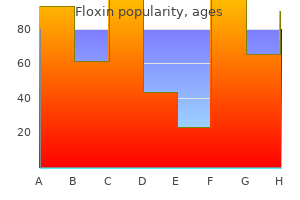



|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD
Conversely bundespolizei virus cheap floxin 400 mg with amex, the fact that autism meets the diagnostic criteria for mercury poisoning are antibiotics for uti expensive cheap floxin 200mg with mastercard, yet has never been described as a mercury-induced disease antibiotics given for uti buy 200mg floxin fast delivery, requires that the disorder must arise from a mode of mercury administration which has not been studied before virus 51 floxin 400 mg low cost. This would rule out other known sources of Hg like fish consumption or occupational mercury hazards, as these have been well characterized. It is possible that another underinvestigated mercury route, such as maternal Hg exposures (e. Historical Precedent Exists There is a precedent for large scale, undetected mercury poisoning of infants and toddlers in the syndrome that came to be known as acrodynia or pink disease. Reports abound of children too miserable to acknowledge their mothers, such as the child who kept repeating, "I am so sad. Most physicians who speculated on the causes of pink disease believed in either the infective or the nutritional theory. It was a tradition to advise student doctors to treat cases of difficult teething with the mercury powders that were eventually to be revealed as the cause of the disease. The ill-effects of mercury on the mouth had been known at least since the time of Paraclesus, but it was not until 1922 that the pediatrician, John Zahorsky, commented on the similarity between pink disease and mercury poisoning. He dismissed rather than pursued his new idea of possible mercury poisoning and suggested a theory that was more in tune with current fashion. Most doctors, even those skilled in the use of calomel, associated mercury poisoning with adults (syphilis, industrial poisoning, hatters shakes) rather than with infants. He and his assistant found large amounts of mercury in the urine of a child with pink disease. They did not publish their findings until 1948, but it is noteworthy that the news seems not to have spread through the small and tightly knit pediatric world, where everyone knew everyone else. It was probably because the idea was unfashionable and contrary to the conventional wisdom. The theory that mercury poisoning caused pink disease was gradually accepted, but against resistance, particularly by older men and those in powerful positions. Mercury was withdrawn from most teething powders after 1954, initially through voluntary action by the manufacturers because of adverse publicity and probably in the hope of avoiding statutory prohibition. Later in the decade the theory was widely accepted and soon pink disease was no longer part of the usual pediatric out-patient clinic. The effects on humans of mercury-containing medicinals and home remedies used to be studied quite regularly by medical researchers (Warkany and Hubbard, 1953); but since, aside from vaccinal thimerosal, such products have declined dramatically in number since the 1950s and 1960s, most mercury researchers today focus on biochemical studies or environmental sources like fish and coal plants. Likewise, it is not surprising that neither mercury experts nor autism professionals have ever investigated autism as a possible disease of mercury exposure. Since its discovery by Kanner, autism has been characterized in almost exclusively psychological terms. The descriptions have been such that the symptoms would be essentially unrecognizable as manifestations of poisoning to any mercury expert not looking closely. A perfect example is Kanner himself, who recorded feeding problems and vomiting in infants and concluded: "Our patients, anxious to keep the outside world away, indicated this by the refusal of food. In 1987, Robert Sternberg would propose a "unified theoretical perspective on autism" by defining the disorder in terms of a "triarchic theory of intelligence," and in the same publication Lorna Wing and Anthony Attwood would write: "Sometimes young autistic children will stand in a dejected posture, with tears streaming down their faces, as if they suddenly felt their helplessness in the face of a world they cannot understand. Thus biomedical research in autism existed, but it was mostly relegated to the margins as psychology held center stage, and the symptomatic characteristics of autism continued to be presented in accord with psychological biases. Congressional mandate led to the public quantification of the cumulative amount of mercury in vaccines, raising interest in understanding its effects. With parents already suspecting a vaccine-autism link, the environment was right for investigations focused on the link between vaccinal mercury and autism. Such research might focus on the following areas, with others undoubtedly still to be identified: (a) Chelation methods which will work across all body tissues and especially the