




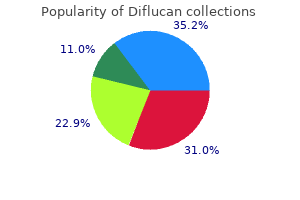
|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
Kena J. Lanham, PharmD, BCPS

https://www.cecentral.com/search/faculty/26031
Arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis anti fungal additive buy diflucan 50mg visa, Wet mount: synovial fluid strongly negatively birefringent urate crystals on the polarizing exam Uric acid: get 2 weeks after attack Resolves fungus in sinuses purchase diflucan 200mg without a prescription, may be false low or normal during attack (>7mg/dl men fungus pronunciation purchase diflucan 100 mg visa, >6mg/dl women) Risk of kidney stones Avoid foods high in purines antifungal diaper rash generic diflucan 100 mg on-line, such as liver and other organ meats, veal, turkey, and some types of fish, including anchovies, shrimp, mackerel, and scallops. The final rule established the national coverage and administrative policies for clinical diagnostic laboratory services payable under Medicare Part B. It promoted Medicare program integrity and national uniformity, and simplified administrative requirements for clinical diagnostic services. A test service might be considered medically appropriate, but nonetheless might be excluded from Medicare coverage by statute. Words such as ``may be indicated' or ``may be considered medically necessary' are used for this reason. Limitations this section lists any national frequency expectations, as well as other limitations on Medicare coverage of the specific test service addressed in the policy-for example, if it would be unnecessary to perform a particular test with a particular combination of diagnoses. In addition, coding guidelines specific to the diagnostic test service addressed in the policy might be included in this section. If a code from this section is given as the reason for the test, the test may be billed to the Medicare beneficiary without billing Medicare first because the service is not covered by statute, in most instances because it is performed for screening purposes and is not within an exception. Description *Encounter for antenatal screening for raised alphafetoprotein level *Encounter for other antenatal screening follow-up *Encounter for antenatal screening for malformations *Encounter for antenatal screening for fetal growth retardation *Z36. Tests for administrative purposes, including exams required by insurance companies, business establishments, government agencies, or other third parties, are not covered. Tests that are not reasonable and necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of an illness or injury are not covered by statute. When a diagnosis has not been established by the physician, codes that describe symptoms and signs, as opposed to diagnoses, should be provided (see also bullet #5 below). Screening tests are performed when no specific sign, symptom, or diagnosis is present and the beneficiary has not been exposed to a disease. In these cases, the sign or symptom should be used to explain the reason for the test. However, on review, the test might still be considered screening and not covered by Medicare. A code is invalid if it has not been coded with all digits/characters required for that code. A urine culture for bacteria might also be used as part of the evaluation and management of another related condition. The procedure includes aerobic agarbased isolation of bacteria or other cultivable organisms present, and quantitation of types present based on morphologic criteria. Elderly or immunocompromised beneficiaries or those with neurologic disorders might present atypically (for example, general debility, acute mental status changes, declining functional status). However, it may be indicated if the beneficiary is being evaluated for response to therapy and there is a complicating co-existing urinary abnormality including structural or functional abnormalities, calculi, foreign bodies, or ureteral/renal stents or there is clinical or laboratory evidence of failure to respond as described in Indications 1 and 2. In surgical procedures involving major manipulations of the genitourinary tract, preoperative examination to detect occult infection may be indicated in selected cases (for example, prior to renal transplantation, manipulation or removal of kidney stones, or transurethral surgery of the bladder or prostate). Urine culture may be indicated to detect occult infection in renal transplant recipients on immunosuppressive therapy. Testing for asymptomatic bacteriuria as part of a prenatal evaluation may be medically appropriate but is considered screening and therefore not covered by Medicare. Preventive Services Task Force has concluded that screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria outside of the narrow indication for pregnant women is generally not indicated. There are insufficient data to recommend screening in ambulatory elderly beneficiaries including those with diabetes. Definitions for sepsis & organ failure & guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Viral quantification may be appropriate for