




|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
Ravi Kapoor, MD, MPH
There is evidence to support a conclusion that a not insignificant portion of the population may refuse to take the vaccine hiv infection rate in peru buy generic amantadine 100 mg. Such a receptacle shall be equipped with a solid tight-fitting cover hiv infection among youth purchase amantadine 100 mg without prescription, unless it can be maintained in a sanitary condition without a cover hiv infection without ejaculation amantadine 100 mg low cost. No food or beverages shall be stored in toilet rooms or in an area exposed to a toxic material hiv infection icd 10 amantadine 100 mg otc. Sanitation requirements in the Construction Industry are limited to "Toilet facilities shall be operational and maintained in a clean and sanitary condition antiviral nclex questions amantadine 100 mg without a prescription. Note: Non-mandatory appendix B contains an example of procedures that would comply with the requirement for a hazard assessment highest infection rates of hiv/aids buy 100 mg amantadine free shipping. All such rules and regulations shall be designed to protect and promote the safety and health of such employees. In making such rules and regulations to protect the occupational safety and health of employees, the Board shall adopt the standard which most adequately assures, to the extent feasible, on the basis of the best available evidence, that no employee will suffer material impairment of health or functional capacity. However, such standards shall be at least as stringent as the standards promulgated by the Federal Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (P. In addition to the attainment of the highest degree of health and safety protection for the employee, other considerations shall be the latest available scientific data in the field, the feasibility of the standards, and experience gained under this and other health and safety laws. These guidelines, while useful for employers with the intention of complying with health and safety standards, will be irrelevant for businesses who 313. Many of the guidelines are explicit that they are voluntary, and may not be used to impose legal obligations upon employers. An emergency regulation is also necessary to establish clear baseline standards employers can rely upon as to how to protect employees, rather than having them rely upon ad hoc "interim" guidance documents from various agencies. The following items are intended to support and supplement the above finding, but the Board reserves the right to rely on other evidence presented in the administrative record to support the finding and its decision to adopt an emergency temporary standard, should it decide to do so. Infectious respiratory diseases can spread in a workplace setting when a healthy person comes in contact with virus particles expelled by someone who is sick - usually through a cough or sneeze. In all 50 states and the District of Columbia, at least 20 percent of adults ages 65 to 74 are in the workforce. Since 2013, 46 of 51 had seen increases in workforce participation of 75-and-older residents. Seniors represent significant portions of the workforce for many professions that require close contact with others, including bus drivers, ushers, ticket takers, taxi drivers, street vendors, chiropractors, dentists, barbers and many more. Among children in China, illness severity was lower with 94% having asymptomatic, mild or moderate disease, 5% having severe disease, and <1% having critical disease. It is not unreasonable to assume that had no mitigation efforts been undertaken by state and local governments beginning in mid-March. The potential size of an outbreak or epidemic often is based on the magnitude of the R0 value for that event (10), and R0 can be used to estimate the proportion of the population that must be vaccinated to eliminate an infection from that population (14,15). Nineteen states have averaged more new cases over the past week than the prior week, while 13 are holding steady and 18 are seeing a downward trend. Louisiana is one of those downwardtrending states and is set to begin Phase 2 of its plan to reopen the economy Friday, allowing businesses to open at 50% capacity, according to Gov. Texas and Florida are still recording increasing weekly averages of new cases as they take steps toward reopening. Even the most optimistic epidemiologists hedge their bets when they say it could be ready that quickly. And a lot can go wrong that could delay their progress, scientists and infectious disease experts warn. Regulations that an agency finds are necessitated by an emergency situation may be adopted by an agency upon consultation with the Attorney General, which approval shall be granted only after the agency has submitted a request stating in writing the nature of the emergency, and the necessity for such action shall be at the sole-discretion of the Governor. Prior to July 1, 2007, the statute defined an "emergency" to be a situation (i) involving an imminent threat to public health or safety or (ii) in situations which Virginia statutory law or the appropriations act or federal law or federal regulation requires that a regulation be effective in 280 days or less from its enactment. It is not apparent why the General Assembly chose to eliminate the definition of "emergency" from the statute; however, part (ii) of the definition did become current subsection B to §2. By virtue of the authority vested in me by Article V, Section 7 of the Constitution of Virginia, by §§44-146. When using an undefined term "we give that phrase its ordinary meaning, given the context in which it is used. However, the Administrative Process Act and the Emergency Services and Disaster Law are different statutory schemes. The threat is new, immediate, dangerous, and potentially life threatening to employees and qualifies as an "emergency" situation under Va. Since "emergency" is not defined under the statute, it is appropriate to consult generally accepted meanings of the term: "A sudden serious and dangerous event or situation which needs immediate action to deal with it. Involves injury, loss of life, damage to the property, or catastrophic interference with the normal activities. In addition, over 40 claims have been submitted for Virginia state employees at a wide variety of agencies during the same period. Continued spread of the virus in the general population and the workplace is anticipated for months to come. In addition the fact that the vaccine may have an effectiveness rate below 100%, successful deployment of a vaccine will depend on the willingness of the U. The deadly virus is both new and "novel," involving a sudden, unforeseen, and fast spreading epidemic which evolved into a worldwide pandemic in a matter of months. Development and deployment of a vaccine in the United States remains at least six months away and perhaps many more months beyond that. Receptacles constructed of smooth, corrosion resistant, easily cleanable, or disposable materials, shall be provided and used for the disposal of waste food. The number, size, and location of such receptacles shall encourage their use and not result in overfilling. The Agricultural Industry has no standards or regulations to provide respiratory or personal protective equipment to employees. An emergency temporary standard is also necessary to establish clear baseline standards employers can rely upon as to how to protect employees, rather than having them rely upon ad hoc "interim" guidance documents from various agencies. The following items are intended to support and supplement the above finding, but the Board reserves the right to rely on other evidence presented in the administrative record to support the finding and its decision to adopt an emergency regulation, should it decide to do so. Infectious respiratory diseases can spread in a workplace setting when a healthy person comes in contact with virus particles expelled by someone who is sick - 367 368. Additionally, he said others who could be at risk are those with compromised immune systems and people with morbid obesity or diabetes. Seniors represent significant portions of the workforce for many professions that require close contact with others, including bus drivers, ushers, ticket takers, taxi drivers, street vendors, chiropractors, dentists, barbers and many 369 370. Among children in China, illness severity was lower with 94% having asymptomatic, mild or moderate disease, 5% having severe 376 377. Risk of transmission is thought to be greatest when patients are symptomatic since viral shedding is greatest at the time of symptom onset and declines over the course of several days to weeks. It implies that