chiropractic adjustments or other forms of spinal manipula- Volume 12, No. This small section of the brain controls movement, especially those of the eye, but also filters or increases the amount of stimulation to the upper brain. To hold balance with the sphenoid, the sacral adjustment may be crucial as they are designed to be synchronized in rhythmic motion (craniosacral rhythm). An issue to be explored is whether ptosis should be viewed as a viscero-somatic or musculoskeletal condition. This report also demonstrates the value of pursuing a second opinion from a different specialty to achieve a more expedient treatment care outcome. This could have resulted in visual impairment and/or neurological stagnation in the long term as well as a more difficult and less successful surgical outcome. The chiropractor in this case was concerned by the long term ramifications of delayed treatment and sought a second opinion from a different ophthalmologist. This coupled with an appropriate treatment plan to facilitate neurological function for the patient may be an illustration of optimizing outcomes through collaboration. More exploration into interdisciplinary cooperation for the benefit of the patient should be embraced. Muscle spindle-derived neurotrophin 3 regulates snyaptic connectivity between muscle sensory and motor neurons. Postoperative ptosis: Etiopathogenesis, clinical analysis and the therapeutic management. A randomized clinical trial of two methods of fascia lata suspension in congenital ptosis. Case report: Maitland assessment and treatment of a patient with eye ptosis secondary to cervcial-thoracic dysfunction. The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses. The treatment of trophic nerve lesions: a study based on a case of mal perforans; of ischemic paralysis; and of erythroelalgia. Chiropractic care for non-musculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review with implications for whole systems research. Somatic dysfuntion and the phenomenon of visceral diseases simulation: a probable explanation for the apparent effectiveness of somatic therapy in patients presumed to be suffering from true visceral disease. J Manipulative Physiol Conclusion Chiropractic care has long been known as a pain relieving health care profession. Further investigation is needed into the possible connection between chiropractic adjustments and effects on non-musculoskeletal complaints 922 Journal of CliniCal ChiropraCtiC pediatriCs Volume 12, No. Practice-based randomized controlledcomparison clinical trial of chiropractic adjustments and brief massage treatment at sites of subluxation in subjects with essential hypertension: pilot study. Cessation of cyclic vomiting in a 7-year-old girl after upper cervical chiropractic care: a case report. Current treatment consisted of laxatives, high fluid intake, and high fiber intake which had not been effective. Intervention and Outcome: the patient received full-spine diversified treatments over a period of 6 weeks. She was able to have a significant bowel movement a few hours after her first treatment. Her bowel function continued to improve with further chiropractic treatments with sustained results. Conclusion: this case suggests that chiropractic full spine diversified adjustments may be helpful in some cases of chronic constipation. Introduction Constipation is a frequent and common occurrence in children, affecting 4%-30% of the population by various estimates, with 1 study of 482 children showing an incidence rate of 22. Allopathic treatment consists of stool softeners (laxatives) and having the child change to a less constipating diet with more fiber and fluids. Constipation is defined as "the slow movement of feces through the large intestine. There are few reports of chiropractic treatment for chronic constipation in children in the literature. The first was reported by Hewitt in 1993 and involved the normalization of bowel function in a 7-month-old female after treatment with full spine and cranial adjusting. In 2008, Alcantara and Mayer described the successful outcome of chiropractic care in 3 pediatric patients with chronic constipation. All 3 patients were under 2 years of age and responded immediately with improved bowel function attributable to chiropractic care. Case Report A 5-year-old female, accompanied by her mother, had a history of chronic constipation and related symptoms including distended abdomen, gas and pain. Her mother stated this had been a recurring problem since birth with the child averaging only one small, hard, painful bowel movement per week.