prognostic use including baseline determination, periodic monitoring, and monitoring of response to therapy. Signs and symptoms of acute retroviral syndrome characterized by fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy and rash in an at-risk individual. The frequency of viral load testing should be consistent with the most current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines for use of anti-retroviral agents in adults and adolescents or pediatrics. Nucleic acid quantification techniques are representative of rapidly emerging & evolving new technologies. When used in concert, the accuracy with which the risk for disease progression and death can be predicted is enhanced. This may occur because the antibody response (particularly the IgG response detected by Western Blot) has not yet developed (that is, acute retroviral syndrome), or is persistently equivocal because of inherent viral antigen variability. The patient has signs and symptoms of acute retroviral syndrome with fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy, and skin rash. Revised classification system for human immunodeficiency virus infection in children less than 13 years of age. These include primary disorders such as anemia, leukemia, polycythemia, thrombocytosis and thrombocytopenia. Many treatments and therapies affect the blood or bone marrow, and blood counts may be used to monitor treatment effects. The symptoms of hematological disorders are often nonspecific, and are commonly encountered in patients who may or may not prove to have a disorder of the blood or bone marrow. Furthermore, many medical conditions that are not primarily due to abnormalities of blood or bone marrow may have hematological manifestations that result from the disease or its treatment. Testing of patients who are asymptomatic, or who do not have a condition that could be expected to result in a hematological abnormality, is screening and is not a covered service. An example is as follows: evaluation prior to invasive procedures or operations of patients with personal or family history of bleeding or who are on heparin therapy Limitations 1. The need to repeat this test is determined by changes in the underlying medical condition and/or the dosing of heparin. Extrinsic pathway factors are produced in the liver and their production is dependent on adequate vitamin K activity. Deficiencies of factors may be related to decreased production or increased consumption of coagulation factors. Warfarin blocks the effect of vitamin K on hepatic production of extrinsic pathway factors. The need to repeat this test is determined by changes in the underlying medical condition and/or the dosing of warfarin. Serum iron may also be altered in acute and chronic inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. High concentrations are found in hemosiderosis (iron overload without associated tissue injury) and hemochromatosis (iron overload with associated tissue injury). Serum ferritin can be useful for both initiating and monitoring treatment for iron overload. Transferrin and ferritin belong to a group of serum proteins known as acute phase reactants, and are increased in response to stressful or inflammatory conditions and also can occur with infection and tissue injury due to surgery, trauma or necrosis. Iron studies may be appropriate in patients after treatment for other nutritional deficiency anemias, such as folate and vitamin B12, because iron deficiency may not be revealed until such a nutritional deficiency is treated. Serum ferritin may be appropriate for monitoring iron status in patients with chronic renal disease with or without dialysis. These tests are not to be used solely to assess acute phase reactants where disease management will be unchanged. For example, infections and malignancies are associated with elevations in acute phase reactants such as ferritin, and decreases in serum iron concentration, but iron studies would only be medically necessary if results of iron studies might alter the management of the primary diagnosis or might warrant direct treatment of an iron disorder or condition. For example, a patient presents with new onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and has a serum ferritin level performed for the suspicion of hemochromatosis. It would not ordinarily be considered medically necessary to do a ferritin as a preoperative test except in the presence of anemia or recent autologous blood collections prior to the surgery. Remodeling is required for the maintenance and overall health of bone and is tightly coupled; that is, resorption and formation must be in balance. The term secondary osteoporosis is applied where the causal factor is something other than menopause or aging, such as long-term administration of glucocorticosteroids, endocrine-related disorders (other than loss of estrogen due to menopause), and certain bone diseases such as cancer of the bone. Bone mass measurements and biochemical markers may have complementary roles to play in assessing effectiveness of osteoporosis treatment.

