




|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
SHALENDER BHASIN, MD
A serious disorder in which part of the intestine slides into an adjacent part of the intestine symptoms for bronchitis order cytoxan 50 mg free shipping. Most often keratin smoothing treatment generic cytoxan 50 mg overnight delivery, leukemia is a cancer of the white blood cells treatment solutions buy generic cytoxan 50 mg online, but some leukemias start in other blood cell types symptoms 37 weeks pregnant purchase 50mg cytoxan fast delivery. Activity of any of the large medicine queen mary discount cytoxan 50mg on line, mononuclear treatment alternatives purchase cytoxan 50mg with visa, highly phagocytic cells derived from monocytes that occur in the walls of blood vessels (adventitial cells) and in loose connective tissue (histiocytes, phagocytic reticular cells). A disease of the lungs characterized especially by inflammation and consolidation of lung tissue followed by resolution and by fever, chills, cough, and difficulty in breathing and that is caused especially by infection the presence of an excess of serum proteins in the urine; called also albuminuria (also known as proteinuria). A dynamic actin-rich extension of the surface of an animal cell used for locomotion or prehension of food. Respiratory activity of cell measured as an immune response; production of extra- and intracellular radicals No definition available. Amyloidosis is a progressive, incurable, metabolic disease characterized by abnormal deposits of protein in one or more organs or body systems. An abnormal expansion of cavities (ventricles) within the brain that is caused by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. A tumor that invades surrounding tissues, is usually capable of producing metastases, may recur after attempted removal, and is likely to cause death unless adequately treated. Any event that changes genetic structure; any alteration in the inherited nucleic acid sequence of the genotype of an organism Blood that is present in amounts too small to be seen and can be detected only by chemical analysis or microscopic examination. A usually nonmalignant growth of tissue protruding from the mucous lining of an organ such as the nose, bladder, or intestine, often causing obstruction. A condition in which an area of the retina (the tissue lining the inside of the back of the eye that transmits visual signals to the optic nerve and brain) has separated into two layers. Formation of a clot in the blood that either blocks, or partially blocks a blood vessel. The thrombus may lead to infarction, or death of tissue, due to a blocked blood supply. A local defect or excavation, of the surface of an organ or tissue, which is produced by the sloughing of inflammatory necrotic tissue. The time from the initial rapid deflection of the atrial wave to the initial rapid deflection of the His bundle (H) potential; it approximates the conduction time through the A-V node (normally 50-120 msec). Ammonia quotient is the ratio between ammonia excreted and oxygen consumed (mol/mol). Delays in conduction below the bifurcation of Bundle of His cause bundle branch or fascicular blocks, while atrioventricular conduction is maintained, unless all three fascicles are simultaneously affected. A measure of the load an object can bear if its ends are supported and a weight is attached to the middle, i. Yield strength is the amount of stress at which permanent deformation becomes measurable. Blood pressure is regulated by the homeostatic mechanisms of the body by the volume of the blood, the lumen of the arteries and arterioles, and the force of cardiac contraction. In the aorta and large arteries of a healthy young adult, blood pressure is approximately 120 mm Hg during systole and 70 mm Hg during diastole. The total quantity of blood in the body; the plasma volume added to the red cell volume. Ratio of Calcium retained (Utilized - Transferred to Egg) to Calcium utilized (ingest - excreted). Per cent of calcium transferred to the egg, Calcium in egg/Calcium utilized x 100. The heart output per unit of time over body surface, usually expressed in terms of liters per minute per square meter. Cell Migration Inhibition is cell-mediated immunity measurement of the in vitro inhibition of the migration or phagocytosis of antigen-stimulated leukocytes or macrophages. Specific cell migration assays have been developed to estimate levels of migration inhibitory factors, immune reactivity against tumor-associated antigens, and immunosuppressive effects of infectious microorganisms. Distinct from the nicotinic cholinergic receptor in having no intrinsic ion channel, the receptor is formed from one protein chain with 7 transmembrane regions. The time required for blood to coagulate; prolonged in haemophilia and in the presence of obstructive jaundice, some anemias and leukemias, and some of the infectious diseases. Any of several minute calcite plates that make up the external covering of certain haptophyte phytoplankton and in a fossilized state form chalk and limestone deposits Resistance to cold the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to reduce size. The rate at which a site contracts Copper excreted by organism No definition available. The calories needed above baseline metabolism to move a given distance, per unit body mass. The ratio of the useful energy delivered by a dynamic system to the energy supplied to it. Pertaining to electrophysiology, the electrical results produced through physiological agencies, or by change of action in a living organism the ratio of light peaks to dark troughs of the waves of the response of the test an in which an electrode is placed on the cornea of the eye to measure the electrical response of the rods and cones in the retina. Electroretinography measures the electrical responses of various cell types in the retina, including the photoreceptors (rods and cones), inner retinal cells (bipolar and amacrine cells), and the ganglion cells the wave amplitude response of the test an in which an electrode is placed on the cornea of the eye to measure the electrical response of the rods and cones in the retina. The wave implicit time response of the test an in which an electrode is placed on the cornea of the eye to measure the electrical response of the rods and cones in the retina. It is useful in the evaluation of hereditary and acquired disorders of the retina. A normal test will show the appropriate pattern responses during moments of increased light intensity. Abnormal results can indicate arteriosclerosis of the retina, retinal detachment, temporal arteritis (with eye involvement) or vitamin A deficiency. The energy cost of transport quantifies the energy efficiency transporting an animal from one place to another. Redness of the skin caused by dilatation and congestion of the capillaries, often a sign of inflammation or infection. The correlated phenomena of the endocrine and generative systems of a female mammal from the beginning of one period of estrus to the beginning of the next. