




|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
Mary Helen Foster, MD

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/mary-helen-foster-md
M Toxicity 1 Myelosuppression is dose-limiting and cumulative toxicity with leukopenia more common than thrombocytopenia women's health clinic evergreen park purchase raloxifene 60mg otc. Consists of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (hematocrit menstruation calculator menstrual cycle generic 60 mg raloxifene visa,25%) menstruation smells bad buy raloxifene 60 mg online, thrombocytopenia ( women's health clinic ne calgary raloxifene 60mg lowest price,100,000/mm3), and renal failure (serum creatinine. Other complications include Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Drugs 307 M pulmonary edema, neurologic abnormalities, and hypertension. Presents with dyspnea, nonproductive cough, and interstitial infiltrates on chest X-ray. Parent compound and its metabolites are excreted mainly through the hepatobiliary system into feces (60%). Variable elimination half-life of up to 160 hours due to storage of drug in adipose tissue. Drug Interaction 1 Warfarin-Mitotane alters the metabolism of warfarin, leading to an increased requirement for warfarin. Drug Interaction 2 Barbiturates, phenytoin, cyclophosphamide-Mitotane alters the metabolism of various drugs that are metabolized by the liver microsomal P450 system, including barbiturates, phenytoin, and cyclophosphamide. If steroid replacement is required, doses higher than those for physiologic replacement may be needed. Adrenal insufficiency may develop, and adrenal steroid replacement with glucocorticoid and/or mineralocorticoid therapy is indicated. Patients should be cautioned about driving, operating complicated machinery, and/or other activities that require increased mental alertness, as mitotane causes lethargy and somnolence. Distribution Rapid and extensive distribution to formed blood elements and to body tissues. Distributes in high concentrations in liver, bone marrow, heart, lung, and kidney. Elimination is mainly through the hepatobiliary route, with 25% of the drug excreted in feces. Advanced, hormone-refractory prostate cancer-Used in combination with prednisone as initial chemotherapy. Drug Interactions Heparin-Mitoxantrone is incompatible with heparin, as a precipitate will form. Avoid extravasation, but ulceration and tissue injury are rare when drug is properly diluted. Risk of cardiac toxicity is higher in elderly patients Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Drugs 313 M. Cumulative doses of 140 mg/m2 in patients with no prior history of anthracycline therapy and 120 mg/m2 in patients with prior anthracycline therapy are associated with increased risk for cardiotoxicity. Patients may experience blue-green urine for up to 24 hours after drug administration. Toxicity 1 Myelosuppression is dose-limiting with neutropenia more common than thrombocytopenia. Chronic toxicity is manifested in the form of a dilated cardiomyopathy with congestive heart failure. Cumulative doses of 140 mg/m2 in patients with no prior history of anthracycline therapy and 120 mg/m2 in patients with prior anthracycline therapy are associated with increased risk for developing congestive cardiomyopathy. A minor route of nelarabine metabolism is via hydrolysis to form methylguanine, which is then demethylated to form guanine. Nelarabine and ara-G are rapidly eliminated from plasma with a half-life in adults of approximately 30 minutes and 3 hours, respectively. The mean clearance of nelarabine is approximately 30% higher in pediatric patients than adult patients, while the clearance of ara-G is similar in the two patient populations. Patients treated previously or concurrently with intrathecal chemotherapy and/or previously with craniospinal radiation therapy may be at increased risk for developing neurotoxicity. Patients should be advised against performing activities that require mental alertness, including operating hazardous machinery and driving. Toxicity 1 Myelosuppression is the most common toxicity with neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. Toxicity 3 Neurotoxicity is dose-limiting with headache, altered mental status, seizures, and peripheral neuropathy with numbness, paresthesias, motor weakness, and paralysis. Toxicity 4 Mild hepatic dysfunction with elevation of serum transaminases and bilirubin. Drug Interaction 2 Drugs such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin, and