brain. Other promising but less studied chelators like alpha lipoic acid can cross the bbb (Fuchs et al, 1997) and should be studied in autism. The work of Hu and colleagues suggests that Hg can cause an immune reaction in any individual, but some are protected by a counteractive immunosuppressive response, and Warkany and Hubbard have pointed out that individuals who are Hg-sensitive can later become "immune". It may be possible to engineer these responses in autistic individuals through careful research. Except for trace amounts, vaccines without thimerosal are currently available for all routinely recommended immunizations for children under 6 years (Institute for Vaccine Safety, 1999). Thus, any issues being raised here are related to how vaccine programs are run, not with vaccines themselves. As Altman and Bland have aptly demonstrated (1995), "absence of evidence is not evidence of absence. Current practice is to track adverse reactions only if they occur within one month of the vaccination. The experience with mercury clearly shows that an adverse event may not manifest for months if not years. Studies on adverse reactions must involve long term tracking of patients; they should investigate the impact of multiple injections as well as compare reactions to vaccines with and without various additives; and sample sizes need to be large enough to include especially sensitive groups. Dev Brain Res, 1984; 12: 1-11 Sakamoto E, Urata H, Ono B, `Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains sensitive to inorganic mercury. Sam Royal Free and University College Medical School University College London London Я 2004 A. First published 2004 Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Hibbert, Allison. Ltd Commissioning Editor: Vicki Noyes Editorial Assistant: Nicola Ulyatt Production Editor: Lorna Hind Production Controller: Kate Charman For further information on Blackwell Publishing, visit our website. Furthermore, the publisher ensures that the text paper and cover board used have met acceptable environmental accreditation standards. We would especially like to thank Dr Raven for his encouragement, guidance and expertise. Foreword It has been a great privilege to be involved in the production of this innovative undergraduate textbook in psychiatry. When one of the students attached to my clinical firm first suggested the concept of a series of specialist textbooks written by students, for students, my reaction was a mixture of curiosity and scepticism. Together with Amir Sam, the authors of this book are among the very best students of psychiatry I have ever had the pleasure to teach. In the process of editing this book, I have learned a huge amount about teaching psychiatry, especially about the way that psychiatry as a subject is perceived by students. It pays particular attention to explaining those topics which students find especially difficult, without losing the emphasis on those conditions which clinicians consider to be important. During the production of this book, I have seen the transformation of these authors from students to doctors. Needless to say, they used the drafts of this book to revise psychiatry for their final exams, and they all passed with flying colours! I hope that you will learn as much from reading this book as we all did from producing it. All patients should be asked about suicidal ideation, depression, obsessional behaviour and psychosis. Note when the problems occurred, for how long they lasted and the treatments received. Approach this section by explaining to the patients that you would like to know more about them in order to understand their problems and to be able to help them better. Enquire about age, occupation, social circumstances, any psychiatric disorders/other health problems, relationship with the patient. Childhood: birth history (difficulties, prematurity); developmental milestones, delay in particular; description of early childhood; family and home atmosphere. School: leaving age; any truancy or school refusal, bullying; relationships with peers, teachers; exams taken and qualifications, further education. Occupations: list all jobs and duration of employment, reasons for leaving and any periods of unemployment. Forensic history: record all offences whether convicted or not (especially note violent crimes, sexual crimes and persistent offending). Present social situation: type of housing, who else is at home; financial circumstances including income, benefits, debts; social support friends, relatives, social services. This part should include an account from an informant, as no individuals can objectively describe their own personality. Behaviour during the interview: restlessness, tearfulness, eye contact, irritability, appropriateness, distractibility. Content: excessive punning, clang association, monosyllabic, spontaneous or only in answer to questions. Circumstantiality (loosening of associations): thoughts become vague and appear muddled.