Association of plasma B lymphocyte stimulator levels and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus fungus gnats yellow 400 mg diflucan with amex. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of biologic therapeutics for treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus fungus forest purchase 50 mg diflucan amex. Disease control and safety of belimumab plus standard therapy over 7 years in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus antifungal cream new zealand buy diflucan 200mg line. Comparison of intravenous and subcutaneous exposure supporting dose selection of subcutaneous belimumab systemic lupus erythematosus Phase 3 program antifungal ketoconazole cream purchase diflucan 150 mg amex. American College of Rheumatology Ad Hoc Committee on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Guidelines. Relationship between appearance of urinary red blood cell/white blood cell casts and the onset of renal relapse in systemic lupus erythematosus. A prospective study of anti-chromatin and anti-C1q autoantibodies in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis treated with cyclophosphamide pulses or 76 azathioprine/methylprednisolone. Outcome of relapse in lupus nephritis: roles of reversal of renal fibrosis and response of inflammation to therapy. Current causes of death in systemic lupus erythematosus in Europe, 2000-2004: relation to disease activity and damage accrual. Prevalence of factors influencing cancer risk in women with lupus: social habits, reproductive issues, and obesity. Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with increased incidence of hematologic malignancies: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Effect of autoimmune diseases on risk and survival in histology-specific lung cancer. High incidence of potentially virus-induced malignancies in systemic lupus erythematosus: a long-term followup study in a Danish cohort. Smoking and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: an updated systematic review and cumulative metaanalysis. Patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus who smoke are less responsive to antimalarial treatment. Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy and coronary disease risk factors in systemic lupus erythematosus. High plasma leptin levels confer increased risk of atherosclerosis in women with systemic lupus erythematosus, and are associated with inflammatory oxidised lipids. Evaluation of risk factors that contribute to high prevalence of premature atherosclerosis in Chinese premenopausal systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Age-specific incidence rates of myocardial infarction and angina in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: comparison with the Framingham Study. Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective proof-ofconcept cohort study. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with angiographically defined coronary artery disease: a retrospective cohort study. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. Prevalence and risk factors for coronary artery calcification following kidney transplantation for systemic lupus erythematosus. Coronary calcium in systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with traditional cardiovascular risk factors, but not with disease activity. Premature atherosclerosis in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus: risk factors for increased carotid intima-media thickness in the atherosclerosis prevention in pediatric lupus erythematosus cohort. Treatment of active lupus nephritis with voclosporin: Rapid remission over 48 weeks. Mycophenolate mofetil as the primary treatment of membranous lupus nephritis with and without concurrent proliferative disease: a retrospective study of 29 cases. Mycophenolate mofetil for refractory haemolytic anemia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rituximab for the treatment of refractory autoimmune hemolytic anemia in children. Evaluation of azathioprine in autoimmune thrombocytopenia and lupus erythematosus. Prolonged immunoglobulin and platelet infusion for treatment of immune thrombocytopenia. Outcome of splenectomy for thrombocytopenia associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmune thrombocytopenia in primary antiphospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: the response to splenectomy. Effective B cell depletion with rituximab in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Use of rituximab in the treatment of refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: Singapore experience. Successful treatment of severe thrombocytopenia with romiplostim in a pregnant patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Cyclosporin A in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: results of an open clinical study. New oral anticoagulants may not be effective to prevent venous thromboembolism in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Management of cutaneous lupus erythematosus with low-dose methotrexate: indication for modulation of inflammatory mechanisms. Mycophenolate sodium for subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus resistant to standard therapy. Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in antimalarialresistant cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Safety and efficacy of a broad-spectrum sunscreen in patients with discoid or subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Refractory subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus successfully treated with rituximab. Intensive immunosuppressive therapy improves pulmonary hemodynamics and long-term prognosis in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease. Steroid-sparing effects of methotrexate in systemic lupus erythematosus: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Printed in the United States of America Last digit indicates print number: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Publisher: Quincy McDonald Manager of Content Development: George W. The author(s) and publisher have done everything possible to make this book accurate, up to date, and in accord with accepted standards at the time of publication. Any practice described in this book should be applied by the reader in accordance with professional standards of care used in regard to the unique circumstances that may apply in each situation. Library of Congress Control Number: 2014945712 Authorization to photocopy items for internal or personal use, or the internal or personal use of specific clients, is granted by F. Julia Halm, Caitlin Masters, Anthony Bishop-Gylys, Matthew Bishop-Gylys, Liam Halm, and the little one, Harrison Robert Halm -B A R B A R A G Y L Y S to my mother, best friend, mentor, and co-author, Barbara A. Julia, and Caitlin, all of whom have given me continuous encouragement and support, and to my grandsons Liam and Harrison who bring me endless joy. The book is written in an engaging, nontechnical language that relates to students of all backgrounds and levels of education. No natural science background is needed to absorb the information in the textbook. Keeping in mind that the needs of students from various educational environments differ, this text and its associated electronic resources are constructed for use in colleges, universities, career schools, online courses, and other educational environments that offer a medical terminology course. The textbook and its associated electronic resources are organized as competency-based instruments. The various learning tools enable students to evaluate their understanding of medical terminology based on guidelines required by the major allied health accrediting agencies. The word-building and competency-based approaches are always evident in the educational materials we have published. Various types of learning reinforcements are found throughout the Medical Terminology Express textbook and supplemental teaching aids available to students and instructors. Nevertheless, the textbook emphasizes the meaning of basic medical terms and demonstrates how the terms are used in the health care environment. Most importantly, the descriptive terms are included in the language of medicine used by health care providers in the clinical environment. This is followed by a section of diagnostic, medical, and surgical procedures and pharmacology.