clarithromycin may decrease the rate of metabolism of nilotinib, resulting in increased drug levels and potentially increased toxicity. Drug Interaction 3 Drugs such as rifampin, Phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and St. Nilotinib tablets should not be taken with food for at least 2 hours before a dose is taken and for at least 1 hour after a dose is taken. Electrolyte abnormalities must be corrected prior to initiation of therapy, and electrolyte status should be monitored periodically during therapy. Avoid Seville oranges, starfruit, pomelos, grapefruit juice, and grapefruit products while on therapy. Toxicity 4 Electrolyte abnormalities with hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hyponatremia. Toxicity 6 Elevations in serum transaminases and/or bilirubin (usually indirect bilirubin). Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Drugs 321 N Nilutamide Trade Name Nilandron Classification Antiandrogen Category Hormonal agent Drug Manufacturer Sanofi-Aventis Mechanism of Action Nonsteroidal, antiandrogen agent that binds to androgen receptor and inhibits androgen uptake. Also inhibits androgen binding in the nucleus of androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cells. Metabolism Extensive metabolism occurs in the liver to both active and inactive metabolites. About 60% of the drug is excreted in urine, mainly in metabolite form, and only minimal clearance in feces. N Drug Interaction 1 Warfarin-Nilutamide can inhibit metabolism of warfarin by the liver P450 system leading to increased anticoagulant effect. Drug Interaction 2 Drugs metabolized by the liver P450 system-Nilutamide inhibits the activity of liver cytochrome P450 enzymes and may therefore reduce the metabolism of various compounds, including phenytoin and theophylline. Drug Interaction 3 Alcohol-Increased risk of alcohol intolerance following treatment with nilutamide. Should be given on the same day or on the day after surgical castration to achieve maximal benefit. Should be used with caution in patients with abnormal liver function and is contraindicated in patients with severe liver impairment. Patients should be advised to abstain from alcohol while on nilutamide as there is an increased risk of intolerance (facial flushes, malaise, hypotension) to alcohol. Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Drugs 323 N Toxicity 1 Hot flashes, decreased libido, impotence, gynecomastia, nipple pain, and galactorrhea. Toxicity 2 Visual disturbances in the form of impaired adaptation to dark, abnormal vision, and alterations in color vision.
Enlargement of the blind spot and constriction of the visual field may be evident women's health clinic deland cheap raloxifene 60 mg online, but visual acuity is often unimpaired (cf menstral cheap 60 mg raloxifene otc. Paradoxical diaphragm movement is a potentially alarming sign since it may indicate incipient respiratory failure womens health magazine careers generic raloxifene 60 mg line. The term paradoxical breathing may also be used to describe thorax and abdomen moving in different directions when breathing menstruation irregularities order 60mg raloxifene with visa, as with increased upper airway resistance. Some authorities reserve the term for spontaneous rather than evoked positive sensory phenomena, as a distinction from dysaesthesia. Paraesthesia is a feature of neuropathy and may occur in the distribution of a compressed or entrapped nerve, perhaps reflecting the mechanosensitivity of nerves in this situation. Paraesthesia is a more reliable indicator of the diagnosis of neuropathy than pain. Paraesthesia may also be provoked by hyperventilation (especially perioral, hands, and feet [acroparaesthesia]). It should be remembered that many movements previously thought to conform to this definition have subsequently been recognized to have an organic basis. The use of the word has not been entirely consistent, for example, paralysis agitans originally used by James Parkinson to describe the disease which now bears his name. The periodic paralyses are a group of conditions characterized by episodic muscular weakness and stiffness (myotonia) associated with mutations in the skeletal muscle voltage-gated sodium and calcium ion channel genes (channelopathies). Cross References Myotonia; Plegia Paramnesia Paramnesia is recalling as memories things which have not in fact taken place, hence a distortion of episodic or autobiographical memory. Cross References Amnesia; Confabulation; Reduplicative