In each prestabilization rating an examination will be requested to be accomplished not earlier than 6 months nor more than 12 months following discharge allergy forecast flint mi cheap prednisolone 40 mg fast delivery. In those prestabilization ratings in which following examination reduction in evaluation is found to be warranted allergy treatment for toddlers cheap prednisolone 40 mg on-line, the higher evaluation will be contin- § 4 allergy medicine fruit juice trusted 20 mg prednisolone. A total disability rating (100 percent) will be assigned without regard to other provisions of the rating schedule when it is established that a serviceconnected disability has required hospital treatment in a Department of Veterans Affairs or an approved hospital for a period in excess of 21 days or hospital observation at Department of Veterans Affairs expense for a serviceconnected disability for a period in excess of 21 days allergy testing doctor order prednisolone 40 mg line. A temporary release which is approved by an attending Department of Veterans Affairs physician as part of the treatment plan will not be considered an absence. An authorized absence of 4 days or less which results in a total of more than 8 days of authorized absence during the first 21 days of hospitalization will be regarded as the equivalent of hospital discharge effective the ninth day of authorized absence. If service connection for the disability under treatment is granted after hospital admission, the rating will be from the first day of hospitalization if otherwise in order. Particular attention, with a view to proper rating under the rating schedule, is to be given to the claims of veterans discharged from hospital, regardless of length of hospitalization, with indications on the final summary of expected confinement to bed or house, or to inability to work with requirement of frequent care of physician or nurse at home. A total disability rating (100 percent) will be assigned without regard to other provisions of the rating schedule when it is established by report at hospital discharge (regular discharge or release to non-bed care) or outpatient release that entitlement is warranted under paragraph (a) (1), (2) or (3) of this section effective the date of hospital admission or outpatient treatment and continuing for a period of 1, 2, or 3 months from the first day of the month following such hospital discharge or outpatient release. When the evidence is inadequate to assign a schedular evaluation, a physical examination will be scheduled and considered prior to the termination of a total rating under this section. The total rating will be followed by an open rating reflecting the appropriate schedular evaluation; where the evidence is inadequate to assign the schedular evaluation, a physcial examination will be scheduled prior to the end of the total rating period. I (7112 Edition) ported by adequate pathology and evidenced by the visible behavior of the claimant undertaking the motion. Weakness is as important as limitation of motion, and a part which becomes painful on use must be regarded as seriously disabled. A little used part of the musculoskeletal system may be expected to show evidence of disuse, either through atrophy, the condition of the skin, absence of normal callosity or the like. In considering the residuals of injury, it is essential to trace the medical-industrial history of the disabled person from the original injury, considering the nature of the injury and the attendant circumstances, and the requirements for, and the effect of, treatment over past periods, and the course of the recovery to date. The duration of the initial, and any subsequent, period of total incapacity, especially periods reflecting delayed union, inflammation, swelling, drainage, or operative intervention, should be given close attention. This consideration, or the absence of clear cut evidence of injury, may result in classifying the disability as not of traumatic origin, either reflecting congenital or developmental etiology, or the effects of healed disease. The importance of complete medical examination of injury cases at the time of first medical examination by the Department of Veterans Affairs cannot be overemphasized. When possible, this should include complete neurological and psychiatric examination, and other special examinations indicated by the physical condition, in addition to the required general and orthopedic or surgical examinations. When complete examinations are not conducted covering all systems of the body affected by disease or injury, it is impossible to visualize the nature and extent of the service connected disability. Incomplete examination is a common cause of incorrect diagnosis, especially in the neurological and psychiatric fields, and frequently leaves the Department of Veterans Affairs in doubt as to the § 4. In every instance where the schedule does not provide a zero percent evaluation for a diagnostic code, a zero percent evaluation shall be assigned when the requirements for a compensable evaluation are not met. Disability of the musculoskeletal system is primarily the inability, due to damage or infection in parts of the system, to perform the normal working movements of the body with normal excursion, strength, speed, coordination and endurance. It is essential that the examination on which ratings are based adequately portray the anatomical damage, and the functional loss, with respect to all these elements. Instability of station, disturbance of locomotion, interference with sitting, standing and weight-bearing are related considerations. For the purpose of rating disability from arthritis, the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle are considered major joints; multiple