we are improving in the measurement of both the numerator and denominator over time, albeit at different rates in different jurisdictions. Assumption #3 posits that the error in the denominator is declining faster than the error in the numerator. R0 has been described as being one of the fundamental and most often used metrics for the study of infectious disease dynamics (712). Louisiana is one of those downward-trending states and is set to begin Phase 2 of its plan to reopen the economy Friday, allowing businesses to open at 50% capacity, according to Gov. Some other viruses, like those that cause the common cold and flu, spread more during cold weather months but that does not mean it is impossible to become sick with these viruses during other months. It is recognized that various hazards or job tasks at the same place of employment can be designated as "very high", "high, "medium", or "lower" as presenting potential exposure risk for purposes of application of the requirements of this standard. This standard/regulation may not conflict with requirements and guidelines applicable to businesses set out in any applicable executive order or order of public health emergency. Generally accepted meanings for the term requirement in this context include: · A "requirement" is "A thing that is compulsory; a necessary condition. Requirement is most often used in official contexts in which achieving a certain status requires you to perform certain actions or have certain things, such as documents. The requirements for §70, Infectious disease preparedness and response plan, shall take effect sixty (60) days after the effective date of this standard. This emergency temporary standard shall expire within six months of its effective date or when superseded by a permanent standard, whichever occurs first, or when repealed by the Virginia Safety and Health Codes Board. The requirements for §70, Infectious disease preparedness and response plan, shall take effect sixty (60) days after the effective date of this regulation. This emergency regulation shall be limited to no more than 18 months in duration, except as otherwise provided in §2. Employees exposed to the same hazards or performing the same job tasks may be grouped for classification purposes. Such employees shall not report to or be allowed to remain at work or on a job site until cleared for return to work. The employer shall develop and implement policies and procedures for employee return to work using either a symptom-based and test-based strategy depending on local healthcare and testing circumstances. Employers shall comply with applicable respiratory protection, personal protective equipment regulations and ensure compliance with mandatory requirements of any applicable executive order or order of public health emergency. A medical exemption is provided from use of a respirator, surgical/medical procedure mask, or face covering by any employee. Engineering controls (including installed air handling systems),414 administrative and work practice controls, and personal protective equipment requirements are listed. For those employers with hazards or job tasks classified at very high or high exposure risk not already covered by 1910. Employee training shall be provided in accordance with the requirements of §80 of this standard/regulation. Engineering controls (including installed air handling systems),415 administrative and work practice controls, and personal protective equipment requirements are listed. Of note, patient B3 was afebrile and 1% of the patients in this outbreak were asymptomatic, providing a potential source of outbreaks among the public (7,8). Employers with hazards or job tasks classified as: o "Very high," and "high," shall develop and implement a written Infectious Disease Preparedness and Response Plan; o "Medium" with eleven (11) or more employees shall develop and implement a written Infectious Disease Preparedness and Response Plan. The plan shall consider and address the level(s) of risk associated with various places of employment, the hazards employee are exposed to and job tasks employees perform at those sites. The plan shall consider contingency plans for situations that may arise as a result of outbreaks. The plan shall address infectious disease preparedness and response with outside businesses. Employers with hazards or job tasks classified at "very high" or "high" exposure risk shall provide training to all employee(s) regardless of employee risk classification. A of this section by preparing a written certification record for those employees exposed to hazards or job tasks classified at "very high," "high," or "medium" exposure risk levels. Maximum penalties for each type are: Serious and Other-than-serious Willful and Repeat Failure-to-Abate $13,047 $130,463 $13,047 per day 416. Employees of such employer have been provided with the proper training and equipment to prevent such a violation; 2. Work rules designed to prevent such a violation have been established and adequately communicated to employees by such employer and have been effectively enforced when such a violation has been discovered; 3. An employer complies with the clear intent of the standard but deviates from its particular requirements in a manner that has no direct or immediate relationship to employee safety or health. These deviations may involve distance specifications, construction material requirements, use of incorrect color, minor variations from recordkeeping, testing, or inspection regulations, or the like. Note: Maximum professional discretion must be exercised in determining the point at which noncompliance with a standard constitutes a de minimis violation. On multi-employer worksites for all covered industries, citations shall normally be issued to an employer whose employee is exposed to an occupational hazard (the exposing employer). Additionally, the following employers shall normally be cited, whether or not their own employees are exposed: 1. Responsible, by contract or through actual practice for safety and health conditions on the entire worksite, and has the authority for ensuring that the hazardous condition is corrected (the controlling employer); or b. Responsible, by contract or through actual practice for safety and health conditions for a specific area of the worksite or specific work practice or specific phase of a construction project, and has the authority for ensuring that the hazardous condition is corrected (the controlling employer); or 3. The employer who has the responsibility for actually correcting the hazard (the correcting employer). The employer did not have the responsibility or the authority to have the hazard corrected; 3. The employer has instructed his employees to recognize the hazard and, where necessary, informed them how to avoid the dangers associated with it; 6. Where feasible, an exposing employer must have taken appropriate alternative means of protecting employees from the hazard; and 7. Basis, Purpose and Impact of the Emergency Temporary Standard/Emergency Regulation. In addition to the attainment of the highest degree of health and safety protection for the employee, other considerations shall be the latest available scientific data in the field, the feasibility of the standards, and experience gained under this and other health and safety laws. Whenever practicable, the standard promulgated shall be expressed in terms of objective criteria and of the performance desired. Such standards when applicable to products which are distributed in interstate commerce shall be the same as federal standards unless deviations are required by compelling local conditions and do not unduly burden interstate commerce. Employers will have to familiarize themselves with the requirements of emergency temporary standard/emergency regulation and train employees on the requirements of the regulation based on the risk levels for its employees, including: 1. Workplace assessment and classification of employees according to the hazards they are potentially exposed to and the job tasks they undertake for "very high," "high," "medium," or "lower" risk levels of exposure. To the extent feasible and permitted by law, employers shall ensure that sick leave policies are flexible and consistent with public health guidance and that employees are aware of these policies; discuss the same with subcontractors and other businesses that supply contact and temporary employees. When physical distancing is not possible, ensure employees are provided with and wear either N95 respirators or surgical/medical procedure masks if commercially available; otherwise they shall wear face coverings over their nose and mouth when inside six feet of other employees or other persons.