paramnesia - 264 - Paraparesis P Paramyotonia Paramyotonia is similar to myotonia in that muscle does not relax normally following contraction (voluntary, percussion), which may prompt a complaint of muscle aching or stiffness, but differs in that repetitive muscle use. For example, repeated forced voluntary eyelid closure in a patient with paramyotonia may, after several attempts, lead to a failure of voluntary eyelid opening, the eyes remaining closed for a minute or so. This type of muscle stiffness may also be sensitive to temperature, being made worse by cooling which may also provoke muscle weakness. During the delayed muscle relaxation, electrical activity is not prominent, and after muscle cooling the resting muscle membrane potential may be reduced from around the normal -80 to -40 mV, at which point muscle fibres are inexcitable (contracture). Mutations in the same gene have been documented in hyperkalaemic periodic paralysis and K+ -aggravated myotonia. Symptomatic treatment with membrane-stabilizing agents like mexiletine and tocainide or with the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor acetazolamide might be tried. Precautions are necessary during general anaesthesia because of the risk of diaphragm myotonia. Paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalaemic periodic paralysis are linked to the adult muscle sodium channel gene. Cross References Contracture; Myotonia; Paralysis; Warm-up phenomenon Paraparesis Paraparesis is a weakness of the lower limbs, short of complete weakness (paraplegia). This may result from lesions anywhere from cerebral cortex (frontal, parasagittal lesions) to peripheral nerves, producing either an upper motor neurone (spastic) or lower motor neurone (flaccid) picture. Cross References Flaccidity; Myelopathy; Paraplegia; Spasticity Paraphasia Paraphasias are a feature of aphasias (disorders of language), particularly (but not exclusively) fluent aphasias resulting from posterior dominant temporal lobe lesions (cf. Paraphasias refer to a range of speech output errors, both phonological and lexical, including substitution, addition, duplication, omission, and transposition of linguistic units, affecting letters within words, letters within syllables, or words within sentences. Morphemic: Errors involving word stems, suffixes, prefixes, inflections, and other parts of words. These may be further classified as: Semantic or categoric: substitution of a different exemplar from the same category. Verbal paraphasias showing both semantic and phonemic resemblance to the target word are called mixed errors. This may result from lower motor neurone lesions involving multiple nerve roots and/or peripheral nerves. Prevention of this situation may be possible by avoiding spasms, which are often provoked by skin irritation or ulceration, bowel constipation, bladder infection, and poor nutrition. Physiotherapy and pharmacotherapy with agents such as baclofen, dantrolene, and tizanidine may be used; botulinum toxin injections may be helpful for focal spasticity. The key anatomical substrates, damage to which causes the syndrome, are probably the interstitial nucleus of Cajal and the nucleus of the posterior commissure and their projections. The incidence of parkinsonism increases dramatically with age; it is also associated with an increased risk of death, particularly in the presence of a gait disturbance. Prevalence of parkinsonian signs and associated mortality in a community population of older people. Cross References Apraxia; Blinking; Bradykinesia; Dysarthria; Dystonia; Hypokinesia; Hypomimia; Hypophonia; Mask-like facies; Micrographia; Orthostatic hypotension; Postural reflexes; Rigidity; Seborrhoea; Sialorrhoea; Striatal toe; Supranuclear gaze palsy; Tremor Parosmia Parosmia is a false smell, i. Such smells are usually unpleasant (cacosmia), may be associated with a disagreeable taste (cacogeusia), and may be difficult for the patient to define. Causes include purulent nasal infections or sinusitis and partial recovery following transection of olfactory nerve fibres after head injury. Transient parosmia may presage epileptic seizures of temporal lobe cortical origin (olfactory aura), particularly involving the medial (uncal) region. The clinical heterogeneity of hemifacial atrophy probably reflects pathogenetic heterogeneity. The syndrome may result from maldevelopment of autonomic innervation or vascular supply, or as an acquired feature following trauma, or a consequence of