




|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
Manuel B. Graeber, MD (Neurology)
As the number of family members with autoimmune disorders increased from one to three birth control for 5 years straight discount 15 mcg mircette fast delivery, the risk of autism was greater birth control wiki trusted mircette 15 mcg, with an odds ratio that increased from 1 birth control pills yaz cheap mircette 15mcg mastercard. In mothers and first-degree relatives of autistic children birth control for 5 days quality 15mcg mircette, there were more autoimmune disorders (16% and 21%) as compared to controls (2% and 4%), with odds ratios of 8. The most common autoimmune disorders in both groups were type 1 diabetes, adult rheumatoid arthritis, hypothyroidism, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Forty-six percent of the autism group reported having relatives with rheumatoid diseases, as compared to 26% of the controls. Prenatal maternal urinary tract, upper respiratory, and vaginal infections; asphyxia; prematurity, and seizures were more common in the autistic group, although the differences were not significant. Thirty-nine percent of the controls, but only 11% of the autistic, group, reported allergies. An increased number of autoimmune disorders suggests that in some families with autism, immune dysfunction could interact with various environmental factors to play a role in autism pathogenesis. Serum autoantibodies to brain in Landau-Kleffner variant, autism, and other neurologic disorders. A comparison of health care utilization and costs of children with and without autism spectrum disorders in a large group-model health plan. Our purpose for this study was to compare health care utilization and costs of children with and without autism spectrum disorders in the same health plan. Data on health care utilization and costs were derived from health plan administrative databases. A higher percentage of children with autism spectrum disorders experienced inpatient (3% vs 1%) and outpatient (5% vs 2%) hospitalizations. Children with autism spectrum disorders were nearly 9 times more likely to use psychotherapeutic medications and twice as likely to use gastrointestinal agents than children without autism spectrum disorders. Mean annual member costs for hospitalizations (550 dollars vs 208 dollars), clinic visits (1373 dollars vs 540 dollars), and prescription medications (724 dollars vs 96 dollars) were more than double for children with autism spectrum disorders compared with children without autism spectrum disorders. The mean annual age- and gender-adjusted total cost per member was more than threefold higher for children with autism spectrum disorders (2757 dollars vs 892 dollars). Among the subgroup of children with other psychiatric conditions, total mean annual costs were 45% higher for children with autism spectrum disorders compared with children without autism spectrum disorders; excess costs were largely explained by the increased use of psychotherapeutic medications. Research is needed to evaluate the impact of improvements in the management of children with autism spectrum disorders on health care utilization and costs. Increased serum albumin, gamma globulin, immunoglobulin IgG, and IgG2 and IgG4 in autism. As a consequence we expected to find that autism is accompanied by abnormalities in the pattern obtained in serum protein electrophoresis and in the serum immunoglobulin (Ig) and IgG subclass profile. The increased serum concentrations of IgGs in autism may point towards an underlying autoimmune disorder and/or an enhanced susceptibility to infections resulting in chronic viral infections, whereas the IgG subclass skewing may reflect different cytokine-dependent influences on autoimmune B cells and their products. Neurosciences Group, Department of Clinical Neurology, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom. Neurodevelopmental disorders could be caused by maternal antibodies or other serum factors. Blood samples were obtained from 10 male autistic children ages 7-15 years and 10 age-matched, male, healthy controls. Lymphocyte subsets (helper-inducer, suppressor-cytotoxic, total T, and total B cells) were enumerated using monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry. Bound and soluble interleukin-2 receptors were assayed in unstimulated blood samples and in cell cultures following 72-hour stimulation with phytohemagglutinin. The children with autism had a lower percentage of helper-inducer cells and a lower helper:suppressor ratio, with both measures inversely related to the severity of autistic symptoms (r = -. A lower percentage of lymphocytes expressing bound interleukin-2 receptors following mitogenic stimulation was also noted, and this too was inversely related to the severity of autistic symptoms. Could one of the most widely prescribed antibiotics amoxicillin/ clavulanate "augmentin" be a risk factor for autism Characterized by multiple deficits in the areas of communication, development, and behavior; autistic children are found in every community in this country and abroad. Recent findings point to a significant increase in autism which can not be accounted for by means such as misclassification. The state of California recently reported a 273% increase in the number of cases between 1987 and 1998. Many possible causes have been proposed which