Adverse Effects Nausea antibiotic resistance and farm animals cheap 200 mg floxin with mastercard, vomiting ear infection 9 month old buy 400 mg floxin otc, abdominal pain; pruritus; less commonly diarrhoea antibiotic essentials 2015 order floxin 200mg line, headache antimicrobial workout clothes cheap floxin 200 mg without a prescription, dizziness, drowsiness and rash; very rarely, fatal liver damage (see Hepatotoxicity above), dyspepsia, raised intracranial pressure, adrenocortical insufficiency, erectile dysfunction, menstrual disorders, azoospermia (with high doses), gynaecomastia, thrombocytopenia, photophobia and alopecia. Nystatin* Pregnancy Category-C Indications Availability Dose Schedule H Oral, oesophageal, intestinal, vaginal and cutaneous candidiasis. Oral Adult- Intestinal candidiasis: 5,00,000 units every six h, doubled in severe infections. Child- 1 month to 12 years: 1,00,000 units 4 times daily, immunocompromised children may require higher doses up to 5,00,000 units. Topical application Dissolve one tablet in glycerine and apply locally 3 to 4 times. Cysticercosis is a systemic infection caused by the larval form (cysticercus) of Taenia solium. In man, echinococcosis is due to the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus or E. The larvae (oncospheres) develop by expansion (cystic echinococcosis) or tumour-like infiltration (alveolar echinococcosis), respectively, in the liver, lungs, or other organs. Diphyllobothriasis: In diphyllobothriasis, niclosamide or praziquantel in a single dose is highly effective. They are contraindicated for the treatment of cestode infections in pregnancy; pregnancy should be excluded before treatment with albendazole (non-hormonal contraception during and for 1 month after treatment). Hymenolepiasis: In hymenolepiasis, praziquantel is more effective than niclosamide, although resistance to praziquantel has been reported. Repeated treatment may be necessary to cure intense infections or to eliminate the parasite within a family group or institution. It thus offers the prospect of a cure for neurocysticercosis, which has been treatable only by surgery, anti-inflammatory corticosteroids and anticonvulsants. However, because dying and disintegrating cysts may induce localized cerebral oedema, treatment with praziquantel must always be undertaken in a hospital setting. In addition, a corticosteroid is usually given to reduce the inflammatory response. Albendazole also kills neurocysticerci when given daily for one month; a corticosteroid or an antihistamine is also given to reduce any inflammatory reaction. Intestinal Nematode Infections: Intestinal nematode infections include ascariasis, capillariasis, enterobiasis, hookworm infection, strongyloidiasis, trichostrongyliasis and trichuriasis. Ascariasis: Ascariasis is an infection, usually of the small intestine, caused by Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm). Single doses of levamisole or pyrantel are effective; the broad-spectrum anthelminthics, albendazole or mebendazole are also effective. Capillariasis: Capillariasis is caused by infection of the intestine with Capillaria philippinensis. Prolonged treatment with mebendazole or albendazole offers the only prospect of cure. Enterobiasis: Enterobiasis is an infection of the large intestine caused by Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm, threadworm). All household members should be treated concurrently with a single dose of mebendazole, albendazole or pyrantel. Since reinfection readily occurs, at least one further dose should be given 2-4 weeks later. Piperazine is also effective but must be taken regularly for at least 7 consecutive days. Hookworm Infections: Hookworm infections are caused by Ancylostoma duodenale (ancylostomiasis) and Necator americanus (necatoriasis); they are a major cause of iron-deficiency anaemia in the tropics and sub-tropics. In hookworm, broad-spectrum anthelminthics are preferred wherever other nematode infections are endemic. There is some evidence to suggest that the use of mebendazole in pregnancy is not associated with an increased incidence of adverse effects on the fetus. However, neither mebendazole nor albendazole should be used during the first trimester of pregnancy to treat nematode infections. Both drugs are contraindicated for the treatment of cestode infections in pregnancy. Levamisole is effective in the treatment of mixed Ascaris and hookworm