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials can singly or in summation reach the trigger threshold for action potentials. The process, act or function of discharging or ejecting waste product of metabolism, especially from the system of an organism. The amount of space occupied by a threedimensional object as measured in cubic units. The rate of uptake of substances from food into microorganisms, tissues, and organs. A ratio expressing the weight of food required to produce a unit gain in the live weight of an animal or the measure of feed consumed per organism to the production of eggs. Excretion of glycolic acid, which often serves as a basic component of the extracellular compounds of microalgae and is also the main substrate of photorespiration. Displaying excessive physical activity sometimes associated with neurological or psychological causes Elevated pressure or tension of a body fluid, as of the intraocular or cerebrospinal fluids. The diminished ability of cells to respond to the action of insulin in transporting glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream into muscle and other tissues. An inflammatory reaction of a bodily part; the elicitation of a response to a stimulus in a plant or animal organ or tissue, especially in a nerve or muscle. Measured junctional resistance is isolated from ground potential by seals and peripheral membrane resistances. The absorption of luecine into an organism the directed movement of leucine, 2-amino-4methylpentanoic acid, into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. The building up of a chemical compound in the physiologic processes of a living organism, in this case lipids. The conversion of lipid, in the stomach and intestines, into soluble and diffusible products, capable of being absorbed by the blood. Metabolism of lipid or fat by an organism Refers to the oxidative degradation of lipids. It is the process in which free radicals "steal" electrons from the lipids in cell membranes, resulting in cell damage. A prolonged increase in synaptic responses that can be induced in certain neural pathways by a brief tetanic stimulation. For cellular membranes they are computed by subtracting the voltage measured outside the membrane from the voltage measured inside the membrane. The ratio of unbound metal to metal binding capacity of metallothionein within an organism. A group of organisms in a self-sufficient community naturally occupying a small area with a uniform environment throughout. A fluid secreted by the mammary glands of females for the nourishment of their young. Constriction of the pupil of the eye, resulting from a normal response to an increase in light or caused by certain drugs or pathological conditions. Of or relating to a movement of a plant that is in response to an external stimulus but is in a direction independent of the direction of the stimulus, as in the diurnal movement of leaves. The absolute refractory period is the interval during which a second action potential absolutely cannot be initiated, no matter how large a stimulus is applied. In neurons, it is caused by the inactivation of the Na+ channels that originally opened to depolarize the membrane. The period between the effective refractory period and the end of the refractory period; fibres then respond only to high intensity stimuli and the impulses conduct more slowly than normally. The ability of an organism to remove nitrate from a substrate and take nitrate into its body. The process of nutrient uptake by plants refers to the transfer of the nutrient ions across the soil root interfaces into the plant cell. A measure of the potential of water to move between regions of differing concentrations across a water-permeable membrane by using this formula: psi pi = - C R T, where psi pi is the osmotic potential, C is the concentration of solutes, R is the universal gas constant (i. The standard potential of an atom or ion that undergoes oxidation at the anode or reduction at the cathode in an electrochemical cell as compared to the potential of a standard hydrogen electrode when it is undergoing the same process. An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two species. An oxidationreduction reaction is any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion changes by gaining or losing an electron. Redox reactions are common and vital to some of the basic functions of life, including photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, and corrosion or rusting. The ability of a membrane or other material to permit a substance to pass through it. The ability of an organism to remove phosphate from a substrate and take phosphate into its body. Ratio of Phosphorus retained (Utilized Transferred to Egg) to Phosphorus utilized (ingested - excreted). Per cent of phosphorus transferred to the egg, Phosphorus in egg/Phosphorus utilized x 100. One of two reaction sequences of the light phase of photosynthesis in green plants which involves a pigment system excited by wavelengths shorter than 685 nanometers and which is directly involved in the splitting or photolysis of water. Also: non-cyclic photophosphorylation Change in the organic processes or functions of a plant or an organism. Examples of effects in this category include caloric content, cough frequency, granule or concretion formation, heartbeat, membrane permeability, metabolic stress, osmoregulation, urine frequency, ventilatory rate. A disturbance of the digestive system where the ejection of pigment plugs from the rectum occurs Quantitative (ie. Potassium excreted by organism Rate of movement of potassium ions across membranes. The act of pressing, or the condition of being pressed; compression; a squeezing; a crushing. Tensions arise as a result of transpiration and are caused by resistance of the tissues to water flow. Pressure potential gradients are responsible for the upward movement of water in the xylem. Excreation of an amine containing the amido group, or a derivative of ammonia in which only one atom of hydrogen has been replaced by a basic radical; - distinguished from secondary & tertiary amines. Any of a group of naturally occurring, chemically related fatty acids that stimulate contractility of the uterine and other smooth muscle and have the ability to lower blood pressure, regulate acid secretion of the stomach, regulate body temperature and platelet aggregation, and control inflammation and vascular permeability; they also affect the action of certain hormones. Nine primary types are labeled A through I, the degree of saturation of the side chain of each being designated by subscripts 1, 2, and 3. The conversion of protein, in the stomach and intestines, into soluble and diffusible products, capable of being absorbed by the blood. The ratio of the energy of a wave reflected from a surface to the energy possessed by the wave striking the surface. Resin is a hydrocarbon secretion of many plants, particularly coniferous trees, containing a complex mixture of different substances including organic acids, named the resin acids. Secretion is the discharge across the cell membrane, into the extracellular space or ducts, of endogenous substances resulting from the activity of intact cells of glands, tissues, or organs. A paroxysmal episode, caused by abnormal electrical conduction in the brain, resulting in the abrupt onset of transient neurologic symptoms such as involuntary muscle movements, sensory disturbances and altered consciousness. Production of natural iron binding compounds that chelate ferric ions (which form insoluble colloidal hydroxides at neutral pH and are then inaccessible) and are then taken up together with the metal ion. The ability of an organism to remove sodium from a substrate and take sodium into its body. Stomata are minute aperture structures on plants found typically on the outer leaf skin layer, also known as the epidermis. They consist of two specialized cells, called guard cells that surround a tiny pore called a stoma. A plant property related to the ease with which water vapor escapes from plant leaves through small pores in the leaves known as stomata. The opposition to transport of quantities such as water vapor and carbon dioxide to or from the stomata (pores) on the leaves of plants. The generation of any compound containing the highly reactive and extremely toxic oxygen radical O2-, a common intermediate in numerous biological oxidations.