range from genetics to environment, with a combination of the two most likely. Since the introduction of clavulanate/amoxicillin in the 1980s there has been the increase in numbers of cases of autism. In this study 206 children under the age of three years with autism were screened by means of a detailed case history. A significant commonality was discerned and that being the level of chronic otitis media. The sum total number of courses of antibiotics given to all 206 children was 2480. A proposed mechanism whereby the production of clavulanate may yield high levels of urea/ammonia in the child is presented. Further an examination of this mechanism needs to be undertaken to determine if a subset of children are at risk for neurotoxicity from the use of clavulanic acid in pharmaceutical preparations. These data support the hypothesis that autism could be due to an immune imbalance occurring in genetically predisposed children. Department of Paediatric Neurology, Paediatric Clinic, University of Catania, Italy. A possible role of the immune system in the pathogenesis of some neurologic disorders, including infantile autism, was recently postulated. This observation prompted the authors to investigate some immunologic aspects in a group of patients with Rett syndrome, a disorder still not completely clarified but with some points of commonality with infantile autism. Humoral and cell-mediated immunity were investigated in 20 females with Rett syndrome. Antineuronal and antimyelin ganglioside antibodies were absent, as were antinuclear antibodies, antistriated muscle antibodies, and antismooth muscle antibodies. Immunoglobulin fractions and complement were normal for age in all of the patients. The main exposure was "autism" (not further defined), from response to the question: "Has a doctor or health professional ever told you that your child has autism Respiratory, food, and skin allergies were reported by parents more often for children with autism, with food allergies having the strongest relative difference between the groups (odds ratio, 4. On the basis of the abnormal metabolic profile, a targeted nutritional intervention trial with folinic acid, betaine, and methylcobalamin was initiated in a subset of the autistic children. Evaluation of an association between gastrointestinal symptoms and cytokine production against common dietary proteins in children with autism spectrum disorders. Proinflammatory and regulatory cytokine production associated with innate and adaptive immune responses in children with autism spectrum disorders and developmental regression. Innate immunity associated with inflammatory responses and cytokine production against common dietary proteins in patients with autism spectrum disorder. Dysregulated innate immune responses in young children with autism spectrum disorders: their relationship to gastrointestinal symptoms and dietary intervention. The frequency of ear infections, ear tube drainage, and deafness was examined through parental reports in autistic and yoke-matched, normal children. Autistic children had a greater incidence of ear infections than matched normal peers. Lower-functioning children had an earlier onset of ear infections than their higher-functioning autistic peers. Ear infections coexisted with low-set ears, and with a higher autistic symptomatology score. The possible adverse consequences of intermittent hearing loss on language, cognitive, and socioaffective development are considered. According to recent epidemiological surveys, autistic spectrum disorders have become recognized as common childhood psychopathologies. Parallel evidence of immune abnormalities in autistic patients argues for an implication of the immune system in pathogenesis. This review summarizes advances in the molecular genetics of autism, as well as recently emerging concerns addressing the disease incidence and triggering factors.
Third birth control pills 84 days buy 15mcg mircette visa, all units excepting those for time relate by factors of 10 birth control for women 24 order mircette 15 mcg with mastercard, in contrast to the numerous conversion factors necessary in converting English units of measurement birth control pills facts generic mircette 15mcg with amex. For these reasons birth control for women lyrics cheap mircette 15mcg with amex, as well as the fact that the metric system is used almost exclusively by the scientific community, it is the system used in this book. For those who are not familiar with the metric system, it is useful to be able to recognize the approximate English system equivalents of metric quantities. All of the relevant units of measurement in both systems and common Englishmetric conversion factors are presented in Appendix C. Because biomechanists come from different academic backgrounds and professional fields, biomechanical research addresses a spectrum of problems and questions. Basic knowledge of biomechanics is essential for competent professional analysts of human movement, including physical education teachers, physical therapists, physicians, coaches, personal trainers, and exercise instructors. The structured approach presented in this book is designed to facilitate the identification, analysis, and solution of problems or questions related to human movement. Locate and read three articles from the scientific literature that report the results of biomechanical investigations. Write a brief discussion about how knowledge of biomechanics may be useful in your intended profession or career. Choose three jobs or professions, and write a discussion about the ways in which each involves quantitative and qualitative work. Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words. Step by step, show how to arrive at a solution to one of the problems you described in Problem 6. Tim starts running at a distance of 15 m from the ball, and Jan starts running at a distance of 12 m from the ball. Select a specific movement or sport skill of interest, and read two or three articles from the scientific literature that report the results of biomechanical investigations related to the topic. Write a short paper that integrates the information from your sources into a scientifically based description of your chosen movement. When attempting to balance your checkbook, you discover that your figures show a different balance in your account than was calculated by the bank. List an ordered, logical set of procedures that you may use to discover the error. Wendell invests $10,000 in a stock portfolio made up of Petroleum Special at $30 per share, Newshoe at $12 per share, and Beans & Sprouts at $2. He runs 2 km west, then 2 km south, and then runs on a path that takes him directly back to the place he started at. Based on your comparative observations, list any differences and similarities that you can detect. Which of these are of potential importance and which are more a matter of personal style Movement Differences Important After viewing the movement several times, list at least three general questions and three specific questions that an analyst might choose to answer regarding the movement. Have one member of your group perform several trials of walking as the group observes from front, side, and rear views. Datta D, Heller B, and Howitt J: A comparative evaluation of oxygen consumption and gait pattern in amputees using Intelligent Prostheses and conventionally damped knee swing-phase control, Clin Rehabil 19:398, 2005. Dubravcic-Simunjak S, Pecina M, Kuipers H, Moran J, and Haspl M: the incidence of injuries in elite junior figure skaters, Am J Sports Med 31:511, 2003. Greenblatt D: Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, Pharmacotherapy 25:574, 2005. Lips P: Epidemiology and predictors of fractures associated with osteoporosis, Am J Med 103:3S, 1997. Pigozzi F, Santori N, Di Salvo V, Parisi A, and Di-Luigi L: Snowboard traumatology: an epidemiological study, Orthopedics 20:505, 1997. Versluys R, Beyl P, Van Damme M, Desomer A, Van Ham R, and Lefeber D: Prosthetic feet: state-of-the-art review and the importance of mimicking human ankle-foot biomechanics, Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol 4:65, 2009. Yoshimitsu K, Shiva N, Matsuse H, Takano Y, Matsugaki T, Inada T, Tagawa Y, and Nagata K: Development of a training method for weightless environment using both electrical stimulation and voluntary muscle contraction, Tohoku J Exp Med 220:83, 2010. Analyzes common fundamental movements such as walking, running, jumping, throwing, climbing, etc. Provides general strategies, as well as specific tools and techniques for solving quantitative problems. Provides information about the organization, conference abstracts, and a list of graduate programs in biomechanics. Identify and describe the reference positions, planes, and axes associated with the human body. Identify and describe the uses of available instrumentation for measuring kinematic quantities. What are the advantages and disadvantages of analyzing a movement captured on video To the untrained observer, there may be no differences in the forms displayed by an elite hurdler and a novice hurdler or in the functioning of a normal knee and an injured, partially rehabilitated knee. What skills are necessary and what procedures are used for effective analysis of human movement kinematics One of the most important steps in learning a new subject is mastering the associated terminology. Likewise, learning a general analysis protocol that can be adapted to specific questions or problems within a field of study is invaluable. In this chapter, human movement terminology is introduced, and the problem-solving approach is adapted to provide a template for qualitative solving of human movement analysis problems. Since linear and angular motion are "pure" forms of motion, it is sometimes useful to break complex movements down into their linear and angular components when performing an analysis. Linear Motion Pure linear motion involves uniform motion of the system of interest, with all system parts moving in the same direction at the same speed. When a body experiences translation, it moves as a unit, and portions of the body do not move relative to each other. For example, a sleeping passenger on a smooth airplane flight is being translated through the air. If the passenger awakens and reaches for a magazine, however, pure translation is no longer occurring because the position of the arm relative to the body has changed. If the line is straight, the motion is rectilinear; if the line is curved, the motion is curvilinear.
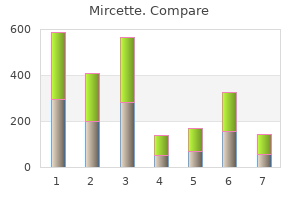
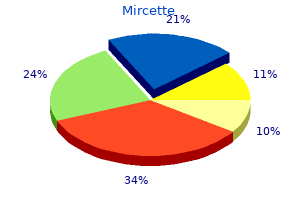
Discount mircette 15mcg without prescription. Does the birth control shot have side effects?.