linear scleroderma (morphoea), in which case a coup de sabre may be seen. There may be a sense that the patient is struggling against these displays of emotion, in contrast to the situation in other forms of emotional lability where there is said to be congruence of mood and affect, although sudden fluctuations and exaggerated emotional expression are common to both, suggesting a degree of overlap. Pathological laughter and crying following stroke: validation of a measurement scale and a double-blind treatment study. Cross References Automatism; Emotionalism, Emotional lability; Pseudobulbar palsy Peduncular Hallucinosis Peduncular hallucinosis is a rare syndrome characterized by hallucinations and brainstem symptoms. Brainstem findings include oculomotor disturbances, dysarthria, ataxia, and impaired arousal. Peliopsia, Pelopsia Peliopsia or pelopsia is a form of metamorphopsia characterized by the misperception of objects as closer to the observer than they really are (cf. Cross References Metamorphopsia; Porropsia Pelvic Thrusting Pelvic thrusting may be a feature of epileptic seizures of frontal lobe origin; occasionally it may occur in temporal lobe seizures. Choreiform disorders may involve the pelvic region causing thrusting or rocking movements. Cross References Automatism; Chorea, Choreoathetosis; Seizure Pendular Nystagmus Pendular or undulatory nystagmus is characterized by eye movements which are more or less equal in amplitude and velocity (sinusoidal oscillations) about a central (null) point. In acquired causes such as multiple sclerosis, this may produce oscillopsia and blurred vision. Cross References Nystagmus; Oscillopsia Percussion Myotonia Percussion myotonia is the myotonic response of a muscle to a mechanical stimulus. For example, a blow to the thenar eminence may produce involuntary and sustained flexion of the thumb. This - 273 - P Periodic Alternating Nystagmus response, which may be seen in myotonic dystrophy, reflects the impaired muscle relaxation which characterizes myotonia. Cross Reference Myotonia Periodic Alternating Nystagmus Periodic alternating nystagmus is a horizontal jerk nystagmus, which damps or stops for a few seconds and then reverses direction. Periodic alternating nystagmus may be congenital or acquired, if the latter then its localizing value is similar to that of downbeat nystagmus (with which it may coexist), especially for lesions at the cervico-medullary junction. Treatment of the associated lesion may be undertaken, otherwise periodic alternating nystagmus usually responds to baclofen, hence the importance of correctly identifying this particular form of nystagmus.
Generic 60 mg raloxifene fast delivery. How to Prove the Equality of Men and Women in Islaam - Dr Zakir Naik.
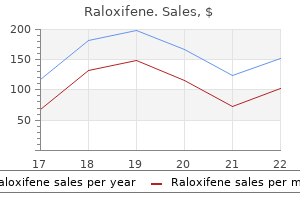
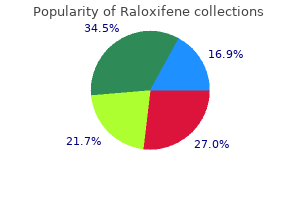
Central stippled and "ring and arc" calcifications are apparent and are typical of cartilaginous matrix breast cancer poems discount raloxifene 60mg line. The size of the lesion and the presence of radiolucent foci are very suggestive of malignancy women's health heartland discount raloxifene 60mg overnight delivery. The majority of chondroid tumors in children and adolescents are chodroblastic osteosarcomas breast cancer 3a purchase raloxifene 60 mg mastercard, not chondrosarcomas pregnancy or period cheap 60 mg raloxifene with amex. Chondrosarcoma is the second most common primary malignant bone tumor after osteosarcoma. There are several variants of chondrosarcoma which differ by their location and histologic subtype. Sometimes, chondrosarcomas are subdivided into primary and secondary to indicate whether they have arisen in a pre-existing benign lesion. Some benign bone lesions (osteochondroma, enchondroma, fibrous dysplasia) may undergo malignant transformation to a chondrosarcoma. Unlike benign cartilaginous lesions, chondrosarcoma has predilection for the trunk bones including the pelvis (particularly, ilium), the ribs, and scapula. Grading system is based on three parameters: cellularity, degree of nuclear atypia and mitotic activity. Characteristic findings are moderate cellular pleomorphism, plump nuclei, frequent bi-nucleated cells, and occasional bizarre cells. Unlike Grade 1 tumors, about 10% to 15% of Grade 2 chondrosarcomas produce metastases. Quite often you will see nodules of enchondroma surrounded by the bone marrow and reactive bone trabeculae. Separation of the nodules by fibrous bands would be another feature highly suggestive