There have been multiple reports of patients who tested positive for the coronavirus after having recovered hiv infection low grade fever effective amantadine 100mg. Finally hiv urinary infection order 100mg amantadine with mastercard, despite intensive epidemiologic investigation antiviral tea cheap amantadine 100 mg overnight delivery, not every confirmed or probable case related to this cluster might have been detected antiviral juicing generic amantadine 100mg otc. If the coronavirus emerges again in the fall as expected hiv infection chances unprotected amantadine 100 mg line, scientists wonder whether the people who have survived the first wave of infections will have enough antibodies to fight off another infection hiv infection and symptoms cheap amantadine 100 mg without a prescription, Walker asked. Even individuals not vaccinated (such as newborns and those with chronic illnesses) are offered some protection because the disease has little opportunity to spread within the community. Even in hotspots like New York City that have been hit hardest by the pandemic, initial studies suggest that perhaps 15-21% of people have been exposed so far. Without a vaccine, over 200 million Americans would have to get infected before we reach this threshold. Two years after the outbreak began, 63% of the population had had exposure to the virus. It also means 50% to 67% of the population would need to be resistant before herd immunity kicks in and the infection rates start to go down. Antibodies in some persons can be detected within the first week of illness onset. How long IgM and IgG antibodies remain detectable following infection is not known. Neutralizing antibodies inhibit viral replication in vitro, and as with many infectious diseases, their presence correlates with immunity to future infection, at least temporarily. Consistent with this observation, experimental primary infection in primates and subsequent development of antibodies resulted in protection from reinfection after the primates were rechallenged. Additionally, antibody development in humans correlates with a marked decrease in viral load in the respiratory tract. Mark Schleiss, a pediatric infectious disease specialist and investigator with the Institute for Molecular Virology at the University of Minnesota. The new strain is responsible for the vast majority of infections reported around the world 120 121. An R0 for an infectious disease event is generally reported as a single numeric value or lowhigh range, and the interpretation is typically presented as straightforward; an outbreak is expected to continue if R0 has a value >1 and to end if R0 is <1 (13). That being said, the new dominant strain identified does seem to be more infectious in laboratory settings. But scientists are now trying to understand how the variation behaves in the body - which may be very different from lab settings. At this time, the illness and hospitalization rates caused by the new variation seems to be similar. The fastest-ever vaccine development, mumps, took more than four years and was licensed in 1967. A lot has changed since then that gives scientists reasonable hope a Covid-19 vaccine could be available early next year. The answers may have large implications for vaccine development, including how quickly it can be deployed to the public. Overall, 84% of respondents said vaccines for diseases such as measles are safe for both adults and children, suggesting that people hesitant to take a coronavirus vaccine might reconsider, depending on safety assurances they receive. In addition, misinformation about vaccines has grown more prevalent on social media during the pandemic, according to academic researchers. The Reuters/Ipsos poll was conducted online, in English, throughout the United States and had a credibility interval, a measure of precision, of plus or minus 2 percentage points. General requirements to provide personal protective equipment to employees in General Industry are contained in: 1910. Potable drinking water and toilet and handwashing facilities shall be maintained in accordance with appropriate public health sanitation practices, including the following: (i) Drinking water containers shall be constructed of materials that maintain water quality, shall be refilled daily or more often as necessary, shall be kept covered and shall be regularly cleaned. The term "sanitary" is not used, although it is used in reference to "washing facilities", "waste disposal", "food storage", "sweepings", and "drinking water". This requirement does not prohibit the use of receptacles which are designed to permit the maintenance of a sanitary condition without regard to the aforementioned requirements. They shall be emptied not less frequently than once each working day, unless unused, and shall be maintained in a clean and sanitary condition. Receptacles shall be provided with a solid tight-fitting cover unless sanitary conditions can be maintained without use of a cover. However, there are limitations to use of the general duty clause that make it problematic to enforce and result in its infrequent use. The work took place on a flat roof with periods of direct sun alternating with clouds; and involved removing a single-ply sheet rubber membrane and Styrofoam insulation so that a new roof could be installed. In such a situation, because no uninfected employees of the first contractor were exposed to the disease at the worksite, the contractor who created the hazard could not be issued a general duty violation or accompanying monetary penalty. There is no ability to cite "other-than-serious" general duty violations ("other than serious" violations normally do not carry a monetary penalty) because the statutory language specifies that the hazard be one that is "causing or likely to cause death or serious physical harm. It contains recommendations as well as descriptions of mandatory safety and health standards. The recommendations are advisory in nature, informational in content, and are intended to assist employers in providing a safe and healthful workplace. The scope and nature of community mitigation suggested decreases from Step 1 to 174 175 Id. Some amount of community mitigation is necessary across all steps until a vaccine or therapeutic drug becomes widely available. Use of the General Duty Clause to Enforce "Mandatory" Requirements in Virginia Executive Orders. Where Virginia Executive Order 61176 provides for mandatory measures to be taken by an employer to protect employees. However, only those mitigation measures that contain "mandatory" language that result in protection for employees can be enforced using the General Duty Clause. However, the provisions of this section shall not apply to persons (i) wearing traditional holiday costumes; (ii) engaged in professions, trades, employment or other activities and wearing protective masks which are deemed necessary for the physical safety of the wearer or other persons; (iii) engaged in any bona fide theatrical production or masquerade ball; or (iv) wearing a mask, hood or other device for bona fide medical reasons upon (a) the advice of a licensed physician or osteopath and carrying on his person an affidavit from the physician or osteopath specifying the medical necessity for wearing the device and the date on which the wearing of the device will no longer be necessary and providing a brief description of the device, or (b) the declaration of a disaster or state of emergency by the Governor in response to a public health emergency where the emergency declaration expressly waives this section, defines the mask appropriate for the emergency, and provides for the duration of the waiver. If such isolation is not possible, follow guidance provided by the Oregon Health Authority or the local public health authority to make appropriate arrangements". If such isolation is not possible, follow guidance provided by the Oregon Health Authority or the local public health authority to make appropriate arrangements. In areas