See the Medicare Benefit Policy Manual birth control pills 2 hormone provera discount mircette 15 mcg fast delivery, Chapter 11 birth control for women long trench purchase mircette 15mcg on line, "End Stage Renal Disease birth control for women men buy discount mircette 15mcg on line," for payment for hemodialysis equipment used in the home birth control 101 mircette 15mcg visa. Moreover, the need for the device cannot be clearly established until the procedure that makes its use possible is successfully performed. Colostomy (and other ostomy) bags and necessary accouterments required for attachment are covered as prosthetic devices. This coverage also includes irrigation and flushing equipment and other items and supplies directly related to ostomy care, whether the attachment of a bag is required. Accessories and/or supplies which are used directly with an enteral or parenteral device to achieve the therapeutic benefit of the prosthesis or to assure the proper functioning of the device may also be covered under the prosthetic device benefit subject to the additional guidelines in the Medicare National Coverage Determinations Manual. Covered items include catheters, filters, extension tubing, infusion bottles, pumps (either food or infusion), intravenous (I. Baby food and other regular grocery products that can be blenderized and used with the enteral system are not covered. The coverage of prosthetic devices includes replacement of and repairs to such devices as explained in subsection D. Payment may be made for the replacement of a prosthetic device that is an artificial limb, or replacement part of a device if the ordering physician determines that the replacement device or part is necessary because of any of the following: 1. An irreparable change in the condition of the device, or in a part of the device; or 3. The condition of the device, or the part of the device, requires repairs and the cost of such repairs would be more than 60 percent of the cost of a replacement device, or, as the case may be, of the part being replaced. It supersedes any rule that that provided a 5-year or other replacement rule with regard to prosthetic devices. Prostheses replacing the lens of an eye include post-surgical lenses customarily used during convalescence from eye surgery in which the lens of the eye was removed. In addition, permanent lenses are also covered when required by an individual lacking the organic lens of the eye because of surgical removal or congenital absence. Medicare does not cover cataract sunglasses obtained in addition to the regular (untinted) prosthetic lenses since the sunglasses duplicate the restoration of vision function performed by the regular prosthetic lenses. Refer to the Medicare Claims Processing Manual, Chapter 14, "Ambulatory Surgical Centers," for more information. However, when a denture or a portion of the denture is an integral part (built-in) of a covered prosthesis. Supplies, Repairs, Adjustments, and Replacement Supplies are covered that are necessary for the effective use of a prosthetic device. Necessary supplies, adjustments, repairs, and replacements are covered even when the device had been in use before the user enrolled in Part B of the program, so long as the device continues to be medically required. A brace includes rigid and semi-rigid devices which are used for the purpose of supporting a weak or deformed body member or restricting or eliminating motion in a diseased or injured part of the body. Elastic stockings, garter belts, and similar devices do not come within the scope of the definition of a brace. Stump stockings and harnesses (including replacements) are also covered when these appliances are essential to the effective use of the artificial limb. Adjustments, repairs and replacements are covered even when the item had been in use before the user enrolled in Part B of the program so long as the device continues to be medically required. These diabetic shoes are covered if the requirements as specified in this section concerning certification and prescription are fulfilled. In addition, this benefit provides for a pair of diabetic shoes even if only one foot suffers from diabetic foot disease. Each shoe is equally equipped so that the affected limb, as well as the remaining limb, is protected. Definitions the following items may be covered under the diabetic shoe benefit: 1. Coverage of Diabetic Shoes and Brace Orthopedic shoes, as stated in the Medicare Claims Processing Manual, Chapter 20, "Durable Medical Equipment, Surgical Dressings and Casts, Orthotics and Artificial Limbs, and Prosthetic Devices," generally are not covered. This exclusion does not apply to orthopedic shoes that are an integral part of a leg brace. In situations in which an individual qualifies for both diabetic shoes and a leg brace, these items are covered separately. Substitution of Modifications for Inserts An individual may substitute modification(s) of custom-molded or depth shoes instead of obtaining a pair(s) of inserts in any combination. Payment for the modification(s) may not exceed the limit set for the inserts for which the individual is entitled. The apex must be positioned behind the metatarsal heads and tapered off sharply to the front tip of the sole. The heel of the shoe tapers off in the back in order to cause the heel to strike in the middle of the heel; Roller Bottoms (Sole or Bar) - these are the same as rocker bottoms, but the heel is tapered from the apex to the front tip of the sole; Metatarsal Bars - An exterior bar is placed behind the metatarsal heads in order to remove pressure from the metatarsal heads. The bars are of various shapes, heights, and construction depending on the exact purpose; Wedges (Posting) - Wedges are either of hind foot, fore