of malignancy. Low-grade (Grades 1 and 2) tumors are locally aggressive and prone to recurrences, but their metastatic potential is low. Experimental data: Studies have shown that p53 overexpression and high Ki-67 proliferation index correlate with clinically aggressive behavior in chondrosarcomas. Recent data suggest that these immunohistochemical stains may be particularly useful for determining the prognosis of patients with Grade 2 chondrosarcomas. Available publications for the topic: Chondrosarcoma, low-grade Selected References. Hasegawa T, Seki K, Yang P, et al: Differentiation and proliferative activity in benign and malignant cartilage tumors of bone. Altered p53 is associated with aggressive behavior of chondrosarcoma: a long-term follow-up study. Nawa G, Ueda T, Mori S, et al: Prognostic significance of Ki-67 (Mib1) proliferation index and P53 over-expression in chondrosarcomas. Pathological Findings:: q Microscopic examination reveals a distinguishing feature of this entity. That is the presence of two distinct components: a lowgrade cartilaginous neoplasm and a high-grade sarcoma. By definition, the hallmark of dedifferentiated neoplasm is the co-existence of two components, a low-grade lesion and a high-grade sarcoma, with abrupt demarcation between them. Clinically, dedifferentiation is heralded by a sudden increase in aggressiveness (eg. Experimental data: Controversy remains as to whether both components of dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma are derived from a common precursor cell or they represent two separate lineages (collision tumor). The current hypothesis is that "high-grade components represent a failure of differentiation, rather than dedifferentiation of mature chondroid cells". In a recent study by Bovee et al, molecular genetic characterization of both components of a dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma has provided evidence for a monoclonal origin and has suggested that the separation may be an early event in the histogenesis of this tumor. Available publications for the topic: Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma Selected References:: 1. Molecular genetic characterization of both components of a dedifferentated chondrosarcoma, with implications for its histogenesis. Characteristic Radiological Findings: q Plain radiograph shows a diaphyseal, ill defined, destructive, radiolucent lesion with permeative margins. Pathological Findings:: q Low power view shows a highly cellular spindle cell neoplasm with focal storiform cellular arrangement and lack of identifiable matrix (osteoid or chondroid). Prognosis is generally poor due to the high grade of the tumors, difficulties at their surgical removal, and the old age of patients. This type of sarcoma is also found in dedifferentiated areas of low-grade neoplasms. Although any bone may be involved, the tumor is most commonly found in the knee area (30% of cases), proximal femur, humerus and pelvis. Those include myxoid, organoid, and hemangiopericytoma-like patterns to name just a few. Eosinophilic, collagenous extracellular matrix may be present and may be confused with osteoid. However, remember that the only absolute diagnostic feature of osteoid is mineralization. His past medical history was noncontributory and negative for surgery or malignancy. Characteristic Radiological Findings: q Plain film shows an illdefined, radiolucent lesion with permeative margins and focal cortical disruption. Before the diagnosis of a primary tumor can be made, a metastatic lesion must be ruled out. Common primary sites for leiomyosarcoma include the uterus, gastro-intestinal tract and soft tissues. Characteristic Radiological Findings: q Plain film shows a large, cortically based, radiolucent lesion partially surrounded by a rim of sclerotic bone, and two smaller lesions of similar appearance. The location in the cortex of the tibial shaft is a major diagnostic clue (about 90% of these tumors are centered in the antero-lateral cortex of the tibial shaft). Some nests demonstrated peripheral palisading reminiscent of basal cell carcinoma. The appearance of the epithelial cells and the cellular arrangement determine a histologic subtype: basaloid (shown above), spindle, tubular, squamoid, and osteofibrous dysplasia-like. Characteristically, epithelial cells of adamantinoma and stromal cells are bland with virtually absent (or very low) mitotic activity. By immunohistochemistry, epithelial cells of adamantinoma are stongly positive