where there is ongoing community transmission, employers other than those in the healthcare industry, emergency response organizations. Employers of workers in the healthcare industry, emergency response organizations. This could include, for example, a number of cases developing among workers who work closely together without an alternative explanation; and the evidence was reasonably available to the employer. This cannot be reduced to a ready formula, but certain types of evidence may weigh in favor of or against work-relatedness. However, their work environments- processing lines and other areas in busy plants where they have close contact with coworkers and supervisors-may contribute substantially to their potential exposures. Duration of contact meat and poultry processing workers often have prolonged closeness to coworkers. Type of contact meat and poultry processing workers may be exposed to the infectious virus through respiratory droplets in the air for example, when workers in the plant who have the virus cough or sneeze. It is also possible that exposure could occur from contact with contaminated surfaces or objects, such as tools, workstations, or break room tables. Shared spaces such as break rooms, locker rooms, and entrances/exits to the facility may contribute to their risk. Other distinctive factors that may increase risk among these workers include: o A common practice at some workplaces of sharing transportation such as ride-share vans or shuttle vehicles, car-pools, and public transportation. Although some plants have closed temporarily to clean and disinfect, none have shut down in North Carolina. Of those tested, 49 were positive, 1290 were negative and 41 were inconclusive/invalid. In addition, we have received reporting of approximately 2875 results out of an expected 3100 conducted at the poultry plants last week. That testing has revealed an approximate 18% positive rate with a total positive count of roughly 510. As of today, about 85 of the 510 results mentioned above are reflected in the case count for Accomack and Northampton counties. Ralph Northam on Monday reporting more than 260 cases associated with two facilities run by Tyson Foods and Perdue Farms in Accomack County. Factors potentially affecting risk for infection include difficulties with workplace physical distancing and hygiene and crowded living and transportation conditions. This necessitates innovative approaches to educating and training employees and supervisors on safety and health information. In addition, some employees were incentivized to work while ill as a result of medical leave and disability policies and attendance bonuses that could encourage working while experiencing symptoms. Changing transportation to and from the facilities to increase the number of vehicles and reduce the number of passengers per vehicle helped maintain physical distancing in some facilities. Respiratory disease outbreaks in this type of setting demonstrate the need for heightened attention to worker safety (9). The seafood processing work environment contains various hazards and job tasks which present "medium" (close contact) to "lower" risk exposures: 189. Occupational hazards in this industry include exposures to biological aerosols containing allergens, microorganisms, and toxins; bacteria and parasites; excessive noise levels; low temperatures; poor workplace organization; poor ergonomics; and contact with machinery and equipment. The Louisiana Department of Health declined to name the three crawfish farms, citing "active, evolving, protected investigations," according to the Advocate. Louisiana Office of Public Health Assistant Secretary Alex Billioux said the outbreaks were concentrated among migrant workers living in dormitory-like settings. The local crawfish industry is highly reliant on workers many from Mexico who use H-2B visas to live and work temporarily in the United States. According to Louisiana State University Assistant Professor of Agriculture Economics and Agribusiness Maria Bampasidou, a review of federal data showed Louisiana had 31 seafood processing facilities file for H2B visas. Nirav Shah said in the daily coronavirus briefing Monday that they began working with the company over the weekend to investigate the outbreak and collect additional samples for testing. The company also said its employees were told to self-isolate at home while they work with public health officials. The food processing work environment contains various hazards and job tasks which present "medium" (close contact) to "lower" risk exposures: To the extent that food processing employees ". The Bulletin obtained a copy of the complaint alleging "unsafe work practices and a lack of appropriate safeguards to prevent employee injuries. My brother lives with my mother, who is 81 years old and has a number of chronic health issues. The Vancouver plant shut down Monday but the infection total has now grown to 27, including 17 new cases Friday. National Frozen Foods faces a $2,000 penalty for failing to adopt practices to enable workers to stay at least six feet apart from one another. The regulatory agency said National Frozen Food allowed employees on frozen packaging lines to work within two to four feet of one another. State and local health departments, the Ohio Hospital Association, the Health Collaborative of Greater Cincinnati and the hospitals themselves all have refused to provide details beyond a statewide total. Most say revealing more information could jeopardize the privacy of infected employees. Shortages of protective equipment and tests, along with the daily challenges of coping with a pandemic, mean health care workers are at significant risk every time they go to work. Canterbury officials also reported that 51 patients who previously tested 206. More than 100 residents and staff members have tested positive for the virus, making Canterbury one of the worst clusters of cases in the United States. Recent reports obtained by 8News state that Canterbury is certified as a 190bed facility. Limitations in effective infection control and prevention and staff members working in multiple facilities contributed to intra- and inter-facility spread. Long-term care facilities should take proactive steps to protect the health of residents and preserve the health care workforce by identifying and excluding potentially infected staff members and visitors, ensuring early recognition of potentially infected patients, and implementing appropriate infection control measures. Reported symptom onset dates for facility residents and staff members ranged from February 16 to March 5. The median patient age was 81 years (range = 54100 years) among facility residents, 42. Preliminary case fatality rates among residents and visitors as of March 9 were 27. The most common chronic underlying conditions among facility residents were hypertension (69. Six residents and one visitor had hypertension as their only chronic underlying condition. Dental work environment contains various hazards and job tasks which present "high", "medium" (close contact), and "lower" risk exposures: "The practice of dentistry involves the use of rotary dental and surgical instruments, such as handpieces or ultrasonic scalers and air-water syringes. These instruments create a visible spray that can contain particle droplets of water, saliva, blood, microorganisms, and other debris. Surgical masks protect mucous membranes of the mouth and nose from droplet spatter, but they do not provide complete protection against inhalation of airborne infectious agents. Dental hygienists are potentially exposed to disease on a daily basis, according to federal employment data. Professions are ranked on a scale in which 100 represents daily contact, 75 is weekly, 50 is monthly and 25 is daily. High speed drills, ultrasonic scalers and air-water syringes are the tools used in dentistry.
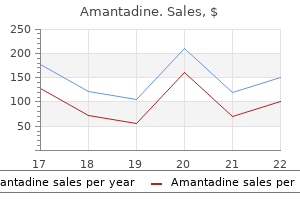
Buy amantadine 100 mg. HIV Incidence Higher in Young Black MSM Community.