involvements of the interphalangeal, metacarpal and carpal joints of the upper extremities, the interphalangeal, metatarsal and tarsal joints of the lower extremities, the cervical vertebrae, the dorsal vertebrae, and the lumbar vertebrae, are considered groups of minor joints, ratable on a parity with major joints. The lumbosacral articulation and both sacroiliac joints are considered to be a group of minor joints, ratable on disturbance of lumbar spine functions. Accurate measurement of the length of stumps, excursion of joints, dimensions and location of scars with respect to landmarks, should be insisted on. The use of a goniometer in the measurement of limitation of motion is indispensable in examinations conducted within the Department of Veterans Affairs. The osseous abnormalities incident to trauma or disease, such as malunion with deformity throwing abnormal stress upon, and causing malalignment of joint surfaces, should be depicted from study and observation of all available data, beginning with inception of injury or disease, its nature, degree of prostration, treatment and duration of convalescence, and progress of recovery with development of permanent residuals. With shortening of a long bone, some degree of angulation is to be expected; the extent and direction should be brought out by X-ray and observation. The direction of angulation and extent of deformity should be carefully related to strain on the neighboring joints, especially those connected with weight-bearing. Inquiry will be directed to these considerations: (a) Less movement than normal (due to ankylosis, limitation or blocking, adhesions, tendon-tie-up, contracted scars, etc. I (7112 Edition) as no less than a moderate injury for each group of muscles damaged. Service department record of superficial wound with brief treatment and return to duty. No cardinal signs or symptoms of muscle disability as defined in paragraph (c) of this section. Through and through or deep penetrating wound of short track from a single bullet, small shell or shrapnel fragment, without explosive effect of high velocity missile, residuals of debridement, or prolonged infection. Service department record or other evidence of in-service treatment for the wound. Record of consistent complaint of one or more of the cardinal signs and symptoms of muscle disability as defined in paragraph (c) of this section, particularly lowered threshold of fatigue after average use, affecting the particular functions controlled by the injured muscles. Entrance and (if present) exit scars, small or linear, indicating short track of missile through muscle tissue. Some loss of deep fascia or muscle substance or impairment of muscle tonus and loss of power or lowered threshold of fatigue when compared to the sound side. Through and through or deep penetrating wound by small high velocity missile or large § 4. Record of consistent complaint of cardinal signs and symptoms of muscle disability as defined in paragraph (c) of this section and, if present, evidence of inability to keep up with work requirements. Entrance and (if present) exit scars indicating track of missile through one or more muscle groups. Indications on palpation of loss of deep fascia, muscle substance, or normal firm resistance of muscles compared with sound side. Tests of strength and endurance compared with sound side demonstrate positive evidence of impairment. Through and through or deep penetrating wound due to high-velocity missile, or large or multiple low velocity missiles, or with shattering bone fracture or open comminuted fracture with extensive debridement, prolonged infection, or sloughing of soft parts, intermuscular binding and scarring. Service department record or other evidence showing hospitalization for a prolonged period for treatment of wound. Record of consistent complaint of cardinal signs and symptoms of muscle disability as defined in paragraph (c) of this section, worse than those shown for moderately severe muscle injuries, and, if present, evidence of inability to keep up with work requirements. Ragged, depressed and adherent scars indicating wide damage to muscle groups in missile track. Palpation shows loss of deep fascia or muscle substance, or soft flabby muscles in wound area. Tests of strength, endurance, or coordinated movements compared with the corresponding muscles of the uninjured side indicate severe impairment of function. If present, the following are also signs of severe muscle disability: (A) X-ray evidence of minute multiple scattered foreign bodies indi- § 4. The congenital condition, with depression of the arch, but no evidence of abnormal callosities, areas of pressure, strain or demonstrable tenderness, is a congenital abnormality which is not compensable or pensionable. In the acquired condition, it is to be remembered that depression of the longitudinal arch, or the degree of depression, is not the essential feature. The attention should be given to anatomical changes, as compared to normal, in the relationship of the foot and leg, particularly to the inward rotation of the superior portion of the os calcis, medial deviation of the insertion of the Achilles tendon, the medial tilting of the upper border of the astragalus. A plumb line dropped from the middle of the patella falls inside of the normal point. In severe cases there is gaping of bones on the inner border of the foot, and rigid valgus position with loss of the power of inversion and adduction. Exercise with undeveloped or unbalanced musculature, producing chronic irritation, can be an aggravating factor. In the absence of trauma or other definite evidence of aggravation, service connection is not in order for pes cavus which is a typically congenital or juvenile disease.