The current recommendations for postmenopausal female hormone replacement are to administer therapy in the smallest beneficial doses for as briefly as possible medications list template buy cheap cytoxan 50 mg. Antiestrogen therapy with central or peripheral acting agents that are not pure receptor antagonists usually aims for complete suppression of E2 production harrison internal medicine purchase cytoxan 50mg overnight delivery, and in the case of aromatase inhibitors treatment of hemorrhoids discount 50 mg cytoxan overnight delivery, complete E1 and E2 suppression medications journal cheap 50mg cytoxan fast delivery. Gynecomastia or other signs of feminization in males may be due to an absolute or relative (in relation to androgens) surplus of estrogens medications 2 cheap 50 mg cytoxan. For adults with gynecomastia symptoms 3dpo cytoxan 50mg without prescription, the work-up should include testosterone and adrenal androgen measurements, in addition to E2 and E1 measurements. Causes for increased E1 or E2 levels include: -High androgen levels caused by tumors or androgen therapy (medical or sport performance enhancing), with secondary elevations in E1 and E2 due to aromatization -Obesity with increased tissue production of E1 -Decreased E1 and E2 clearance in liver disease -Estrogen producing tumors -Estrogen ingestion Normal male E1 and E2 levels also may be associated with feminization or gynecomastia if bioavailable testosterone levels are low due to primary/secondary testicular failure. This may occur, for example, when patients are receiving antiandrogen therapy or other drugs with antiandrogenic effects (eg, spironolactone, digitalis preparations). Elevation of E2 or E1 alone suggests pseudo precocious puberty, possibly due to a sex steroid-producing tumor. Persistently low estrogens and elevated gonadotrophins suggest primary ovarian failure, while low gonadotrophins suggest hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism. E2 and E1 levels are above the male reference range, usually within the female reference range, and testosterone levels are very high. Bidlingmaier F, Wagner-Barnack M, Butenandt O, Knorr D: Plasma estrogens in childhood and puberty under physiologic and pathologic conditions. As the level of alcohol increases, the degree of impairment becomes progressively increased. In most jurisdictions in the United States, the level of prima facie evidence of being under the influence of alcohol for purposes of driving a motor vehicle is 80 mg/dL. Useful For: Detection of ethanol (ethyl alcohol) in blood to document prior consumption or administration of ethanol Quantification of the concentration of ethanol in blood correlates directly with degree of intoxication Interpretation: the presence of ethanol in blood at concentrations >30 mg/dL (>0. These levels are frequently associated with loss of manual dexterity and with sedation. A patient who chronically consumes ethanol will develop a tolerance to the drug, and requires higher levels than described above to achieve various states of intoxication. In most jurisdictions in the United States, the level of prima facie evidence of being under the influence of alcohol for purposes of driving a motor vehicle is a blood ethanol concentration 80 mg/dL (0. Useful For: Detection of ethanol (ethyl alcohol) in serum to document prior consumption or administration of ethanol. Quantification of the concentration of ethanol in serum correlates with degree of intoxication. A patient who chronically consumes ethanol will develop a tolerance to the drug and requires higher levels than described above to achieve various states of intoxication. An individual who can function in a relatively normal manner with a blood ethanol level >150 mg/dL (>0. Ethanol acts on cerebral functions as a depressant similar to general anesthetics. Useful For: Detection and quantitation of prior consumption or administration of ethanol Interpretation: Individuals who chronically consume ethanol develop a tolerance to the drug, and require higher levels than described above to achieve various states of intoxication. Ethosuximide is completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, reaching a peak plasma concentration in 1 to 7 hours. Approximately 10% to 20% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine; the remainder is metabolized by hepatic microsomal enzymes. Ethosuximide produces a barbiturate-like toxicity, characterized by central nervous system and respiratory depression, nausea, and vomiting when the blood level is > or =101 mcg/mL. However, metabolism of ethylene glycol by alcohol dehydrogenase results in the formation of a number of acid metabolites, including oxalic acid and glycolic acid. These acid metabolites are responsible for much of the toxicity of ethylene glycol. After a delay of 4 to 12 hours, severe metabolic acidosis develops from accumulation of acid metabolites. Finally, delayed renal insufficiency follows deposition of oxalate in renal tubules. Useful For: Confirming and monitoring ethylene glycol toxicity Interpretation: Toxic concentrations are > or =20 mg/dL Reference Values: Toxic concentration: > or =20 mg/dL Clinical References: 1. Everolimus has a shorter half-life than sirolimus, which allows for more rapid achievement of steady-state pharmacokinetics. The most common adverse effects include hyperlipidemia, thrombocytopenia, and nephrotoxicity. Everolimus is useful as adjuvant therapy in renal cell carcinoma and other cancers. The utility of therapeutic drug monitoring has not been established for everolimus as an oncology chemotherapy; however, measuring blood drug concentrations is common practice for its use in transplant. Therapeutic targets vary depending on the transplant site and institution protocol. Guidelines for heart and kidney transplants suggest that trough (immediately prior to the next scheduled dose) blood concentrations between 3 to 8 ng/mL provide optimal outcomes. Useful For: Management of everolimus immunosuppression in solid organ transplant Interpretation: Therapeutic targets vary by transplant site and institution protocol. Heart and kidney transplant guidelines suggest a therapeutic range of 3 to 8 ng/mL. Measurement of drug concentrations in oncology chemotherapy is less common, thus no therapeutic range is established for this application. Rothenburger M, Zuckermann A, Bara C, et al: Recommendations for the use of everolimus (Certican) in heart transplantation: results from the second German-Austrian Certican Consensus Conference. The small, round cell group of tumors also includes rhabdomyosarcomas, desmoplastic small, round cell tumors, and poorly differentiated synovial sarcomas. Although immunohistochemical markers can be helpful in the correct diagnosis of these tumors, recent molecular studies have shown the specificity of molecular markers in differentiating specific subtypes of small, round blue-cell tumors. Accurate diagnosis of each tumor type is important for appropriate clinical management of patients. These tumors are usually bland and undifferentiated with relatively low mitotic indexes, which is misleading in light of the rapid growth commonly observed clinically. These translocations produce highly specific gene fusions that help define and characterize subtypes of sarcomas that are useful in the diagnosis of these lesions. Delattree O, Zucman J, Melot T, et al: the Ewing family of tumors - A subgroup of small-round-cell tumors defined by specific chimeric transcripts. Zucman J, Melot T, Desmaze C, et al: Combinatorial generation of variable fusion proteins in the Ewing family of tumours. Reduced alpha-Gal A activity results in accumulation of glycosphingolipids in the lysosomes of both peripheral and visceral tissues. By middle age, most patients develop renal insufficiency leading to end-stage renal disease, as well as cardiac and cerebrovascular disease. Individuals with the renal variant may or may not have other symptoms of classic Fabry disease. Individuals with the cardiac variant are often asymptomatic until they present with cardiac