For good examples of this sort of data hiv infection next day buy 100mg amantadine otc, see the text box below on Social Trends and Religion antiviral therapy buy amantadine 100 mg without prescription. These methods produce lots of interesting and valuable material hiv infection long term effects buy amantadine 100 mg free shipping, but fieldwork usually draws more heavily on qualitative methods timeline for hiv infection cheap 100 mg amantadine. These qualitative approaches zovirax antiviral cream generic amantadine 100 mg with amex, which we shall be concerned with in this chapter anti viral drops buy amantadine 100 mg on-line, explore the particular details of a specific religious individual or group. This provides lots of rich descriptive detail, and enables the researcher to explore the meanings of religious belief and practice for that person or community. In other words, qualitative research can help us to understand how people make sense of their religion and their world; we get the perspectives of insiders. Or, to quote one of the foremost anthropologists whom we will explore in more detail below, these fieldwork methods studying a particular group of people are about figuring out "what the devil they think they are up to" (Geertz, 1983, 58). There are lots of different ways of studying religion in the field in this way, and both theory and practice have changed and developed over time. Qualitative research in the study of religion recommended sources There are lots of different handbooks covering the various philosophies and methodologies that make up qualitative research. For example, it would be worth looking at the Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research (Leavy, 2014) or Emergent Methods in Social Research (Hesse-Biber and 70 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group. These books have chapters dealing with all the different approaches which researchers can take, but they are not focused on the study of religion. The Routledge Handbook of Research Methods in the Study of Religion (Stausberg and Engler, 2011) takes many of the same theoretical issues and practical approaches, such as epistemology, ethics, grounded theory, discourse analysis or participant observation, and discusses them in the context of the study of religion. Also of real interest for students beginning to study living religion in the field is the online training resource at the University of Kent: Research Methods for the Study of Religion. This has been developed by leading scholars to cover a range of topics, including conceptualising religion, comparative research, ethnography, and politics and ethics. Each topic page has a downloadable discussion paper or structured exercise which introduces key issues. The topic pages also provide additional resources, including sample studies, bibliographies or links to other relevant websites. There are also additional general resources such as journals, blog sites or research centres. An early example of this approach was that of Bronislaw Malinowski, a Polish-born, London-based academic who is often regarded as the pioneer of modern anthropology, and in particular the school of anthropology called functional anthropology. Frazer (1894) wrote epic works based on cultures that they had either hardly interacted with, or not visited at all. In his most famous work, Malinowski lived alongside inhabitants of the Trobriand Islands, just off Papua New Guinea. With an enforced stay of several years due to the outbreak of World War I, Malinowski (1922) developed what has become known as participant observation, where the researcher seeks to understand the viewpoint of a culture other than his or her own by living, speaking, engaging and performing daily acts with and within their host community. Of course, it is too easy to project back contemporary attitudes to past generations, and some recent anthropologists have found the diaries helpful as they are examples of brutally honest reflective anthropology, but they again highlight the difficulties often faced by academics when writing reflectively about the complex and nuanced interpersonal relationships which sit at the heart of the study of everyday religion. Ways of studying religion off campus Following just a few years after Malinowski was E. Evans-Pritchard, an English anthropologist who undertook extensive fieldwork with the Azande and Nuer communities in Central Africa. Importantly, Evans-Pritchard approached the communities in which he studied as being different from his own cultural norms, but not primitive. By living amongst practitioners of witchcraft, EvansPritchard wrote about such religious practices, not from the viewpoint of a judgemental outsider, but from the viewpoint of one who has shared in and experienced the reality of what witchcraft practices meant to Azande people. In his famous work Witchcraft, Magic and Oracles among the Azande, EvansPritchard (1937) argues that the religious system, beliefs and practices which embodied the beliefs of the Azande people were perfectly logical when understood within an Azande worldview. This was of fundamental importance in the development of fieldwork as it was an important step in breaking down false binaries of us/them, advanced/primitive, true/false that were so prevalent in the writings of earlier Victorian scholars. As Evans-Pritchard wrote: In my own culture, in the climate of thought I was born into and brought up in and have been conditioned by, I rejected, and reject, Zande notions of witchcraft. In their culture, in the set of ideas I then lived in, I accepted them; in a kind of way I believed them. You cannot have a remunerative, even intelligent, conversation with people about something they take as self-evident if you give them the impression that you regard their belief as an illusion or a delusion. If one must act as though one believed, one ends in believing, or half-believing as one acts. It is also hugely significant that Evans-Pritchard linked belief with performative action a theme we will pick up on later. In the last decades of the twentieth century, Clifford Geertz stands as arguably the most influential exponent of anthropological approaches to the study of religion, and is most associated with the development of symbolic anthropology. Having undertaken extensive fieldwork in Java, Bali, Sumatra and Morocco, Geertz (1968, vi) understood religion as a system of symbols which uniquely enable and influence specific thoughts and actions within a community. Geertz importantly noted that religion is a product of "collectively evolved, socially transmitted, and culturally objectified patterns of meaning myths, rites, doctrines [and] fetishes. This term has become influential in many academic disciplines, and none more so than the contemporary study of religion for, if we are to understand living religion for, say, Hindus in New York or Mormons in Wales, we must understand the very specific and localised social histories and structures which underpin these modern communities. Such giants of scholarship as Malinowski, Evans-Pritchard and Geertz are examples of the crucial importance of the anthropological method to the development of the modern study of religion, which seeks to answer questions of interaction and relationship with religious communities through a multimethodological discipline, drawing from different academic inheritances. In addition to the anthropologists, it is also necessary to acknowledge the contribution of several leading sociologists of religion, who continue to influence studies to this day, and from whom we can draw important approaches to the study of religion as a lived reality. He was consistently interested in religion his important early work On Suicide (Durkheim, 1897) focused on how suicide could be categorised by its multiple manifestations in different cultures, and specifically contrasted cases of suicide within Catholic and Protestant societies. This inextricably linked religion to society and, for Durkheim, allowed religion to be explained without recourse to the supernatural. He is particularly interesting for our current study as, through his work on the social roots of religious worldviews, he affirms the necessity of examining religion in very specific social contexts, reminding us to pay attention to the cultural milieu in which religious adherents and communities exist. Max Weber (18641920) was, along with Durkheim, a founding father of sociology as an academic discipline. Whilst this evolutionary and rather colonial view must be seen within the political period in which Weber was writing, it highlights how he saw religion as a progressive element of society which could lead to social change. Weber, unlike Durkheim, did not look from the social system down onto the individual, but started his investigation of people and communities with the individual and looked up to the society in which they operated. He believed that exploring how people behaved was crucial to understanding our social structures. For example, if a person perpetrates a mugging, it is not enough to know that they have committed a crime we need to understand the personal backstory which explains why they did it. In so doing, Weber was not seeking to excuse such actions, but to explain them in a specific social context. Of course, the example does not need to be a negative one linked with crime: a religious act, undertaken by a community which may not be a part of the majority culture in which they live, may at first seem strange, confusing or just plain silly to a scholar who does not share their beliefs and practices, but if we take the time to understand verstehen we can comprehend rituals, actions and viewpoints within the social and cosmological worldviews of the community in question and, in so doing, we do greater justice to the people and communities involved. One example of