for cytokeratin. Cytogenetic studies usually reveal complex chromosomal abnormalities involving multiple translocations and extra chromosomes. Despite its sometimes "benign" clinicoradiological appearance, adamantinoma behaves as a low-grade malignant neoplasm characterized by local aggressiveness, high recurrence rate, and ability to produce metastases. Characteristic Radiological Findings: q Plain film shows a small, intracortical, radiolucent focus (nidus), surrounded by dense reactive periosteal bone. Pathological Findings:: q If the nidus is removed intact, it appears as a circumscribed portion of red, trabecular bone, usually less than 1cm in size. The lesional tissue, called a "nidus", usually appears as a small radiolucent focus, less than 1cm in size, either within the cortex or adjacent to it. The lesion is thought to produce prostoglandin/prostocyclin-mediated effects on the surrounding tissues inducing exuberant, reactive, periosteal sclerosis, soft tissue edema and pain. Aspirin, which acts through inhibition of prostaglandin/prostacyclin, has dramatic pain-relieving effect in patients with osteoid osteomas. Other skeletal locations include the humerus, the small bones of the hands and feet, and the spine. If the lesion occurs in a close proximity to the articular surface of the joint, it causes severe reactive synovitis. Precise localization of the lesion at surgery is difficult due to its small size and extensive reactive bone sclerosis. Once the tissue has been removed, the pathologist should X-ray and thinly section the specimen to identify the nidus (lesional tissue). Osteoblastoma is a benign bone-forming neoplasm, which is closely related to osteoid osteoma. However, remember that osteoblastoma is characterized by a larger size (more than 1. Other important entity in the differential diagnosis is intracortical osteosarcoma. Look for the presence of significant nuclear atypia and invasive growth pattern indicative of malignancy.
In addition to aggressive supportive care womens health haverhill buy generic raloxifene 60mg, which of the following should be performed in this patient? Administration of activated charcoal 50 g orally followed by additional doses of 25 g every 6 hours menopause 2014 speaker slides 60mg raloxifene mastercard. In the previous patient women's health issues and solutions purchase raloxifene 60 mg, gastrointestinal decontamination is performed and deferoxamine is started at 15 mg/kg/hr women's health big book of exercises ebook cheap raloxifene 60 mg free shipping. In the previous patient, she has a follow-up appointment as an outpatient approximately four weeks after her ingestion. Severe ingestions may present with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hematemesis, altered mental status, and possibly hypotension. Stage 2 occurs at 6 to 12 hours postingestion and is referred to as the quiescent or "danger" phase because the child can appear to be improving or asymptomatic. Stage 3, from 12 to 24 hours postingestion, is marked by major symptoms of toxicity including 7. Although iron pills may be identified by radiograph, the physician should not rely on the absence of pill identification to continue treatment. Activated charcoal is not effective in absorbing iron in the gastrointestinal tract. A level greater than 350 g/dL is considered toxic if the patient is symptomatic, but levels greater than 500 g/dL suggest potentially life-threatening toxicity regardless of symptoms. However, the resolution of metabolic acidosis is now thought to be a more reliable endpoint. Ferrous fumarate contains 33% elemental iron, ferrous sulfate contains 20% elemental iron, ferrous gluconate contains 12% elemental iron, and multivitamins typically contain <5% of elemental iron. When dealing with iron, it is important to estimate the amount of elemental iron ingested in the worst-case scenario. The patient could have ingested ten tablets of 325 mg ferrous sulfate, which contains 20% elemental iron. This patient clearly has a significant ingestion of iron and whole bowel irrigation should be performed. Orogastric lavage and syrup of ipecac have little to no role in the poisoned patient. In stages 3 and 4 of iron toxicity, patients are mostly likely to die from the complications of hepatic failure. In stage 5 of iron toxicity, patients may form gastrointestinal strictures (usually at the gastric pylorus), which have significant morbidity. Smoke inhalation from building fires is the most common source for hydrogen