findings such as cardiomyopathy or mitral insufficiency later in life. Female carriers of Fabry disease can have clinical presentations ranging from asymptomatic to severely affected. Useful For: Confirmation of a diagnosis of classic or variant Fabry disease in affected males with reduced alpha-Gal A enzyme activity Carrier or diagnostic testing for asymptomatic or symptomatic females, respectively Interpretation: An interpretive report will be provided. Symptoms result from a deficiency of the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal A). Severity and onset of symptoms are dependent on the residual alpha-Gal A activity. Males with >1% alpha-Gal A activity may present with a variant form of Fabry disease. Female carriers of Fabry disease can have a clinical presentation ranging from asymptomatic to severely affected. Measurement of alpha-Gal A activity is not generally useful for identifying carriers of Fabry disease, as many of these individuals have normal levels of alpha-Gal A. See and Fabry Disease: Newborn Screen-Positive Follow-up algorithm and Fabry Disease Testing Algorithm in Special Instructions. See the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hypercoagulability States, Mayo Medical Laboratories Communique 2001 Nov;26(11) for more information regarding diagnostic strategy. Typically, there is a predominance of polyps on the left side of the colon, however other areas of the colon my also be affected. Useful For: Predictive testing for familial adenomatous polyposis when a mutation has been identified in an affected family member Interpretation: An interpretive report will be provided. Common constellations of colonic and extracolonic manifestations have resulted in the designation of 3 clinical variants: Gardner syndrome, Turcot syndrome, and hereditary desmoid disease. See Colorectal Adenomatous Polyposis Algorithm in Special Instructions for additional information. American Society of Clinical Oncology policy statement update: genetic testing for cancer susceptibility Clin Oncol. Useful For: Carrier screening for individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry Prenatal diagnosis for at-risk pregnancies Confirmation of a clinical diagnosis in individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry Interpretation: An interpretive report will be provided. A less frequently occurring mutation at that same codon, which results in a tryptophan substitution (R3500W), is more prevalent in individuals of Chinese and Malay descent, and has been identified in the Scottish population as well. The carrier rate in the Ashkenazi Jewish population is 1/89 and the detection rate for this mutation using this assay is >99%. Useful For: Carrier screening for individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry Prenatal diagnosis for at-risk pregnancies Confirmation of suspected clinical diagnosis of Fanconi anemia in individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry Interpretation: An interpretive report will be provided. Steatorrhea (increased fecal excretion of fat) may reflect a number of pancreatic or intestinal disorders, including chronic pancreatitis with or without stone obstruction, cystic fibrosis, neoplasia, Whipple disease, regional enteritis, tuberculous enteritis, gluten-induced enteropathy (celiac disease), Giardia-associated enteropathy, sprue, or the atrophy of malnutrition. Useful For: Diagnosing fat malabsorption due to pancreatic or intestinal disorders Monitoring effectiveness of enzyme supplementation in certain malabsorption disorders Interpretation: Excretion of >7 grams fat/24 hours, when on a diet of 100 to 150 g of fat, is suggestive of a malabsorption defect. Abnormal results from a random specimen should be confirmed by submission of a timed collection. Test values for timed fecal fat collections will be reported in terms of g/24 hours; the duration of the collection may be 24, 48, 72, or 96 hours. Test values for random fecal fat collections will be reported in terms of percent fat. Commonly used metabolite screens such as urine organic acids, plasma acylcarnitines, and fatty acids are influenced by dietary factors and the clinical status of the patient. This often leads to incomplete diagnostic information or even false-negative results. Enzyme assays are limited to 1 enzyme per assay, and molecular assays for common mutations are limited by the frequent occurrence of compound heterozygous patients with uncommon, private mutations that must be distinguished from unaffected carriers. Furthermore, neither specific enzyme assays nor molecular genetic testing is available for each of the known defects. Interpretation: Abnormal results will include a description of the abnormal profile, in comparison to normal and abnormal co-run controls. In addition, the concentration of those acylcarnitine species that abnormally accumulated in the cell medium are provided and compared to the continuously updated reference range based on analysis of normal controls. Deficient enzymes at any step in this pathway prevent the production of energy during periods of physiologic stress such as fasting or intercurrent illness and can frequently result in life-threatening episodes of metabolic decompensation. Quantitative determination of C8 to C18 fatty acids is an important element of the work-up and differential diagnosis of candidate patients. Fatty acid profiling can detect quantitatively modest, but nevertheless significant, abnormalities even when patients are asymptomatic and under dietary treatment. Fatty Acid Deficiency/Excess: Fats are important sources of energy for tissues and for the function and integrity of cellular membranes. Deficiencies are commonly caused by inadequate dietary intake of lipids due to an unbalanced diet or long-term parenteral nutrition or by intestinal malabsorption. Biochemical abnormalities may be detected before the onset of recognizable clinical manifestations. Excess dietary fatty acids have also been linked to the onset of cardiovascular disease. Elevated levels of linoleic acid can contribute to overproduction of the proinflammatory 2-series local hormones. Peroxisomal Disorders: Peroxisomes are organelles present in all human cells except mature erythrocytes. Peroxisomal disorders consist of 2 major groups, disorders of peroxisomal biogenesis (eg, Zellweger syndrome), in which the organelle is not formed, and defects of single peroxisomal enzymes. Fatty acid oxidation disorders are recognized on the basis of disease-specific patterns that are correlated to the results of other investigations in plasma (carnitine, acylcarnitines) and urine (organic acids, acylglycines). Increased concentrations of serum phytanic acid (along with normal pristanic acid concentrations) are seen in the Refsum disease (phytanase deficiency). Deficiencies are commonly caused by inadequate dietary intake of lipids due to an unbalanced diet or long-term parenteral nutrition, or by intestinal malabsorption, which is common in conditions such as cystic fibrosis and irritable bowel syndrome. Deficiencies can also be caused by an impairment of biomolecular transformations among fatty acids, such as linoleic acid to arachidonic acid. Linoleic and linolenic acids cannot be made by the body and are essential components of the diet (ie, essential fatty acids). It can also be detected by increases in the ratio triene/tetraene ratio (Holman index): (eicosatrienoic [mead] acid [C20:3w9]/arachidonic acid [C20:4w6]). The dietary contents of saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated fatty acids influence the concentration of cholesterol in low-density and high-density lipoproteins, and consequently the development of atherosclerosis. Regular consumption of, or supplementation with, polyunsaturated fatty acids may have a beneficial effects on long-term cardiovascular prognosis due to their anti-inflammatory and possibly antiarrhythmic effects.
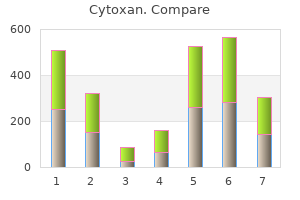
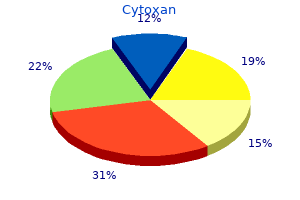
Cheap cytoxan 50mg without prescription. Useless I.D. - "Dissolve" 2/7/11.