infections and pyrantel has been highly effective in some community-based control programmes, although several doses are often needed to eliminate Necator americanus infection. Patients with iron-deficiency anaemia caused by hookworm infection require supplementary iron salts and should receive ferrous sulphate (200 mg daily for adults) for at least 3 months after the haemoglobin concentration of 12g/100 ml is obtained. Strongyloidiasis: Strongyloidiasis is an infection of the small intestine caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. Ivermectin in a single dose of 200 µg/kg or 200 µg/ kg/day on two consecutive days is the treatment of choice for chronic strongyloidiasis but it may not be available in all countries. Albendazole 400 mg once or twice daily for 3 days is well tolerated by both adults and children aged over 2 years and it may eradicate up to 80% of infections. Mebendazole has also been used but, to be effective, it must be administered for longer periods as it has a limited effect on larvae and hence the prevention of autoinfection. Trichostrongyliasis: Trichostrongyliasis is an infection of the small intestine caused by Trichostrongylus spp. In symptomatic trichostrongyliasis, a single dose of pyrantel (10 mg/kg) or albendazole (400 mg) is effective. Trichuriasis: Trichuriasis is an infection of the large intestine caused by Trichuris trichiura (whipworm). Chemotherapy is required whenever symptoms develop or when faecal samples are found to be heavily contaminated (up to 10,000 eggs per gram). Tissue Nematode Infections: Tissue nematode infections include angiostrongyliasis, anisakiasis, cutaneous larva migrans, dracunculiasis, trichinellosis and visceral larva migrans. Angiostrongyliasis: Angiostrongyliasis is caused by infection with the larvae of the rat lungworm, Parastrongylus cantonensis (Angiostrongylus cantonensis). Anisakiasis: Anisakiasis is caused by infection with seafood containing larvae of Anisakis, Contracaecum or Pseudoterranova spp. Prevention is dependent upon informing communities of the hazards of eating raw or inadequately prepared salt-water fish; and early evisceration of fish after capture and freezing of seafood at -20C for at least 60 h before sale. Cutaneous Larva Migrans: Cutaneous larva migrans (creeping eruption) is caused by infection with larvae of animal hookworms, usually Ancylostoma braziliense and A. Dracunculiasis: Dracunculiasis (dracontiasis, guinea-worm infection) is caused by infection with Dracunculus medinensis, acquired through drinking water containing larvae that develop in small freshwater crustaceans. It also weakens the anchorage of the worms in the subcutaneous tissues and they can then be removed by traction. However, since it has no effect on the larvae of pre-emergent worms, it does not immediately prevent transmission. Trichinellosis: Trichinellosis (trichinosis) is caused by infection with the larvae of Trichinella spiralis. Each case of confirmed or even suspected trichinellosis infection should be treated in order to prevent the continued production of larvae. In both adults and children, mebendazole (200 mg daily for 5 days), albendazole (400 mg daily for 3 days) and pyrantel (10 mg/kg daily for 5 days) are all effective. Prednisolone (40-60 mg daily) may be needed to alleviate the allergic and inflammatory symptoms. Visceral Larva Migrans: Visceral larva migrans (toxocariasis) is caused by infection with the larval forms of Toxocara canis and less commonly, T. A 3 week oral course of diethylcarbamazine kills the larvae and arrests the disease, but established lesions are irreversible. To reduce the intensity of allergic reactions induced by dying larvae, dosage is commonly commenced at 1 mg/kg twice daily and raised progressively to 3 mg/kg twice daily (adults and children). Ocular larva migrans occurs when larvae invade the eye, causing a granuloma which may result in blindness. In order to suppress allergic inflammatory responses in patients with ophthalmic lesions, prednisolone should be administered concurrently, either topically or systemically. Albendazole* Pregnancy Category-C Indications Schedule H Echinococcus multilocularis and E. Hydatid disease: 400 mg twice daily with meals for 28 days (therapy may be repeated after 14 days in three cycles). Contraindications Pregnancy, adequate measures must be taken for non-hormonal contraceptive during and one month after therapy; hypersensitivity.