Navigational Note: Ventricular arrhythmia Asymptomatic antifungal face wash discount 200 mg diflucan mastercard, intervention Non-urgent medical Urgent intervention indicated Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated consequences; hemodynamic compromise Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia that originates in the ventricles fungus remedies diflucan 100mg otc. Navigational Note: Ventricular tachycardia Non-urgent medical Symptomatic antifungal home remedy for scalp generic diflucan 100mg with mastercard, urgent Life-threatening Death intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences; hemodynamic compromise Definition: A disorder characterized by a dysrhythmia with a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute that originates distal to the bundle of His antifungal resistant ringworm cheap diflucan 100mg fast delivery. Navigational Note: Delayed puberty No breast development by No breast development by age 13 yrs for females; testes age 14 yrs for females; no volume of <3 cc or no Tanner increase in testes volume or Stage 2 development by age no Tanner Stage 2 by age 16 14. Navigational Note: Virilization Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; medical not indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by inappropriate masculinization occurring in a female or prepubertal male. Navigational Note: Corneal ulcer Corneal ulcer without Perforation in the affected eye perforation in the affected eye Definition: A disorder characterized by an area of epithelial tissue loss on the surface of the cornea. Navigational Note: Retinal tear No retinal detachment and No retinal detachment and treatment not indicated treatment indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a small laceration of the retina, this occurs when the vitreous separates from the retina. Navigational Note: If retinal detachment is present, grade under Eye disorders: Retinal detachment Retinal vascular disorder Retinal vascular disorder Retinal vascular disorder with without neovascularization neovascularization Definition: A disorder characterized by pathological retinal blood vessels that adversely affects vision. Navigational Note: If vitreous hemorrhage is present, report under Eye disorders: Vitreous hemorrhage. Navigational Note: Vision decreased Moderate decrease in visual acuity (best corrected visual acuity 20/40 and better or 3 lines or less decreased vision from known baseline) Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in visual acuity. Navigational Note: Cheilitis Asymptomatic; clinical or diagnostic observations only; intervention not indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by inflammation of the lip. Navigational Note: Colonic perforation Invasive intervention not Invasive intervention indicated indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the colonic wall. Navigational Note: Dental caries One or more dental caries, Dental caries involving the Dental caries resulting in not involving the root root pulpitis or periapical abscess or resulting in tooth loss Definition: A disorder characterized by the decay of a tooth, in which it becomes softened, discolored and/or porous. Navigational Note: Duodenal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention indicated; hospitalization Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the duodenum. Navigational Note: If reporting a known abnormality of the colon, use Gastrointestinal disorders: Colitis. If reporting a documented infection, use Infections and infestations: Enterocolitis infectious. Navigational Note: Esophageal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention indicated; hospitalization Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the esophagus. Navigational Note: Fecal incontinence Occasional use of pads Daily use of pads required Severe symptoms; elective required operative intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by inability to control the escape of stool from the rectum. Navigational Note: Gastroesophageal reflux Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; medical Severe symptoms; operative disease not indicated intervention indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by reflux of the gastric and/or duodenal contents into the distal esophagus. Navigational Note: Gastrointestinal fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between any part of the gastrointestinal system and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Ileal perforation Invasive intervention not Invasive intervention indicated indicated Grade 4 - Grade 5 - Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Death Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the ileal wall. Navigational Note: Intra-abdominal hemorrhage Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; intervention indicated invasive intervention indicated; hospitalization Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding in the abdominal cavity. Navigational Note: Lower gastrointestinal Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; hemorrhage not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention indicated; hospitalization Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract (small intestine, large intestine, and anus). Navigational Note: Oral hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention indicated; hospitalization Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the mouth. Navigational Note: Pancreatitis Enzyme elevation; radiologic findings only Grade 4 Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Grade 5 Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Death Severe pain; vomiting; medical intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Periodontal