The number of cases failing to fit this picture led to a reconsideration of the pathophysiology medicine over the counter buy cytoxan 50mg on line, which suggests that the syndrome can occur with simple exposure to small amounts of amniotic fluid fungal nail treatment generic cytoxan 50 mg free shipping. Pathophysiologic studies sug- - Chapter K 15 Chapter K gest that left heart failure and pulmonary vasospasm are prime etiologic factors in cardiovascular collapse medicine in balance buy cytoxan 50mg on-line, but that the underlying mechanism may be an anaphylactic-like event with an associated 41 percent incidence of atopy or allergy medicine 4h2 pill discount cytoxan 50mg overnight delivery. Two large bore intravenous catheters should be placed and aggressive fluid replacement using crystalloid solution begun medicine while breastfeeding order cytoxan 50mg without a prescription. Blood should be drawn for complete hemogram symptoms just before giving birth cytoxan 50mg with mastercard, coagulation panel, and chemistry panel, including electrolytes and renal function. Urinary output should be monitored via indwelling Foley catheter, and a portable chest x-ray and 12-lead electrocardiogram should be obtained. Hemodynamic monitoring will probably be required, using an arterial access line and possibly a Swan-Ganz catheter. Coagulation factors should be assessed every two hours and blood component therapy initiated as needed with packed red cells, platelets (if the platelet count is less than 50,000/mcL), fresh frozen plasma, or cryoprecipitate. Given the possible anaphylactoid nature of the condition, epinephrine is theoretically useful. Positive end expiratory pressure is usually required to prevent alveolar collapse and to recruit atelectatic alveoli. Fluids, dopamine and furosemide should be administered based on hemodynamic parameters. The syndrome begins with respiratory distress (tachypnea and dyspnea) accompanied by restlessness, cyanosis, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. In many cases, these events progress quickly so that only the most rudimentary diagnostic studies and resuscitative efforts can be made. If time permits, helpful laboratory values include blood gases and coagulation factors. The differential diagnosis includes other catastrophic causes of cardiopulmonary compromise, such as massive pulmonary embolism, bilateral pneumothorax, myocardial infarction, or gastric fluid aspiration. Summary the rate of cardiac arrest in pregnancy appears to have increased and is now estimated to occur in one in 20,000 pregnancies. An aggressive medical approach seems justified and certainly can do no harm for the patients who survive the initial catastrophic event. Emergency hysterotomy within four minutes of maternal cardiac arrest improves maternal and neonatal outcomes. Part 12: cardiac arrest in special situations: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Department of Health, Welsh Office, Scottish Office Department of Health, Department of Health and Social Services, Northern Ireland. Report on confidential enquiries into maternal deaths in the United Kingdom 20002002. The Eighth Report of the Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths in the United Kingdom. Advanced Cardiac Life Support for Experienced Providers: Manual and Resource Text, Chapter 18: Cardiac Arrest Associated with Pregnancy. Part 8: Advanced life support: 2010 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations. Trauma during pregnancy: an analysis of maternal and fetal outcomes in a large population. Blunt abdominal trauma: are there any predictive factors for abruptio placentae or maternal-fetal distress? Fetal outcome in motor-vehicle crashes: effects of crash characteristics and maternal restraint. American Academy of Pediatrics and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Screening for intimate partner violence and abuse of elderly and vulnerable adults: U. Screening for Intimate Partner Violence and Abuse of Elderly and Vulnerable Adults: Recommendation Statement Am Fam Physician. Perimortem cesarean delivery 30 minutes after a laboring patient jumped from a fourth-floor window: baby survives and is normal at age 4 years. Maternal cardiac arrest and perimortem caesarean delivery: evidence or expert-based? Labor room setting compared with the operating room for simulated perimortem cesarean delivery: a randomized controlled trial. The Injury Severity Score: a method for describing patients with multiple injuries and evaluating emergency care. Uterine Displacement Supine with Uterine Displacement · Ensures chest compressions are directed toward spine · Chest compression force is 80% stronger when performed supine (compared to chest compressions performed in the left lateral tilt position) · Manual displacement of the uterus increases cardiac output by 25% Chest compressions Manual two handed 2 Maternal Complications after Resuscitation · Susceptible to rib fractures · More susceptible to other iatrogenic injuries Liver laceration Pneumothorax Trauma in Pregnancy · Complicates 1 in 12 pregnancies · Leading nonobstetric cause of death in pregnant women · 9 out of 10 traumatic injuries during pregnancy are minor · However, 60% to 70% of fetal losses result from minor injuries · In patients with preeclampsia and thrombocytopenia Watch for internal bleeding Hematomas of the liver Trauma in Pregnancy Cause Motor vehicle accidents Falls Assaults Gunshot wounds Suicide Burns Others Intimate partner violence Homicide Poisonings Frequency 48% 25% 17% 4% 3. Summary · Physiologic changes in pregnancy can have an impact on both trauma and cardiac arrest · Basic Life Support, Advanced Cardiac Life Support and Trauma care should be appropriately modified in the pregnant patient · Perimortem cesarean delivery should be considered after four minutes in the pregnant patient without a pulse and non responsive to resuscitation · Amniotic fluid embolism is a rare but important obstetrical cause of cardiovascular collapse 6 Chapter L Safety in Maternity Care Lee T. Discuss risk management issues in obstetrics and possible solutions (the Five Cs). The plane landed on the Hudson River near New York City, and all 155 individuals aboard survived. Preflight training and simulations prepared airline personnel for their roles when the accident occurred. Communication was effective between pilots, crew members, passengers, ground control, and rescuers. The courses ideally include participants from different disciplines and different settings. Courses have been taken by many attending physicians (family medicine, obstetrics/gynecology and emergency medicine), midwives, nurses, residents, students and others. Standardization is a key patient-safety element that can reduce variation in practice, alleviate duplication of time and resources, and provide reliability of patient care procedures. Knowledge of the content plus practice of manual skills and the use of mnemonics can reduce the propensity for error and reduce maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Importance of Safety in Maternity Care Approximately 289,000 women died from childbirth related causes worldwide in 2013. With greater than four million births occurring in the United States annually,2 this equates to more than 80,000 adverse obstetrical events. According to the Joint Commission (an organization that accredits health care organizations in the United States), between 2004 and 2014, communication was the root cause in 48% of maternal and 70% of perinatal sentinel events. Fortunately, most errors do not result in harm, and fatal errors are relatively rare. One study found that 87% of adverse events and potential adverse events were preventable, and that poor teamwork, protocol violation, and staff unavailability were the most common problems. For example, a maternity care unit with 81 obstetricians, 50 registered nurses, 16 