For a period of time in the 20th century Autism was considered mistakenly as part of schizophrenia antibiotic 3 days uti buy 400 mg floxin. Later it was realised that Autism had an onset generally before three years and schizophrenia typically showed itself in adolescence antibiotics overuse purchase floxin 200 mg without prescription. The relationship is complex as Konstantareas et al (2000 infection streaking order 200 mg floxin fast delivery, 26) point out that co-morbid disorders maybe "(a) different expressions of the same disorder virus 68 ny floxin 400mg cheap, (b) involve one disorder leading to another disorder, (c) be chance factors, (d) present different stages of the same disorder, (e) be separate but related disorders due to linked genes or environmental risk factors" (Kraemer, 1996). Fleming & Martin (2010), 21, point out that "25% of people have reported voice hearing experience and 5-21% have reported delusions in studies of people from the general population". There are significant overlapping features between Autism Spectrum Disorder and schizophrenia and also some clear differences. One of the major differences is that Autism Spectrum Disorders have an onset before three and schizophrenia has an onset in adolescence. Rausch and Johnson (2008) point out that in terms of social interaction Autism Spectrum Disorders show "impaired social interaction" while schizophrenia shows "limited social contact". In terms of non-verbal social skills they point out that in the Autism Spectrum Disorders there are "impaired non-verbal social behaviours" and in schizophrenia "reduced body language". In terms of body language they point out that in the Autism Spectrum Disorders there are "impaired body posture, impaired gestures" while in schizophrenia there is "posturing; reduced body language". In terms of eye contact they point out that in Autism Spectrum Disorders there is "impaired eye to eye gaze" while in schizophrenia "the face appears immobile and unresponsive, with grimacing". In terms of relatedness and social motivation they point out that in Autism Spectrum Disorders there is "failure to develop peer relationships" while in schizophrenia there is "avolition, limited social contacts". The language difficulties in Autism Spectrum Disorders and schizophrenia 218 A Comprehensive Book on Autism Spectrum Disorders can easily be confused. I often noticed persons with Autism Spectrum Disorders have very restricted dialogue and give very brief answers to questions. Rausch and Johnson (2008) point out that "autistic subjects show worse performance on the facial recognition test than do schizophrenic subjects". Emotional perception is much more severely involved in autism than in schizophrenia. Both Autism Spectrum Disorders and schizophrenia have difficulty understanding irony, humour, metaphor, and proverbs. Both Autism Spectrum Disorders and schizophrenia can show rocking behaviour and stereotyped behaviour. Nevertheless persons with Autism Spectrum Disorders are far more rigid, inflexible, dominant and controlling in comparison to schizophrenia. They can show similar impairment in living skills but in acute psychosis or schizophrenia, in the acute phase the impairment in living skills is greater in schizophrenia. Crespi and Badock (2008) proposed that psychosis and autism are diametrical disorders of the social brain. Indeed it was believed for a long time that they were one and the same and they both were covered by the term child psychosis. Crespi and Badcock (2008) point out that autism shows a general pattern "of constrained overgrowth, whereas schizophrenia involves undergrowth". They also point out that "these disorders exhibit diametrical patterns for traits related to social brain development, including aspects of gaze, agency, social cognition, local versus global processing, language and behaviour". Another reason for misdiagnosis of Autism as schizophrenia is the impression given of Thought Disorder by persons with Autism which is well put by Katz (1989), as reported by Konstantareas (2001) "Some of them make remarks that are out of context, carry on conversations with themselves. Kostantareas et al (2001) showed in their study that "more patients with Autism than schizophrenia were rated as displaying negative symptoms such as affect flattening, alogia and attentional difficulties". A delusion is partly the best explanation a person can come up with in the context of gene/ environment interaction. I have the experience of a patient with Autism where one room was reconstructed in the home and this sent the patient into paranoid psychosis. All autistic and psychotic phenomena are on a continuum of severity and are on spectrums or dimensions. Most conditions in psychosis are on dimensions and there is a great deal of overlap between psychiatric conditions. The brain the brains of persons with autism are unusual in the sense that they have atypical cerebral asymmetry. They also have problems with minicolumns of the brain which is the smallest functioning units of the brain (Casanova, 2008), Casanova (2008) points out that "it does appear that minocolumnar pathology may provide an overarching explanation to many of the signs and symptoms observed in autism. Supernumeracy minicolumns provide for cortical expansions and consequently brain growth. Resutls indicated that minicolumns were smaller and their components cells more dispersed than normal". The brain with its increased local connectivity is more creative in certain areas and the poor long range connectivity is a feature that is probably underlying the language and poor social skills. A study by Casanova, Switala, Trippe and Fitzgerald (2007) confirmed these findings in relation to three distinguished scientists. Lyons & Fitzgerald (2005) put (forward) the theory that right hemisphere impairment leads to a dysfunctional Self development in autism/Asperger syndrome. Substantial behavioural evidence of infants who later developed autism is supporting the theory of disrupted intersubjective behaviour. These infants did not engage in early mother-infant dyadic experiences which are vital for the maturation of the right brain system. In the majority of cases the causes can be traced to abnormal brain development beginning very early in development, probably in the embryo period. Cognitive neuroscience studies have shown that the right hemisphere plays a special role in personal relatedness which is intimately linked to the development of the Self. There is evidence for the centrality of the right brain in socio-emotional functioning, cognitive self related processes as shown in face-recognition and autobiographical memory studies as well as its importance for the development of a physical sense of self and its dominance for the Social Self in general. Genetics Freitag et al (2010) points out that "molecular genetic studies in autism disorder have come a long way from the early linkage studies, which aimed at describing a few loci and subsequently finding one of a few genes of major effect relevant for all cases of autistic disorder. Freitag et al (2010) concludes that "despite the high-heritability estimates for autistic disorder, no major gene has been observed to be relevant for the majority of autistic disorder diagnoses. In contrast, rare mutations of large effect and a few common variants of small effect in several different genes, which are also involved in different cellular pathways, seem to be caused for many cases of autistic disorder. Freitag et al (2010) recommends that it is important "to perform a detailed cytogenetics analysis in every individual with autistic disorder and additional testing for Fragile X syndrome in individuals with autistic disorder and low intelligence mental retardation in clinical and research settings". Happe and Frith (2009) points out that there is research focussing on "rare single-gene disorders with a high prevalence of autism, with a recent suggestion that some molecular defects in autism may interfere with mechanisms of synaptic protein synthesis linked, theoretically, to both cognitive impairment and savant skills". Children of older fathers and mothers have more children with autism (Badcock, 2008). Badcock (2008) also emphasised the possibility of "faulty genomic imprinting in schizophrenia". There are some chromosomal regions which show the overlap for both autism and schizophrenia. From a statistical point of view autism and schizophrenia can occur together (Rausch & Johnson (2008). A large body of evidence suggests that, on average, females spontaneously empathise to a greater degree than do males". These are all very valuable human characteristics which women on average have stronger traits of. Baron-Cohen et al (2003) points out that "there is evidence for a male advantage in systematising. Baron-Cohen (2002) points out that on average females are better at "sharing and turn-taking"; are more sensitive to facial expressions; put more value in relationships; use more cooperative reciprocal language; and talk more about emotions. Males with autism are typical examples of impaired brain functioning or high systematisation. It would appear that the minicolumns problems that I have described earlier increase local connectivity and decrease long range connectivity and these underlie the problems with social brain which of course are underpinned by genetic differences and neural cell migration difficulties in the utero and with problems after birth with pruning of nerve cells. This leads to often a larger brain which helps systematising and mathematical creativity but which inhibits the development of the social brain and good language. Creativity Psychosis Autism and the Social Brain 221 A well functioning social brain has an emotional understanding of themselves and other people. They can recognise when other people are happy or sad or in pain from the tone of their voice and from reading their faces and particularly their eyes. They can express caring words to a person in distress in a meaningful empathetic way.
Discount floxin 200 mg amex. Antibiotic Sensitivity-Kirby Bauer diffusion test.
Diseases