foot, or both and may be in the middle or to the side. The function is to shift or transfer weight bearing upon standing or during ambulation to the opposite side for added support, stabilization, equalized weight distribution, or balance; and Offset Heels - this is a heel flanged at its base either in the middle, to the side, or a combination, that is then extended upward to the shoe in order to stabilize extreme positions of the hind foot. Separate Inserts Inserts may be covered and dispensed independently of diabetic shoes if the supplier of the shoes verifies in writing that the patient has appropriate footwear into which the insert can be placed. This footwear must meet the definitions found above for depth shoes and custom-molded shoes. Furnishing Footwear the footwear must be fitted and furnished by a podiatrist or other qualified individual such as a pedorthist, an orthotist, or a prosthetist. The certifying physician may not furnish the diabetic shoes unless the certifying physician is the only qualified individual in the area. In addition to the following, see Pub 100-01, the Medicare General Information, Eligibility, and Entitlement Manual, Chapter 5, Definitions and Pub 3, the Medicare National Coverage Determinations Manual for specific services which may be covered when furnished by a dentist. If an otherwise noncovered procedure or service is performed by a dentist as incident to and as an integral part of a covered procedure or service performed by the dentist, the total service performed by the dentist on such an occasion is covered. However, when the reconstruction of a ridge is performed as a result of and at the same time as the surgical removal of a tumor (for other than dental purposes), the totality of surgical procedures is a covered service. The extraction of teeth to prepare the jaw for radiation treatment of neoplastic disease is also covered. This is an exception to the requirement that to be covered, a noncovered procedure or service performed by a dentist must be an incident to and an integral part of a covered procedure or service performed by the dentist. When an excluded service is the primary procedure involved, it is not covered, regardless of its complexity or difficulty. Similarly, an alveoplasty (the surgical improvement of the shape and condition of the alveolar process) and a frenectomy are excluded from coverage when either of these procedures is performed in connection with an excluded service. In a like manner, the removal of a torus palatinus (a bony protuberance of the hard palate) may be a covered service. However, with rare exception, this surgery is performed in connection with an excluded service, i. Dental splints used to treat a dental condition are excluded from coverage under 1862(a)(12) of the Act. On the other hand, if the treatment is determined to be a covered medical condition. Whether such services as the administration of anesthesia, diagnostic x-rays, and other related procedures are covered depends upon whether the primary procedure being performed by the dentist is itself covered. Thus, an x-ray taken in connection with the reduction of a fracture of the jaw or facial bone is covered.
Basic laboratory studies should focus on chemical abnormalities (glucose birth control pills kariva 15 mcg mircette amex, creatinine birth control pills grapefruit juice buy cheap mircette 15 mcg online, bilirubin birth control pills over the counter cvs buy 15mcg mircette fast delivery, serum sodium levels) and evidence of hypoxia birth control pills levonorgestrel generic mircette 15 mcg fast delivery. The two threatening and potentially easily reversible conditions-hypoxia and hypoglycemia-should be immediately investigated and treated. Delirium in the geriatric population can be the presenting manifestation of any acute illness, with an incidence of up to 10% on admission and up to 30% during an acute hospitalization. Causes of delirium in the elderly include pneumonia, urinary tract infection, myocardial infarction, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, traumatic injury, or virtually anything else that precipitates an acute hospitalization. This is even more of a problem after major surgery; nearly half of individuals (usually elderly) who suffer hip fractures develop delirium postoperatively. Persons at any stage of dementia may develop delirium during an acute illness or injury or with additional pharmaceutical agent(s). Additionally, an acute delirium may "unmask" an early underlying, undetected dementia. The management of delirium is first and foremost the identification and treatment of the acute underlying illness. Adequate hydration, oxygenation, good nursing care, and round the clock careful supervision are always the initial measures. Management of agitation and disruptive behavior is the most challenging aspect of care of the delirious patient. If no specific treatable problem is identified, physical restraint should be used as a last resort. Frequent reassurance and orientation from familiar persons or constant supervision from a nurse or hospital aide are preferable. Agitation with psychotic symptoms (hallucinations and delusions) can be treated with a neuroleptic such as low-dose haloperidol. Older patients are more likely to experience extrapyramidal side effects, however, so newer atypical antipsychotics such as risperidone may be used. Benzodiazepines have a rapid onset of action but may worsen confusion and sedation. Risk factors for the development of delirium tremens include a history of sustained drinking, prior withdrawal symptoms, age older than 30 years, and a concurrent medical illness. Withdrawal can coexist with or mimic other conditions, such as infection, intracranial bleeding, hepatic failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, or other drug overdose. In contrast to other causes of delirium, benzodiazepines are the drugs of choice in alcohol withdrawal. If symptoms have already developed, benzodiazepines can be given according to one of two strategies. Long-acting benzodiazepines such as diazepam or chlordiazepoxide can be given in high doses until withdrawal symptoms cease and then the slow clearance of the drug is allowed to prevent further withdrawal symptoms. Alternatively, shorter-acting agents such as lorazepam can be given as needed, only when the patient has symptoms. In either case, the key to successful management is initially aggressive upward titration of dosage until the patient is heavily sedated but responsive, followed by rapid downward titration as agitation decreases, usually over 48 to 72 hours. Supportive measures are also important, such as adequate hydration, replacement of electrolytes such as magnesium, and supplementation with thiamine and other B vitamins in malnourished, chronic alcoholics to prevent the development of Wernicke encephalopathy. In addition to the typical 6- to 8-Hz tremor, which can be violent or subtle, insomnia, anxiety, gastrointestinal upset, diaphoresis, and palpitations can occur. Tremor typically diminishes over 48-72 h, but anxiety, easy startling can persist for 2 weeks. Hallucinations are most often visual (eg, bugs, pink elephants) but can be auditory or tactile. Most dramatic and serious form of alcohol withdrawal, but occurs in only 5% of patients with withdrawal symptoms. Characterized by hallucinations, agitation, tremor, and sleeplessness, as well as signs of sympathetic hyperactivity: dilated pupils, low-grade fever, tachycardia, hypertension, diaphoresis, and hyperventilation. Delirium tremens is a serious condition with an in-hospital mortality of 5%-10%, usually from arrhythmias or infection, which is often unsuspected. Auditory hallucinations are unique to alcohol withdrawal and cannot be caused by a brain tumor. If the serum blood alcohol level is higher than the legal limits of intoxication, these symptoms cannot be alcohol withdrawal. If the patient also has hypertension, fever, and tachycardia, he has a 5%-10% chance of mortality. Auditory hallucinations can occur from a number of illicit agents or even brain tumors. The fall in serum blood alcohol level and not the absolute level may induce symptoms of withdrawal. An individual who abuses alcohol should first be given thiamine, before glucose is administered, to prevent acute Wernicke encephalopathy. Delirium requires urgent investigation to search for serious underlying systemic or metabolic causes. Frequent reassurance and orientation and constant observation are useful in managing the agitated delirious patient. Delirium tremens is the most severe and dramatic form of alcohol withdrawal, with abrupt onset from 2 to 4 days after cessation of drinking and sudden resolution several days later, and is associated with a mortality rate of 5%-10%. Therapy for alcohol withdrawal syndromes includes benzodiazepines, hydration, electrolyte replacement, and B vitamins to prevent Wernicke encephalopathy. She volunteers that her menopause occurred at age 51 years and that she is currently taking an estrogen pill along with a progestin pill each day. Pelvic examination shows a normal multiparous cervix, a normal-size uterus, and no adnexal masses. The patient states that she has regular Papanicolaou (Pap) smears, and that the last one performed 1 year ago was normal. Understand which health maintenance studies should be performed for a patient older than 65 years. Understand that preventive maintenance consists of immunizations, cancer screening, and screening for common diseases. Considerations the approach to health maintenance consists of three parts: (1) cancer screening, (2) immunizations, and (3) addressing common diseases for the particular patient group. For a 66-year-old woman, this includes annual mammography for breast cancer screening, colon cancer (annual stool for occult blood and either periodic colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy), tetanus booster every 10 years, pneumococcal vaccine, and yearly influenza immunization. Screening for hypercholesterolemia every 5 years up to age 75 years and fasting blood glucose levels every 3 years also are recommended. Cervical cancer screening can be stopped at age 65 or 70 years if all previous Pap smears have been normal. An optimal screening test has high sensitivity and specificity, is inexpensive, and is easy to perform. For example, the most common cause of death in a 16-year-old is motor vehicle accidents; hence, the teenage patient is well served by the physician encouraging her to wear seat belts and to avoid alcohol intoxication when driving. In contrast, a 56-year-old woman is most likely to die of cardiovascular disease, so the physician might focus on exercise and weight loss, and screen for hyperlipidemia. Additionally, physicians should seek to identify high-risk behaviors in a nonjudgmental fashion and promote lifestyle modification: Patients should be screened for tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drug use. They should be advised to quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men. Adjuvant pharmacologic agents are more successful in tobacco cessation, including bupropion and varenicline. Annual screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia is recommended for all sexually active women 25 years and younger. Obesity can lead to numerous complications including diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, menstrual irregularities, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea and respiratory difficulties, and hyperlipidemia.
References