cyanide from combustible synthetic materials. Ingestion of cyanide is less common and may occur from acetonitrile in nail removal agents, potassium cyanide in metal cleaning solutions imported from Asia, and cyanogenic glycosides found in the seeds and pits of certain plants such as apples, apricots, and peaches. Early symptoms include headache, anxiety, confusion, blurred vision, palpitations, nausea, and vomiting. In the previous patient you decide to treat on the clinical presentation and suggestive lab findings for cyanide toxicity with the Taylor Antidote Kit. Which of the following tests should be closely monitored in patients who received the Taylor Antidote Kit? Elevated carboxyhemoglobin levels correlate with cyanide levels in smoke inhalation victims. In children, smoke inhalation from building fires is the most common source for hydrogen cyanide from combustible synthetic materials. Arterial blood gases show a significant metabolic acidosis and an elevated lactate or anion gap acidosis are common and helpful in making the diagnosis. Hydroxocobalamin (a precursor to vitamin B12) detoxifies cyanide to form nontoxic cyanocobalamin. Hydroxocobalmin is not associated with hypotension or excessive methemoglobinemia. Hypotension is common with nitrite therapy and methemoglobin levels should be monitored during administration. A 10-year-old male is brought in after being trapped in a clothing store that caught fire. What test result often correlates with significant cyanide poisoning from a house/ building fire? Since cyanide levels cannot be obtained emergently, what laboratory test is highly suggestive of cyanide poisoning? As such, identification of North American mushroom poisoning relies primarily on clinical features. If samples or pictures of the suspected toxic mushroom are available, the regional poison center may be able to assist in identification. Enjabert F, Rapior S, Nouguier-Soule J, et al: Treatment of amatoxin poisoning: 20-year retrospective analysis. Which clinical feature is most consistent with poisoning from a mushroom of this cyclopeptide group and might be expected in this patient? A family member states that earlier in the day he went mushroom hunting for morels with his uncle. Which of the following does not correctly pair the mushroom toxin with its potential clinical feature? Cyclopeptide-containing mushrooms classically produce a delayed (>6 hours postingestion) gastroenteritis. Ingestion of mushrooms containing orellanine can produce interstitial nephritis and renal failure. Visual hallucinations often develop soon after ingesting mushrooms containing the psychoactive indole psilocybin. Ingestion of G esculenta, the "false morel," may produce intractable seizures, primarily through inhibition of pyridoxal phosphate enzyme systems. N-acetylcysteine and silybinin have been used with limited success to treat toxicity from cyclopeptidecontaining mushrooms. Activated charcoal, while a standard treatment modality for some mushroom poisonings, is not safe to administer to a patient with active seizure activity. Phenytoin and other antiepileptics are not recommended for toxin-induced seizures. Coprinecontaining mushrooms can produce a disulfiram-like reaction when ingested with alcohol. Severe rhabdomyolysis has been described after ingestion of T equestre; the toxin is unknown. Alternatives suggested in the medical literature include: vinegar, topical antacids, vegetable oil, and 2% lidocaine gel. The plants produce green berries, which mature into red berries that are attractive to small children. Admission may be required for observation and continued care in the setting of large or markedly symptomatic pokeweed ingestions. Jimsonweed grows wild throughout the United States, and its seeds have been abused by adolescents and teenagers due to their psychotropic effects. An anticholinergic toxidrome with tachycardia, mydriasis, dry skin and mucous membranes, hypoactive bowel sounds, urinary retention, and hyperthermia may be noted. Central anticholinergic effects result in altered mental status, ranging from somnolence to severe agitation and delirium with hallucinations. Physostigmine has been safely and effectively utilized as an antidote in anticholinergic plant poisoning, usually in cases with refractory delirium, hyperthermia, seizures, or significant arrhythmias. Patients with marked delirium, seizures, cardiopulmonary instability, or those treated with physostigmine should be admitted to an intensive care unit.