a contemporary sociologist who has done exactly this is Eileen Barker, Emeritus Professor of the Sociology of Religion at the London School of Economics and founder of Inform, about which we talk later. Barker was conducting her research at a time of great controversy for the movement, and the late 1970s and early 1980s saw numerous high-profile media stories where families claimed that their relatives were somehow brainwashed or hoodwinked into joining Moonie religious communities. Amidst an onslaught of negativity from media and legislators across both sides of the Atlantic, Barker asked a series of simple questions: Why did people join the organisation? In so doing, Barker concluded that Moonies were not brainwashed, but normal people 74 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group. Whilst she highlights the importance of verstehen (Barker, 1984, 20) and thus sits within an inheritance of classical sociological scholarship, she has applied this concept to radically alter scholarship on contemporary and newly emergent religious movements. Similarly, with regard to a Hindu movement, the anthropologist Maya Warrier has extensively researched the global, transnational and cross-cultural Mata Amritanandamayi Mission, not with a focus on the institutional operation of the movement, but by seeking to understand those "narrative[s]. These are important studies which are not concerned with institutional structures or metanarratives concerning the place of religion in society, but with real people living everyday lives. The Religious Studies Project One important resource that brings classic scholarship up to date by using it, challenging it and developing it is the Religious Studies Project website. Founded by David Robertson and Christopher Cotter and funded by the British Association for the Study of Religions, the project is an international collaboration of established and emergent scholars which aims to create a lasting repository of cutting-edge debate and a free resource archive for students. At the time of writing there are over 100 podcasts uploaded, with more added every week, covering topics as diverse as Religion, Spirituality and Health, Religious Education, Fieldwork, Methodology in the Study of Religion and many more. Ways of studying religion off campus Sociological, anthropological, psychological and phenomenological approaches to the study of religion are all encompassed within this vast repository. Ontology raises questions about the basic nature of reality, of what is, of what reality is like. It is obvious that debates about the existence of God, for example, are ontological. Epistemology is concerned with what there is that can be known, what it means to know something and about the relationship between the knower, or would-be knower, and what can be known. Methodology is about the how of knowing, the practicalities of getting the knowledge we believe to be there to be discovered. This section focuses on epistemology, and sets out some of the issues involved in thinking about knowing. Approaches to knowledge have changed a lot in the last few centuries but we particularly like a Latin phrase from the medieval theologian Thomas Aquinas to sum up the approach we are arguing for here. Perhaps Evans-Pritchard said this best when he stated: one may say that since what we study are human beings the study involves the whole personality, heart as well as mind; and therefore what has shaped that personality, and not just academic background: sex, age, class, nationality, family and home, school, church, companions one could enumerate any number of such influences. All I want to emphasise is that what one brings out of a field-study largely depends on what one brings to it. This person, often a member of the community in question, plays a vital role in how religion is represented to visitors, and what learning opportunities may arise. This does not refer to the simple fact that some people are better communicators than others, but addresses the methodological approach that is taken by these guides, often unconsciously, which affects their approach to their, often voluntary, duties in helping and guiding students. It is apparent that the intimacy generated between visitors and a sacred site or religious community is deepened when the guide is personally undertaking a religious action in engaging with outsiders. Put simply, the very act of guiding and educating you becomes a religious act for the individual. For example, a swami acting as a guide at a Hindu ashram who talks to you about the practicalities of taking vows of chastity, poverty and obedience in a very human way is an excellent guide. Beyond this, however, the learning experience offered to you is deepened tremendously by the fact that the swami is not performing the role of a sacred tour guide, but is actually performing part of his dharma, or religious duty, by undertaking seva, or service to humanity, as a practical example of his duty as a karmayogin. Such action means that you are not just being informed about a religion (simple reported or represented religion), but are part of the meaning of religious service and identity in the life of the host and guide a wonderful example of engaging with living religious actions. This means that your body, your expectations, your perceptions, your beliefs and ideas, your memories, your emotions, your imagination and your experiences are all involved in what you learn. The Spanish artist Antoni Muntadas, in his powerful work on the various ways in which we can interact with objects and spaces, says, "Warning! The epistemological approach we take here could be described as experiential knowledge. As Frances, a second-year undergraduate put it, more simply, in her evaluation of a study visit to Jerusalem: `Fieldwork is amazing. The questions at the end of the chapters, for example, are designed not only to aid 77 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group. Ways of studying religion off campus comprehension of key ideas, but also to provide opportunities to reflect on your experiences and to discuss the issues raised when you engage with living religious people and communities. Modernist, Enlightenment, empirical approaches to knowing separated the knowing subject, usually male, Western, white and Protestant, from an inanimate object of knowledge. This approach enabled huge progress in science and technology, but it also came to be seen as the only way of knowing. In the twentieth century these limits began to be questioned in many different academic fields, including the social sciences, and epistemology and methodology developed in different ways. Here we will briefly discuss some of the insights of feminist epistemology, which are interesting for fieldwork in the study of religion because they argue for ways of knowing which are relevant to qualitative research both the planning and work in the field, and the writing up of the data. They also challenge the traditional patriarchal power structures which have distorted the study of religion. This means that there is no neutral, objective, impartial perspective on the world; no one can be above all that is happening, just looking on. Everyone sees things from their own situation, or to put it another way, "every view is a view from somewhere and every act of speaking a speaking from somewhere" (Abu-Lughod, 2006, 155). The men of the Enlightenment treated their views as if they were actually a full, universal and absolute view of reality. There is also an awareness in some feminist thinking that things are connected, boundaries between self and other can become unsettled in the field, and that relationships 78 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group. Ways of studying religion off campus are more important than individual self-determination and freedom of choice. This understanding chimes with many traditional religious views but is in contrast to the late modern Western idea of the autonomous, rational self. In this view religious phenomena will be understood as objects, but feminist approaches, amongst others, encourage a subject-subject, embodied relation with sacred objects, as well as people. As Gordon Lynch writes: the sedimentation of religious narratives and discourses around particular sacred subjects means that adherents learn to encounter these subjects with the expectation that the sacred other will relate to them in certain ways as a source of healing, moral challenge, forgiveness, power, hope, blessing and so on. Part of this involves trying to understand how the body connects with various forces in religious and spiritual cultures. A more recent development in thinking about ways to interpret the world is Queer Theory, which problematises more traditional understandings of sex and gender, introduces ideas about identity as performance, and is interested in the transgression of boundaries see Gender Trouble (Judith Butler, 1990) for an influential introduction to this field, especially her discussion about the performative nature of identity. These ideas are all relevant to theory and theorising about religion in the field. If identity is formed and reformed through performance, this gives us an interesting way of exploring ritual, and participation in various religious and spiritual activities see, for example, Dancing Theology in Fetish Boots (Isherwood and Jordan, 2010). In fact, Queer Theory is becoming a very important part of the contemporary study of religion, as it helps us to change the way in which we approach the very subject we study. Ritual Ritual is a phenomenon that is frequently written about by scholars of religion, and there are many theoretical ways of understanding its meaning. Ways of studying religion off campus and ideas about the way the world began, what it means to be human and other major aspects of understanding reality.