anesthesiologists, 12 neonatal nurse practitioners, 14 surgical technologists, and 35 nurse anesthetists could results in 381 million different teams. Even the most knowledge and skilled specialist cannot function to the best of his or her ability without support from a wide array of colleagues. The next frontier lies in making effective teamwork, as seen in high-performance teams, an essential element in high-reliability organizations. The health care team includes the birth attendant, nurses, support personnel (eg, nursing assistants), and consultants. The presence of a doula or professional support person can increase the probability of spontaneous vaginal delivery and reduce the need for pain drugs and instrumental delivery. Patient-centered interviewing, caring communication skills, and shared decision making will promote effective patient-provider communi- Evidence for Teamwork Improving Outcomes A growing body of evidence shows that improving teamwork improves outcomes. The University of Minnesota and the Fairview Health System in Minneapolis have provided an evidence-based framework for the dissemination of in situ simulation to enhance interdisciplinary communication 2 Chapter L - Safety in Maternity Care cation. The health care team can improve patient safety and satisfaction through good communication, a readily available birth attendant, and consultants who are willing to assist in a timely manner. Characteristics of effective teams include having shared mental models, having clear roles and responsibilities, having a clear, valued, and shared vision, optimizing resources, giving and receiving assistance, managing and optimizing performance outcomes, having strong team leadership, engaging in a regular discipline of feedback, developing a strong sense of collective trust and confidence, and creating mechanisms for cooperation and coordination. Impediments to team function include personality conflicts, competitive pressures, fixed beliefs about abilities or roles, biases regarding management, and inadequate resources. First, separate the people from the problem: be hard on the problem, soft on the people. Focus on what is right for the patient, not who is right; this includes focusing on interests, not positions, and focusing on concerns and desired outcomes. Insisting on the use of objective criteria provides the basis for further improvement. An important part of developing an effective response team involves identifying appropriate triggers for activating the team. Team function can be optimized through simulations, feedback, and quality review when activation occurs. Important concepts and tools that can improve teamwork and patient safety include situational awareness, standardized language, closed-loop communication, and a shared mental model. Situational Awareness In an emergency, it is easy to become fixated on a particular task and lose sight of the complete situation. For example, a provider may fixate on decelerations on the electronic fetal monitor and overlook elevated blood pressure levels, headache, and hyper-reflexia prior to an eclamptic seizure. Another provider may focus on preterm contractions and miss an abruption that worsens dangerously with administration of a tocolytic. A provider may focus on difficult family dynamics and fail to prepare the team to deal with shoulder dystocia despite a large estimated fetal weight and prolonged second stage of labor. Team members can help each other remain aware of active issues and potential complications by cross monitoring. Early briefings followed by huddles when new issues arise can ensure that all team members have the same understanding of the situation. Situational monitoring is an important patient safety tool that facilitates situational awareness. Standardized Language Inadequate communication at shift change can compromise patient safety. For example, failing to mention the presence of meconium at a signout that occurs just prior to delivery may result in inadequate newborn resuscitation preparation. Call-outs are used to quickly inform all team members simultaneously when new critical events - Chapter L 3 Chapter L arise, particularly during an emergency when several caregivers are at the bedside. When dealing with a postpartum hemorrhage, a call-out of high blood pressure can alert the managing provider that methylergonovine is contraindicated. Miscommunications in the transfer of care from one provider or care team to another can result in life-threatening errors. Effective patient handoffs should include interactive communications, limited interactions, a process for verification, and an opportunity to review relevant historical data. One of the significant difficulties in many countries is having an organized and respectful process for handing off a patient from her community care provider to prehospital transport, and timely referral and transport to the appropriate level of hospital care. For example, a physician may request 10 units of oxytocin intramuscularly after delivery of the anterior shoulder, and a nurse may repeat back that the physician requested 10 units of oxytocin intramuscularly after delivery of the anterior shoulder as confirmation that the message was understood. In this example, the oxytocin may not have been given or a wrong dose may have been given. Shared Mental Model Situational awareness, standardized language, and closed-loop communication can allow a team to have a shared mental model. Briefings, Huddles, and Debriefings Before any patient care episode, a briefing session allows team members to review risk factors, designate roles, and ensure that everyone has a shared mental model regarding how to proceed. Huddles are brief gatherings of team players to discuss patient status and the management plan when issues arise in the course of patient care. Examples of events that should precipitate a huddle are development of high blood pressure levels, fever, and concerning fetal heart tracings during labor. A huddle may take place in person or via teleconference if a key team member is not physically present when the huddle is needed. Debriefing allows team members to learn from patient care episodes regardless of the outcome. Closed-Loop Communication Closed-loop communication means that the individual receiving a message confirms, or repeats back, what they have heard from the individual sending the message so that he/she can affirm that the message is correct or offer a correction. Closed-loop communication allows for a clear, shared mental model of the care plan 4 Chapter L - Safety in Maternity Care During debriefings it can be helpful to discuss three levels of emergency care management: 1. Debriefings can also be useful for reinforcing positive practices after deliveries in which everything went well. This happened in 2006 when a healthy 16-year-old woman who was in active labor was admitted to a hospital in Madison, Wisconsin. The anesthesiologist left the epidural infusion bag on the counter and left the room. A nurse entered the room and hung the epidural bag, thinking it contained penicillin. Prescribing errors can be reduced by avoiding nonstandard abbreviations and using the always lead, never follow rule of placing a zero before numbers less than one and not placing a zero after a decimal point. However, too many alerts may lead to desensitization: 49% to 96% of alerts are overridden. These errors can be reduced through systematic, careful medication reconciliation on admission, transfer, and discharge. Areas for dispensing medications can be established as noise-free, distraction-free zones. As with other aspects of patient safety, communication problems are often at the root of errors. Fatigue Fatigue can affect patient safety factors including memory, speed, and mood. Work-hour limits such as those introduced for medical residents may prevent the fatigue often involved with medical errors.