disease Gingival recession or Moderate gingival recession Spontaneous bleeding; severe gingivitis; limited bleeding on or gingivitis; multiple sites of bone loss with or without probing; mild local bone loss bleeding on probing; tooth loss; osteonecrosis of moderate bone loss maxilla or mandible Definition: A disorder in the gingival tissue around the teeth. Navigational Note: Rectal fissure Asymptomatic Symptomatic Definition: A disorder characterized by a tear in the lining of the rectum. Navigational Note: Rectal perforation Invasive intervention not Invasive intervention indicated indicated Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Death - - Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Death Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the rectal wall. Navigational Note: Also report Investigations: Neutrophil count decreased Upper gastrointestinal Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; hemorrhage not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention indicated; hospitalization Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract (oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, and stomach). Signs and symptoms may include induration, erythema, swelling, burning sensation and marked discomfort at the infusion site. Navigational Note: Injection site reaction Tenderness with or without Pain; lipodystrophy; edema; Ulceration or necrosis; severe Life-threatening Death associated symptoms. Navigational Note: Neck edema Asymptomatic localized neck Moderate neck edema; slight Generalized neck edema. Navigational Note: Budd-Chiari syndrome Medical management Severe or medically significant Life-threatening indicated but not immediately lifeconsequences; moderate to threatening; hospitalization or severe encephalopathy; coma prolongation of existing hospitalization indicated; asterixis; mild encephalopathy Definition: A disorder characterized by occlusion of the hepatic veins and typically presents with abdominal pain, ascites and hepatomegaly. Navigational Note: Gallbladder necrosis Life-threatening consequences; urgent invasive intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the gallbladder. Navigational Note: Portal hypertension Decreased portal vein flow Reversal/retrograde portal vein flow; associated with varices and/or ascites Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in blood pressure in the portal venous system. Navigational Note: If related to infusion, use Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: Infusion related reaction. Symptoms include fever, arthralgias, myalgias, skin eruptions, lymphadenopathy, chest marked discomfort and dyspnea. Navigational Note: Bacteremia Blood culture positive with no signs or symptoms Definition: A disorder characterized by the presence of bacteria in the blood stream. Navigational Note: For symptoms and no intervention, consider Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Sore throat or Hoarseness. Navigational Note: Myelitis Asymptomatic; mild signs Moderate weakness or Severe weakness or sensory Life-threatening. Symptoms include weakness, paresthesia, sensory loss, marked discomfort and incontinence. Symptoms include fullness, itching, swelling and marked discomfort in the ear and ear drainage. Navigational Note: For Grade 1 Consider Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Sore throat Phlebitis infective Localized, local intervention Oral intervention indicated indicated. Burns can be caused by exposure to chemicals, direct heat, electricity, flames and radiation. The extent of damage depends on the length and intensity of exposure and time until provision of treatment. Navigational Note: Dermatitis radiation Faint erythema or dry Moderate to brisk erythema; Moist desquamation in areas Life-threatening Death desquamation patchy moist desquamation, other than skin folds and consequences; skin necrosis mostly confined to skin folds creases; bleeding induced by or ulceration of full thickness and creases; moderate edema minor trauma or abrasion dermis; spontaneous bleeding from involved site; skin graft indicated Definition: A finding of cutaneous inflammatory reaction occurring as a result of exposure to biologically effective levels of ionizing radiation. Navigational Note: Fall Minor with no resultant Symptomatic; noninvasive Hospitalization indicated; injuries; intervention not intervention indicated invasive intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of sudden movement downward, usually resulting in injury. Navigational Note: Pharyngeal anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a pharyngeal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Postoperative thoracic Extubated within 24 - 72 hrs Extubated >72 hrs procedure complication postoperatively postoperatively, but before tracheostomy indicated Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated Death Life-threatening airway compromise; urgent intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Prolapse of urostomy Asymptomatic; clinical or Local care or maintenance; Dysfunctional stoma; elective Life-threatening diagnostic observations only; minor revision indicated operative intervention or consequences; urgent intervention not indicated major stomal revision intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of displacement of the urostomy. The inflammatory reaction is confined to the previously irradiated skin and the symptoms disappear after the removal of the pharmaceutical agent. Navigational Note: Rectal anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive Life-threatening Death finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent indicated operative intervention indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a