Glucocorticosteroids and other immunosuppressants have been used for this purpose and to control autoimmune disorders allergy testing maine discount prednisolone 40 mg on-line. Frequent infections in a child with neurological and cutaneous and/or skeletal symptoms might prompt the evaluating physician to consider these diagnoses allergy medicine expired buy prednisolone 20 mg low price. Additional neurological manifestations include oculomotor apraxia allergy shots nausea purchase 40 mg prednisolone visa, dysarthria allergy symptoms 7dpiui generic 40 mg prednisolone mastercard, swallowing dyscoordination, and peripheral neuropathy. Bacterial respiratory tract infections predominate, although viral and fungal infections can also occur. Low IgA levels, abnormalities of IgG subclasses (eg, IgG2 deficiency), and impairment of pneumococcal polysaccharide responses can also be seen. There is a highly characteristic increase in numbers of T cells bearing the g/d receptor. Bloom syndrome is characterized by growth deficiency, unusual facies, sun-sensitive telangiectatic erythema, immunodeficiency, and predisposition to cancer. Infectious complications, including opportunistic microorganisms suggesting T-cell dysfunction, were reported in approximately 70% of patients; these presented from 3 months to 4 years of age and consisted primarily of frequent bacterial respiratory tract infections. Growth retardation occurs in about half of patients, and some degree of cognitive or developmental impairment is seen in about two thirds of patients. Cells from 1 patient with recurrent infections and cafe-au-lait spots and 2 other patients with mismatch repair syndrome were found to have deficient classswitch recombination defects. However, diagnostic sensitivity and specificity take precedence over this theoretical concern, and radiographic methods should be applied when they represent the best modality to support clinical decisions. Until recently, the toxicity of myeloablation has not been considered generally justifiable for attempted correction of immune dysfunction alone. However, newer partial ablation regimens make stem cell therapy for immune reconstitution or therapy for malignancy a therapeutic option for some patients. In most patients serum immunoglobulin levels are normal, as is antibody production, unless severe T-cell depletion is found. In fact, the trend is usually toward increase, although not always to the normal range. Registry data from the United States and Europe suggest that approximately 6% overall are hypogammaglobulinemic and 3% receive IgG replacement. The immuno-osseous dysplasias should be considered in patients with severe growth retardation, skeletal abnormalities, and T-cell lymphopenia. Frequent viral infections might represent defective cellular immunity, as determined by T-cell lymphopenia with very low numbers of naive T cells. Medical management of immunoosseous syndromes should include antibiotic prophylaxis and IgG supplementation appropriate to the severity of the immune dysfunction. IgG supplementation is recommended for patients with decreased specific antibody responses. The hair is often brittle and can have nodules and invaginations (trichorrhexis invaginata). Immunologic abnormalities include increased IgE levels, hypogammaglobulinemia, and impaired antibody response to pneumococcal immunization. These patients are prone to lung damage, including bronchiectasis and pneumatoceles. Other manifestations can include neonatal dermatitis, midline anomalies, and lymphoma. However, they do not have skeletal or dental abnormalities and do not tend to have pneumatoceles. Patients tend to have severe allergic manifestations, eosinophilia, and disseminated cutaneous viral infections. Some exhibit autoimmunity (vasculitis and neutropenia), intellectual disability, and hypomyelination. These patients also have recurrent infections, failure to thrive, severe eczematous dermatitis, and multiple food and environmental allergies with increased IgE levels. The risk of fracture with relatively minor trauma is high and should be prevented where possible. Children should be monitored carefully for scoliosis, and retained primary teeth should be extracted. Pulmonary fibrosis, bone marrow