Any disappearance of a child constitutes a family crisis with both victims and families at high risk for developing physical and emotional problems medications xanax order cytoxan 50 mg free shipping. Any child who is the object of a custody dispute is vulnerable to parental snatching symptoms 6 months pregnant generic 50mg cytoxan, running away and/or being abused medications similar to abilify order cytoxan 50 mg amex. Comprehensive standards of health care should be developed for the national network of runaway centers medicine just for cough generic cytoxan 50mg otc. Physicians should be consultants to and work with governing boards of these agencies treatment bipolar disorder purchase cytoxan 50 mg otc. Educational programs should address the reactions of physicians to these complex and frustrating social problems symptoms 3 weeks pregnant generic 50 mg cytoxan fast delivery. Physicians must play an active role in advocating increased services for victims and abusers. Protective services for abused children and elders need to be better funded and staffed, and follow-up services should be expanded. Shelters and safe homes for battered women and their children must be expanded and better funded. Mechanisms to coordinate the range of services, such as legal aid, employment services, welfare assistance, day care, and counseling, should be established in every community. Mandatory arrest of abusers and greater enforcement of protection orders are important law enforcement reforms that should be expanded to more communities. There should be more research into the effectiveness of rehabilitation and prevention programs for abusers. For minors who are not deemed mature enough to give informed consent, consent for emergency interventions need not be obtained from their parents. Physicians can obtain authorization for further interventions from a court order or a court-appointed guardian. The safety of the child or elderly person must be ensured prior to disclosing the diagnosis when the parents or caretakers are potentially responsible for the abuse. For competent adult victims physicians must not disclose an abuse diagnosis to caregivers, spouses, or any other third party without the consent of the patient. Where possible, physicians should refer the patient to social support groups that can help them cope with changing societal mores. HealthGrades legal disclaimer "HealthGrades obtains its information from sources it believes to be reliable. However, because of the possibility of human and mechanical error as well as other factors, HealthGrades makes no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy or Appx198 Case: 17-1460 Document: 126 Page: 202 Filed: 01/03/2018 Resolution: 612 (A-08) Page 2 timeliness of its information, and cannot be responsible or liable for any errors or omissions in its information or the results obtained from the use of such information. Kaiser Family Foundation Online Health Information Poised to Become Important Resource For Seniors, But Not There Yet (January 12, 2005). Online users can access innumerable informational or interactive online sites, many of which are maintained by physicians or rely on their services. Physician involvement should be guided by the following considerations: (1) Physicians responsible for the health-related content of an online site should ensure that the information is accurate, timely, reliable, and scientifically sound, and includes appropriate scientific references. General standards include truthfulness, protection of privacy, principles of informed consent, and disclosures such as limitations inherent in the technology. This can be achieved through safeguards for disclosure and honesty in funding and advertising. It also requires that physicians not place commercial interests ahead of patient health; therefore, physicians must not use health-related online sites to promote unnecessary services, refer patients to entities in which they have ownership interests, or sell products outside of established ethical guidelines. Recognizes that appropriately evaluated transgender and gender variant individuals can benefit greatly from medical and surgical gender transition treatments. Advocates for removal of barriers to care and supports both public and private health insurance coverage for gender transition treatment. Opposes categorical exclusions of coverage for such medically necessary treatment when prescribed by a physician. Issue: Significant and long-standing medical and psychiatric literature exists that demonstrates clear benefits of medical and surgical interventions to assist gender variant individuals seeking transition. However, private and public insurers often do not offer, or may specifically exclude, coverage for medically necessary treatments for gender transition. Access to medical care (both medical and surgical) positively impacts the mental health of transgender and gender variant individuals. Rosenblum, Darren, "Trapped" in Sing Sing: Transgendered Prisoners Caught in the Gender Binarism" (2000). Smith Yolanda L S; Van Goozen Stephanie H M; Kuiper Abraham J; Cohen-Kettenis Peggy T. The lack of consistency in how a transgender condition is defined by some institutions further marginalizes these individuals based on their subjective, surgical and hormonal status (2). In addition, treatment is not always accessible to wards of governmental agencies, such as transgender and gender variant individuals in foster care and prison systems. Lack of access to care adversely impacts the mental health of transgender and gender variant people, and both hormonal and surgical treatment have been shown to be efficacious in these individuals (3-7). Practice guidelines have been developed based on peer-reviewed scientific studies and are published and available for clinicians to access (3, 8, 9). The American Medical Association and the American Psychological Association both have position statements stating the critical importance of access to care for transgender and gender variant individuals (10, 11). This assistance may include primary care, gynecologic and urologic care, reproductive options, voice and communication therapy, mental health services. Some individuals who present for care will have made significant self-directed progress towards gender role changes or other resolutions regarding their gender identity or gender dysphoria. Transexual, transgender, gender dysphoria, Standards of Care this is the seventh version of the Standards of Care. Health is promoted through public policies and legal reforms that promote tolerance and equity for gender and sexual diversity and that eliminate prejudice, discrimination, and stigma. These departures should be recognized as such, explained to the patient, and documented through informed consent for quality patient care and legal protection. This documentation is also 1 Formerly the Harry Benjamin International Gender Dysphoria Association. Changes in this version are based upon significant cultural shifts, advances in clinical knowledge, and appreciation of the many health care issues that can arise for transsexual, transgender, and gendernonconforming people beyond hormone therapy and surgery (Coleman, 2009a, 2009b, 2009c, 2009d). Some patients who present for care will have made significant self-directed progress towards gender role changes, transition, or other resolutions regarding their gender identity or gender dysphoria. From place to place, both across and within nations, there are differences in all of the following: social attitudes towards transsexual, transgender, and gender-nonconforming people; constructions of gender roles and identities; language used to describe different gender identities; epidemiology of gender dysphoria; access to and cost of treatment; therapies offered; number and type of professionals who provide care; and legal and policy issues related to this area of health care (Winter, 2009). For example, in a number of cultures, gendernonconforming people are found in such numbers and living in such ways as to make them highly socially visible (Peletz, 2006). Many grow up and live in a social, cultural, and even linguistic context quite unlike that of Western cultures. Gender-nonconforming people in these settings are forced to be hidden and, therefore, may lack opportunities for adequate health care (Winter, 2009). Terminology in English may not be easily translated into other languages, and vice versa. Such stigma can