rectal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Seroma Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; simple Symptomatic, elective diagnostic observations only; aspiration indicated invasive intervention intervention not indicated indicated Definition: A finding of tumor-like collection of serum in the tissues. Navigational Note: Spermatic cord anastomotic Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive Life-threatening Death leak finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent indicated operative intervention indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a spermatic cord anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Stomal ulcer Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; elective diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated operative intervention intervention not indicated indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the jejunal mucosal surface close to the anastomosis site following a gastroenterostomy procedure. Navigational Note: Tracheal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the trachea. Navigational Note: Tracheostomy site bleeding Minimal bleeding identified Moderate bleeding; medical Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening on clinical exam; intervention intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent not indicated indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the tracheostomy site. Navigational Note: Urethral anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a urethral anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Urostomy leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage of contents from a urostomy. Navigational Note: Urostomy site bleeding Minimal bleeding identified Moderate bleeding; medical on clinical exam; intervention intervention indicated not indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the urostomy site. Vaginal anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a vaginal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Vas deferens anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated indicated Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated - Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Death Life-threatening consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Death Definition: A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a vas deferens anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Also consider Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic failure Blood corticotrophin Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Hospitalization indicated decreased diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated intervention not indicated Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an decrease in levels of corticotrophin in a blood specimen.
You can do it right before a workout antifungal wipes order diflucan 100 mg line, as well: Just five minutes before will give you results! This is great for maintaining your muscle health xylitol fungus sinus 200mg diflucan visa, which will mean less chance of injury and less pain fungus gnats bonsai generic 50mg diflucan with mastercard. This will keep your tissue hydrated antifungal youtube purchase 50 mg diflucan fast delivery, which will make them more flexible, thus more receptive to your Foam Rolling. This will aid in both prepping your muscles for a workout and for helping them recover. Starting with the smooth inner roller is great, because it is gentle and can work as an introduction to the Foam Rolling regimen. This will make your workouts more effective and will give you the massage therapy you need after a strenuous exercise. It works best for mild or moderate injuries, or those which are caused by restricted movement. A word of warning: If you have an injury that worries you, or that is causing more than moderate pain, you should speak to your physician. The recommended movements take about two minutes, and are done two to three times per week. Because it takes two minutes each for both sides of your body, as well as working out all sections of muscle, it will probably take a beginner approximately half an hour for each session. Holding them in a shortened position, which is all-too-common, will limit how much motion your ankle can take. Slowly and deliberately, roll from the bottom of the calf muscle to the top, which is just below your knee. It is made up of a thick band of fascia tht runs from the side of your leg, knee to pelvis. It limits lower body movement, making certain exercises (squats, lunges) more difficult. The best way to do this si to start on your stomach, your knee bent up and positioned out towards the side. Sitting down all day will cause your Piriformis muscle to be very tight and uncomfortable. Start by resting on your side, the arm on the bottom extended out, but not rigid; keep it relaxed. To provide your head with support, you can use your clasped hands to cradle the back of your hand. Because the power plate offers three planes (moving in all directions, from forward and back, side to side, and even up and down), it will force your muscles to compensate for this. This will exercise your muscles, leaving them lean, healthy, strong, and flexible. Avoid Critical Foam Rolling Mistakes To help you foam roll successfully, remember to avoid: 1. Instead of directly rolling the painful area, try to roll the areas around it, focusing on any connecting muscles. That can cause problems, ranging from bruising and inflammation to nerve and tissue damage. But, if you find yourself falling out of the posture needed for each exercise, you should regroup and then continue. You can always do your Foam Rolling later, so that you can be