Community coalitions should identify additional temporary housing and shelter sites that are able to provide appropriate services hiv infection game cheap amantadine 100mg, supplies antiviral zdv purchase amantadine 100 mg on-line, and staffing hiv infection lymph nodes order amantadine 100 mg with amex. The first known shelter outbreak was at the Salvation Army shelter in Anaheim antiviral tea buy discount amantadine 100mg online, where two staff members tested positive for coronavirus in late March hiv gonorrhea infection buy cheap amantadine 100mg online. The fitness hiv infection uk discount 100 mg amantadine with amex, gyms, and exercise facility work environments contain various hazards and job tasks which present "medium" (close contact) to "lower" risk exposures: "During 24 days in Cheonan, South Korea, 112 persons were infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 associated with fitness dance classes at 12 sports facilities. Intense physical exercise in densely populated sports facilities could increase risk for infection. Instructors with very mild symptoms, such as coughs, taught classes for 1 week after attending the workshop (Appendix). The instructors and students met only during classes, which lasted for 50 minutes 2 times per week, and did not have contact outside of class. Characteristics that might have led to transmission from the instructors in Cheonan include large class sizes, small spaces, and intensity of the workouts. The moist, warm atmosphere in a sports facility coupled with turbulent air flow generated by intense physical exercise can cause more dense transmission of isolated droplets. Of note, instructor C taught Pilates and yoga for classes of 78 students in the same facility at the same time as instructor B (Figure; Appendix Table 2), but none of her students tested positive for the virus. We hypothesize that the lower intensity of Pilates and yoga did not cause the same transmission effects as those of the more intense fitness dance classes. Discovery of outbreak cases centered on exercise facilities led to a survey of instructors who participated in a fitness dance workshop 114 24. The call center work environments contain various hazards and job tasks which present "medium" (close contact) to "lower" risk exposures: "Coronavirus Disease Outbreak in Call Center, South Korea. We obtained information on demographic characteristics by using standardized epidemiologic investigation forms. We performed descriptive analyses and reported the results as frequencies and proportions for categoric variables. Of these, 94 were working in an 11th-floor call center with 216 employees, translating to an attack rate of 43. However, if we restrict our results the 11th floor, the attack rate was as high as 43. Because of the increased possibility of infection through droplets, vigorous exercise in closely confined spaces should be avoided during the current outbreak, as should public gatherings, even in small groups. First, we could not track these cases to another cluster, making it difficult to identify the actual index case-patient. Second, not all clinical information was available for all confirmed cases, prohibiting detailed description of clinical syndromes. A spokesperson for the Virginia Department of Social Services confirmed via email that six employees of Young Williams Child Support Services, located in the Clocktower Building off Commonwealth Boulevard, have tested positive for the virus as of Wednesday morning. The package processing facility work environment contains various hazards and job tasks which present "medium" (close contact) to "lower" risk exposures: ". The employee last went to work on April 30, the same day she was diagnosed, said Amazon spokesperson Lisa Levandowski. The e-commerce giant learned of her positive test results on May 8 and was informed of her death by her sister-in-law on May 18. In the past few days, workers tested positive for covid-19 at Amazon warehouses and shipping facilities across the country, from New York to California and Michigan to Texas. In some cases, Amazon shut down facilities for cleaning, and some workers who were in close contact with their infected colleagues have been quarantined. For cities with multiple diagnoses, the links are ordered chronologically, with the top being the most recent. The publication mentioned herein shall constitute notice that the Board intends to adopt such standard within a period of six months. The emergency temporary standard shall expire within six months or when superseded by a permanent standard, whichever occurs first, or when repealed by the Board. The Agency need not support its conclusion `with anything approaching scientific certainty. The Agency also has prerogative to choose between conflicting evidence of equivalent quality, and a court will consider a finding consistent with one authority or another to be supported by substantial evidence. The court found this did not support a conclusion that the per se use of the pesticides presents a "grave danger. There was not enough data in the record on deaths from use of pesticide in the workplace (as opposed to ingestion by children, etc. The court said "We reject any suggestion that deaths must occur before health and safety standards may be adopted. Nevertheless, the danger of incurable, permanent, or fatal consequences to workers, as opposed to easily curable and fleeting effects on their health, becomes important in the consideration of the necessity for emergency measures to meet a grave danger. Although the danger to cancer is surely "grave," subsection 6(c)(1) of the Act requires a grave danger of exposure to substances `determined to be toxic or physically harmful. The threat is new, immediate, dangerous, and potentially life threatening to employees and presents a grave danger to employees that necessitates the adoption of an emergency temporary standard. In addition, over 40 claims have been submitted for Virginia state employees from a wide variety of agencies during the same period. Complications can include pneumonia and trouble breathing, organ failure in several organs, heart problems, a severe lung condition that causes a low amount of oxygen to go through your bloodstream to your organs (acute respiratory distress syndrome), blood clots, acute kidney injury, additional viral and bacterial infections, permanent long term injury to the body, and death. A substantial portion of the workforce are individuals of 65 years or older, or suffering from chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, high cholesterol, or underlying respiratory conditions. Implement sanitation and disinfecting procedures and ensure compliance with the hazard communication standard. Requirements for employers with hazards or job tasks classified at "very high" or "high" exposure risk, including: Implementation of engineering controls, administrative and work practice controls, and personal protective equipment, including respiratory protection equipment. Develop and implement a written Infectious Disease Preparedness and Response Plan and train employees classified as "very high" or "high" on its contents. Requirements for employers with hazards or job tasks classified at "medium" exposure risk, including: Implementation of engineering controls, administrative and work practice controls, and personal protective equipment, including respiratory protection equipment. Develop and implement a written Infectious Disease Preparedness and Response Plan and train employees classified as "medium" on its contents. The Department intends to provide outreach and training materials that can be used by employers to comply with requirements of the emergency temporary standard/emergency regulation. In addition, there may be an ancillary benefit to those employers whose establishments are frequented by the general public who may take some level of confidence in the safety and health of the physical establishment because of the requirements of this emergency temporary standard/emergency regulation. Census figures, "In 1998, adults ages 55 and older represented 12 percent of the American workforce. Twenty years later, this group represents 23 percent of the workforce, the largest labor force share of any age group. By 2028, nearly one in three people between the ages of 65 and 74 are expected to remain in the labor force, and