lead to prejudice and discrimination, resulting in "minority stress" (I. Minority stress is unique (additive to general stressors experienced by all people), socially based, and chronic, and may make transsexual, transgender, and gendernonconforming individuals more vulnerable to developing mental health problems such as anxiety and depression (Institute of Medicine, 2011). However, these symptoms are socially induced and are not inherent to being transsexual, transgender, or gender-nonconforming. Treatment is available to assist people with such distress to explore their gender identity and find a gender role that is comfortable for them (Bockting & Goldberg, 2006). This process may or may not involve a change in gender expression or body modifications. Diagnoses Related to Gender Dysphoria Some people experience gender dysphoria at such a level that the distress meets criteria for a formal diagnosis that might be classified as a mental disorder. All of these systems attempt to classify clusters of symptoms and conditions, not the individuals themselves. Thus, transsexual, transgender, and gendernonconforming individuals are not inherently disordered. Rather, the distress of gender dysphoria, when present, is the concern that might be diagnosable and for which various treatment options are available. The existence of a diagnosis for such dysphoria often facilitates access to health care and can guide further research into effective treatments. Health professionals should refer to the most current diagnostic criteria and appropriate codes to apply in their practice areas. Even if epidemiologic studies established that a similar proportion of transsexual, transgender, or gender-nonconforming people existed all over the world, it is likely 3 Incidence-the number of new cases arising in a given period. While in most countries, crossing normative gender boundaries generates moral censure rather than compassion, there are examples in certain cultures of gender-nonconforming behaviors. For various reasons, researchers who have studied incidence and prevalence have tended to focus on the most easily counted subgroup of gender-nonconforming individuals: transsexual individuals who experience gender dysphoria and who present for gender-transition-related care at specialist gender clinics (Zucker & Lawrence, 2009). Most studies have been conducted in European countries such as Sweden (W° linder, 1968, 1971), the United Kingdom a (Hoenig & Kenna, 1974), the Netherlands (Bakker, Van Kesteren, Gooren, & Bezemer, 1993; Eklund, Gooren, & Bezemer, 1988; van Kesteren, Gooren, & Megens, 1996), Germany (Weitze & Osburg, 1996), and Belgium (De Cuypere et al. De Cuypere and colleagues (2007) reviewed such studies, as well as conducted their own. Leaving aside two outlier findings from Pauly in 1965 and Tsoi in 1988, ten studies involving eight countries remain. The prevalence figures reported in these ten studies range from 1:11,900 to 1:45,000 for male-to-female individuals (MtF) and 1:30,400 to 1:200,000 for female-to-male (FtM) individuals. The trend appears to be towards higher prevalence rates in the more recent studies, possibly indicating increasing numbers of people seeking clinical care. Support for this interpretation comes from research by Reed and colleagues (2009), who reported a doubling of the numbers of people accessing care at gender clinics in the United Kingdom every five or six years. Similarly, Zucker and colleagues (2008) reported a four- to five-fold increase in child and adolescent referrals to their Toronto, Canada, clinic over a 30-year period. The numbers yielded by studies such as these can be considered minimum estimates at best. The published figures are mostly derived from clinics where patients met criteria for severe gender dysphoria and had access to health care at those clinics. By counting only those people who present at clinics for a specific type of treatment, an unspecified number of gender dysphoric individuals are overlooked. Overall, the existing data should be considered a starting point, and health care would benefit from more rigorous epidemiologic study in different locations worldwide. Although Harry Benjamin already acknowledged a spectrum of gender nonconformity (Benjamin, 1966), the initial clinical approach largely focused on identifying who was an appropriate candidate for sex reassignment to facilitate a physical change from male to female or female to male as completely as possible. Satisfaction rates across studies ranged from 87% of MtF patients to 97% of FtM patients (Green & Fleming, 1990), and regrets were extremely rare (1%1. Indeed, hormone therapy and a surgery have been found to be medically necessary to alleviate gender dysphoria in many people (American Medical Association, 2008; Anton, 2009; World Professional Association for Transgender Health, 2008). As the field matured, health professionals recognized that while many individuals need both hormone therapy and surgery to alleviate their gender dysphoria, others need only one of these treatment options and some need neither (Bockting & Goldberg, 2006; Bockting, 2008; Lev, 2004). Often with the help of psychotherapy, some individuals integrate their transor cross-gender feelings into the gender role they were assigned at birth and do not feel the need to feminize or masculinize their body. Page: 240 Filed: 01/03/2018 171 others, changes in gender role and expression are sufficient to alleviate gender dysphoria. Some patients may need hormones, a possible change in gender role, but not surgery; others may need a change in gender role along with surgery but not hormones. Some individuals describe themselves not as gendernonconforming but as unambiguously crosssexed (i. Other individuals affirm their unique gender identity and no longer consider themselves to be either male or female (Bornstein, 1994; Kimberly, 1997; Stone, 1991; Warren, 1993). Instead, they may describe their gender identity in specific terms such as transgender, bigender, or genderqueer, affirming their unique experiences that may transcend a male/female binary understanding of gender (Bockting, 2008; Ekins & King, 2006; Nestle, Wilchins, & Howell, 2002). For example, some youth identifying as genderqueer have always experienced their gender identity and role as such (genderqueer). Greater public visibility and awareness of gender diversity (Feinberg, 1996) have further expanded options for people with gender dysphoria to actualize an identity and find a gender role and expression that are comfortable for them. Options for Psychological and Medical Treatment of Gender Dysphoria For individuals seeking care for gender dysphoria, a variety of therapeutic options can be considered. In children and adolescents, a rapid and dramatic developmental process (physical, psychological, and sexual) is involved and there is greater fluidity and variability in outcomes, particularly in prepubertal children. Boys in these studies were more likely to identify as gay in adulthood than as transgender (Green, 1987; Money & Russo, 1979; Zucker & Bradley, 1995; Zuger, 5 Gender-nonconforming behaviors in children may continue into adulthood, but such behaviors are not necessarily indicative of gender dysphoria and a need for treatment. Newer studies, also including girls, showed a 12%27% persistence rate of gender dysphoria into adulthood (Drummond, Bradley, Peterson-Badali, & Zucker, 2008; Wallien & Cohen-Kettenis, 2008). In contrast, the persistence of gender dysphoria into adulthood appears to be much higher for adolescents. However, in a follow-up study of 70 adolescents who were diagnosed with gender dysphoria and given puberty-suppressing hormones, all continued with actual sex reassignment, beginning with feminizing/masculinizing hormone therapy (de Vries, Steensma, Doreleijers, & CohenKettenis, 2010). Another difference between gender dysphoric children and adolescents is in the sex ratios for each age group. In clinically referred, gender dysphoric children under age 12, the male/female ratio ranges from 6:1 to 3:1 (Zucker, 2004). In clinically referred, gender dysphoric adolescents older than age 12, the male/female ratio is close to 1:1 (Cohen-Kettenis & PfЁ fflin, a 2003). Additional research is needed to refine estimates of its prevalence and persistence in different populations worldwide. Phenomenology in Children Children as young as age two may show features that could indicate gender dysphoria.
References