sure to maintain posture. And finally - Enjoy using your Reehut Foam Roller, and enjoy the increased benefits that it is sure to bring to you! No part of this work may be photocopied, published, adapted, broadcast, transmitted or reproduced in any form or by any means, without the prior consent of Reehut. It begins with an overview of relevant statistical terminology; touches on medical screening, toolbox questionnaires, and clearing the lumbosacral spine; and examines special tests and related statistics for the hip, knee, and ankle. Conclusion, Additional Resources, References, and Exam (15 minutes) Welcome to lower extremity examination tests, an evidence-based course designed to provide you with state of the art literature on how to perform and interpret orthopedic examination techniques for the lower extremity. Client history and visual inspection are components you most likely already know very well. We will, however, discuss medical screening, because not everything that causes joint pain is always musculoskeletal. Pain with motion and tenderness to palpation may imply the problem is musculoskeletal. However, it is important to also consider the possibility that the signs and symptoms may be the result of appendicitis. It is essential to look at the viscera as a potential source of some of this pain, and make the appropriate referrals for the things that are outside our scope of practice. To earn continuing education credit for this course, you must achieve a passing score of 80% on the final exam. Cancellation In the unlikely event that a self-study course is temporarily unavailable, already-enrolled participants will be notified by email. Customers who cancel orders within five business days of the order date receive a full refund. Cancellations can be made by phone at (888)564-9098 or email at support@pdhacademy. Contact customer service by phone at (888)564-9098 or email at support@pdhacademy. Her areas of expertise are orthopedics, sports medicine, modalities, and medical screening. She also provides athletic training services from the middle school to elite Olympic/Paralympic level. Gulick has provided medical coverage at numerous national and international events. Gulick is the author of 4 books (Ortho Notes, Screening Notes, Sport Notes, Mobilization Notes), 4 book chapters, and over 50 peer-reviewed publications, and has made over 100 professional and civic presentations. They can also help you to do serial measurements: doing a test at the time of the examination, and then doing another questionnaire or the same questionnaire two weeks later (or three or four weeks later, or at discharge) helps you to see that serial level of improvement. Finally, they help you to take rote data like range of motion and manual muscle testing and put it into a functional context. By that, I mean if a person gains ten degrees of external rotation over the course of two or three treatments, it is certainly very promising. Range of motion, manual muscle testing, sensation, and palpation are certainly important components of an examination, but will not be a part of this course. Well, particularly in the area of orthopedics, what tends to happen is someone names a test after him/herself, and then somebody else picks up that test, tweaks it slightly, and renames it. To that end, you have to be able to figure out for yourself which of these tests are good and which of these are not good. When a test is highly sensitive and the results are negative, we can rule out the suspected pathology. Thus, a test that is highly sensitive is used to rule out the pathology when the test result is negative. Here is a situation where we have 12 people with a disease and 12 people without a disease: the ones on the left are red and they have the disease; the ones on the right are green and they do not have the disease. Statistics As we discuss special tests, we are going to talk about their clinical significance and clinical application: basically, "What do they mean to us? If you graduated from school more than ten years ago, If we explore using a test that is 100% sensitive, then that would mean if a person tests negative for that disease, we can rule it out. In the image below, the people on the left tested positive and the people on the right tested negative. As you can see, every single person who tested negative does not have the disease, so it is 100% accurate for sensitivity. Again, we have people on the right who tested negative that have the disease, and this test would be a false negative for those people.
Diagnostic of congenital heart disease xenopus fungus 150 mg diflucan for sale, chronic pulmonary disease or arteriovenous shunts fungus pictures purchase 400 mg diflucan with mastercard. They are not normally palpable due to size (1-5mm diameter) with softness and mobility fungus under toe generic diflucan 50mg visa. Most common cause of enlargement is due to infection within the body from which lymphatic channels drain toward the node antifungal bar soap purchase diflucan 100 mg overnight delivery. This leads to enlargment and transfer of disease from one part of the body to another. Moderate sized node which is firm, seperate and tender, denotes a node which is draining infection. Hemorrhoid (piles-vari cosities or the blood vessels in the rectal passage or anus. C&S will reveal no pathogens in urethral, bladder, & prostatic secretions in chronic nonbacterial prostatitis c. After 10 days from first appearance, crusting occurs, infection and pain subsides, healing then follows. During first 10 days, fever and swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin occurs d. Mode of transmission is direct contact with discharges from buboes or open lesions. The student will be able to