failure, leukemias, and compromise of other organs can also occur. Antibiotic prophylaxis and IgG supplementation can reduce the risk of infections in these patients. Although lymphopenia might not be seen, function is poor, with absent mitogen response and hypogammaglobulinemia and impaired antibody formation. Megaloblastic anemia is also characteristic, although this could be masked by concurrent iron deficiency. Infants with severe vitamin B12 or folate deficiency should be treated aggressively with folate or cobalamin replacement as soon as the diagnosis is made. It is unclear whether the intestinal inflammation and atresia is secondary to the immune defect, and many of the surviving reported patients have continued to require multiple operations for intestinal atresia and remain dependent on total parenteral nutrition. Patients with very low or undetectable serum immunoglobulin concentrations and very low or undetectable circulating B lymphocytes with normal T-cell numbers and function should be given a diagnosis of agammaglobulinemia. If given an early diagnosis, many patients might have had only recurrent otitis media. Some patients present with an overwhelming infection, often with associated neutropenia. There are no other consistent physical findings in patients with agammaglobulinemia. Measurement of specific antibodies might not be necessary in patients with IgG levels in the agammaglobulinemic range. Laboratory findings and diagnostic criteria for antibody deficiencies are summarized in Table E10. Agammaglobulinemia should be managed aggressively with antimicrobials, IgG replacement, and careful attention to pulmonary status. Lung transplantation should be considered for patients with agammaglobulinemia and lifethreatening chronic lung disease. Common pathogens include encapsulated (nontypeable H influenzae and S pneumococcus) or atypical (Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma species) bacteria. Specific B-cell subsets are developmentally regulated, and age-adjusted values should be used in these instances. Rare cases of monogenic autosomal recessive forms of hypogammaglobulinemia have been described. However, autoimmune, lymphoproliferative, and malignant complications are not seen. Giardiasis and enteritis with C jejuni and salmonellosis are the most common enteric infections. Autoimmune cytopenias (autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura and autoimmune hemolytic anemia) are the most common autoimmune disorders, occurring in 11% to 12% patients. Other autoimmune diseases, such as seronegative arthritis and vasculitides, have also been observed. Estimates of the relative risk of nonHodgkin lymphoma range from 30- to 400-fold greater than in the general population. There is also an approximately 10-fold increase in the relative risk for gastric cancer compared with the healthy population. Patients having hypogammaglobulinemia and thymoma should be given a diagnosis of Good syndrome. Autoimmune disease is a frequent complication of Good syndrome, most notably pure red cell aplasia and neutropenia. Thymectomy is not followed by normalization of immune phenotype or function or remission of associated autoimmune diseases. Approximately two thirds of subjects with IgA levels of less than 7 mg/dL have a lower detectable level of IgA; in one third of subjects, it appears to be completely absent. Patients with serum IgA levels of less than the normal range for age but greater than 7 mg/dL should not be given a diagnosis of IgA deficiency. Clinical manifestations can include respiratory and gastrointestinal tract infections, atopy, autoimmune diseases, celiac disease, and malignancy. Infections include recurrent viral infections, recurrent otitis media, and frequent sinopulmonary infections, as well as gastrointestinal infections. In addition to infections, IgA-deficient patients are at increased risk for autoimmune diseases, including lupus-like illnesses and arthritis; hematologic disorders, including neutropenia and thrombocytopenia; and gastrointestinal illnesses, including Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease.
Buy prednisolone 5 mg on line. What is Gluten in Hindi | Gluten free Diet | Celiac Disease and TTG test.
References