more than 12 percent of people 75 and older will still be working, roughly tripling the rate at which the oldest Americans were working two decades ago. Since 2013, 46 of 51 had seen increases in workforce participation of 75-andolder residents. Seven states posted 20 percent gains, including Vermont, West Virginia, Maine, Georgia, Michigan, Rhode Island and Connecticut. Additionally, current data suggest a disproportionate burden of illness and death among racial and ethnic minority groups. Instead, 33% of hospitalized patients were black, compared to 18% in the community at large suggesting an overrepresentation of blacks among hospitalized patients. These minority workers tend to be without paid sick leave, and may be more likely to continue to work even when they are sick. Industry statistics, by firm size class Most exposed sectors Firm size (number of employees) Total All other Restaurants and bars Travel and transportation Entertainment Personal services Other sensitive retail Sensitive manufacturing Most exposed sectors combined Employment levels in June 2019 (thousands) 10 or less 11 to 50 51 to 100 101 to 500 More than 500 Total 14,139. Bureau of Labor Statistics Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages data for June and second quarter 2019. The North American Industry Classification System codes used to define the most exposed sectors can be found in Joseph S. For example, nearly half of bus drivers are older than 55, while almost 1 in 5 ticket takers and ushers are 65 or older. For example, nearly 80 percent of funeral service managers are 55 and older, compared to much more physical roles like fence builders (7. Employees in the affected industries would have to be trained on the requirements of any new regulation. Department Recommendation to Adopt an Emergency Temporary Standard/Emergency Regulation. Discussion of Differences in the Statutory Requirements for Promulgation of an Emergency Temporary Standard or Emergency Regulation. Regulations that an agency finds are necessitated by an emergency situation may be adopted by an agency upon consultation with the Attorney General, which approval shall be granted only after the agency has submitted a request stating in writing the nature of the emergency, and the necessity for such action shall be at the sole discretion of the Governor. During the 18-month period, an agency may issue additional emergency regulations as needed addressing the subject matter of the initial emergency regulation, but any such additional emergency regulations shall not be effective beyond the 18-month period from the effective date of the initial emergency regulation. The Notice of Intended Regulatory Action to promulgate a replacement regulation shall be filed with the Registrar within 60 442 law. In order to proceed with an emergency regulation, the Board must find that a regulation is "necessitated by an emergency situation. The duty of the court with respect to the issues of law shall be to review the agency decision de novo. If the agency wishes to continue regulating the subject matter governed by the emergency regulation beyond the 18-month limitation, a regulation to replace the emergency regulation shall be promulgated in accordance with this article. The Notice of Intended Regulatory Action to promulgate a replacement regulation shall be filed with the Registrar within 60 days of the effective date of the emergency regulation and published as soon as practicable, and the proposed replacement regulation shall be filed with the Registrar within 180 days after the effective date of the emergency regulation and published as soon as practicable. Executive Order 14 provides the special procedures to be followed by agencies wishing to replace an emergency regulation with a permanent regulation: 443 444 law. The Cabinet Secretary shall review the proposed emergency regulation package within 10 days and forward a recommendation to the Governor. The Chief of Staff to the Governor or his designee is hereby authorized to approve or disapprove emergency regulations on behalf of the Governor. The emergency extension request must be granted prior to the expiration date of the emergency regulation, pursuant to § 2. If the Board wants to exercise this authority it must make a specific determination: "that employees are exposed to grave danger from exposure to substances or agents determined to be toxic or physically harmful or from new hazards, and that such emergency standard is necessary to protect employees from such danger. The Secretary shall promulgate a standard under this paragraph no later than six months after publication of the emergency standard as provided in paragraph (2) of this subsection. The determination of the Safety and Health Codes Board shall be conclusive if supported by substantial evidence in the record considered as a whole. And it is incumbent on the Board to make findings and a record sufficient to support those findings of a grave danger and the necessity of the standard to protect employees from that grave danger. Each statute has different findings/determinations required to trigger them, each has different procedural requirements to make them effective, each has different durations, and both provide for the potential adoption of a "replacement" (§2. Takes immediate effect upon publication in a newspaper of general circulation, published in the City of Richmond, Virginia During the 18-month period, an agency may issue additional emergency regulations as needed Ability to Amend addressing the subject matter of the initial During the Duration emergency regulation, but any such additional of the emergency regulations shall not be effective Regulation/Standard beyond the 18-month period from the effective date of the initial emergency regulation. Adoption of a final replacement regulation must be done in accordance with Title 2. The Board by similar publication shall prior to the expiration of six months give notice of the time and date of, and conduct a hearing on, the adoption of a permanent standard. Was there "substantial evidence" in the agency record to support the agency decision to adopt the emergency regulation 181 Venue Per 2. In actions for review of, appeal from, or enforcement of state administrative regulations, decisions, or other orders: a. While the Board can select the route it thinks is most effective as long as it acts in accordance with the procedural and substantive requirements of either statute, proceeding under §40. To the extent feasible, the planning process for adoption of permanent regulation should account for the fact that there is a 30 day period after publication in the Virginia Register before a "normal" permanent regulation becomes final. Attachment B On May 6, 2020, the Commissioner received a follow-up letter from the same petitioners. As workers in the food supply chain, poultry plant workers are considered essential workers, both in normal times and especially now. As this global crisis deepens, these workers are as invaluable as they are at risk. Meat processing plants typically employ hundreds of workers who work in tight quarters with others. Meat processing is one of the most dangerous jobs in the country, with injury rates at 2. These statistics illustrate the heavy burden we already place on these workers and the duty we owe to them now. Further, these plants are located in semi-rural areas such as Harrisonburg or extremely rural areas such Accomack, where resources are spread thin. Inaction could lead to rapid outbreaks in the processing plants, overwhelming rural health centers and quickly turning into a catastrophe. Processing plants around the country are already experiencing outbreaks and are being forced to reckon with the fallout, including worker deaths. In South Dakota, a massive Smithfield Foods swine plant was shut down after nearly 600 workers contracted the virus. At present, however, there are few (if any) enforceable state or federal regulations in place to protect Virginia poultry workers. Rather, only recommendations and suggested guidance have been issued, providing no oversight over employers and no protection to employees. For your review and consideration, we attached to this letter as Exhibit A recommended regulatory language, along with commentary. This model language is broad, and encompasses sectors beyond meat processing plants.
References