identify different components of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat. The student will be able to identify the proper techniques for a basic exam of ears, eyes, nose, and throat. Examine the eye using fluorescein stain for detection of abrasion/laceration/burns/ulcerations 5. Common in swimmers Page 130 of 215 Hospital Corpsman Sickcall Screeners Handbook d. Results from wax in ear that absorbs water, macerates the skin & canal, which affords a basis for infection. Develops thick, purulent otorrhea, dull post-auricular pain, low grade fever, post-auricular swelling and erythema, displacement of auricle outward, pain most intense over mastoid. When force is applied to the orbit causing contents to spill either medially or inferiorly. Physical exam - indirect (mirror) laryngoscopy reveals vocal cords to be red and swollen 2. Treatment - symptomatic; voice rest, vaporization, do not whisper, antibiotics rarely needed. Be able to identify side effects and contraindications of different immunizations. Most live attenuated virus vaccines are made from viruses grown in chicken embryo or egg cultures. Reactions (normal sensitivity) include mild fever 7-14 days after administration, headache, malaise, & myalgias. Rabies - invariably fatal acute encephalomyelitis caused after exposure to an affected animal. Vaccine varies each year and depends on virus strains likely to cause disease during the flu season. The vaccine has a low seroconversion rate and is no longer recommended by the World Health Organization. Pertusis - (whooping cough) an acute, highly contagious infection of the respiratory tract. A modified toxin that does not cause illness is called a toxoid and is used to stimulate the body to produce antibodies that work against the toxin. Pneumovax 23 and pnu-immune 23 are the trade names of a vaccine made from a mixture of highly purified capsular polysaccharides from the 23 most common or most invasive pneumococcal types. Those at risk include individuals without a spleen; chronic renal, respiratory, or cardiac disease. Hemophilus influenza - used to protect against hemophilus, influenza subtype B infection, the most common cause of bacterial meningitis and a leading cause of serious systemic illness in young children in the U. Recently approved vaccine includes the hemophilus, diptheria, tetanus and pertusis. Be able to select the different enzymes and their values by selecting the correct response. Page 149 of 215 Hospital Corpsman Sickcall Screeners Handbook the most common cause of anemia in our population is acute and chronic blood loss and the inherited anemias. Keep in mind that lab values may vary from place to place depending on the equipment used. There are several types of white blood cells which may be distinguished when stained by Wrights Stain on a microscope slide. Basophils are characterized by scattered large, dark-blue to purple granules, which are darker than the nucleus. The differential is usually written as a series of numbers that add up to 100% in the following order: segmented neutrophils, bands, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils. Notice that the numbers are moving to the left of the series, which is where the term "left shift" comes from when describing differentials. Platelets are small, round cells that can be seen on a microscope slide and are important in blood coagulation. There is a tendency to bleed or bruise easily when the platelet count falls to 20,000-50,000 cells/mm3. A number of tests may be performed by dipping a chemical analysis strip into a cup of urine and reading the color coded patches against the references on the strip bottle. Epithelial cells: a few of these cells may be seen in a normal sample, but many epithelial cells may mean the sample is dirty and not collected properly. A common cause of microscopic hematuria in our population is excess exercise, particularly running and humping. The next morning they should urinate into the container and bring the sample to the lab. Sodium is an important ion that acts to preserve a balance between other ions such as calcium and potassium to maintain normal heart actions and equilibrium of the body. Creatinine is the end product of creatine metabolism and is excreted by the kidney. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment that is a breakdown product of hemoglobin and is Processed and excreted by the liver. Increased blood breakdown or liver disease or obstruction will cause bilirubin to rise above normal 0. When bilirubin reaches between 2 to 4 the sclera and the skin become tinted yellow. Total protein is the sum of the circulating proteins in the serum and is difficult to interpret without knowledge of the individual fractions. Urine culture: Patients should be given a sterile urine cup and instructed as follows: 1. Gonorrhea culture: Specimen may be obtained from the cervix, vagina, urethra, rectum, throat or joint fluid. Rub the swab vigorously over the posterior pharynx and tonsils, avoiding the tongue, uvula and buccal mucosa. Blood cultures: Usually obtained in very ill patients with fever of unknown origin and in other clinical situations. Sputum culture: Should be obtained when the patient suspected of pneumonia has a productive cough. Early morning samples are best, and a gram stain should be ordered on the same sample. Page 155 of 215 Hospital Corpsman Sickcall Screeners Handbook Male Genitalia Allotted Time: References: Instructional Aids: Terminal Learning Objective: To recognize potential problems and perform the needed exam. Inspect/palpate anterior thigh in the region of the femoral canal noting tenderness/swelling.
Purchase 400 mg diflucan fast delivery. After clipping and bathing the Cavalier King Charles X Pt 4.