




|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
Stanley J. Kogan, MD
Epifluorescence microscopy for acquisition of images and performance of morphometric analyses gastritis recovery 150mg zantac for sale. In-situ hybridization analyses that include all elements from acquisition and amplification of the gene of interest gastritis meals buy zantac 300mg on line, probe synthesis gastritis diet ÷óæîé buy generic zantac 150mg online, optimization of hybridization conditions gastritis diet ñåðèàëû generic 300mg zantac with amex, and performance of multigene analyses on a moderate scale gastritis or pancreatitis order zantac 300 mg. The University of Colorado Cancer Center Informatics Core gastritis diet 7-up generic 150 mg zantac fast delivery, located on the 6th Floor of Building 500 on the Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora, was established to work with researchers and clinicians to design, implement and maintain information technology applications that support the Cancer Center research enterprise. When the project is small or unanticipated, the hourly charge back is appropriate. Database design and development: analysis and development of table structures for appropriate security and performance. Data quality assurance: loading and querying databases to ensure timely and proper data collection. How to order services To order services, you will need to consult with either the Core Director or Core Manager by telephone or email. For an estimate of the time your project is likely to require, contact the Core Manager (See the contact panel on the right for phone and email information). Service Member NonMember $97 $78 Application Development & Support $84 Network Administration & Workstation Support: Complete administration of file and print servers $67 (backups, access, security). We are also voluntarily accredited by the Association for the Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care, International. Other services and discounts for collection of pilot data or junior investigators may be discussed with Dr. Operating procedures will be written up on an as needed basis for other protocols. To reveal accurate, cell-type specific expression profiles that otherwise might be obscured in mixed cell samples. You can focus the laser to capture single cells, or use a broader area to capture cell clusters. Laser Capture Prices the Laser Capture Core offers discounted prices to University of Colorado Cancer Center Members. The Pathology Core is responsible for processing tissues and the endpoint of this tissue processing is frequently an excellent histologic preparation. The animal tissues that we process generally are not an emergency and so those are queued, and depending on the workload in the Pathology Core, the queue may be a few days to a few weeks. Also, tissue microarrays depending on the number of tissues being evaluated may require 2 or 3 weeks. For research in the Core Laboratory, tissues are returned to the investigator, and investigators are responsible for interpreting their own histologic data. We have standard operating procedures for all components of the core laboratories and these are available on request. Finally, the Southwest Oncology Group Solid Tumor Bank is tracked in real time on a web site that maintains an inventory of specimens accessioned into the core. New Users: You will need to be trained to use the microscope(s) and related instruments. We are especially interested in working with grant applicants to have support funds requested on grant applications for projects that will involve this facility. Cancellation policy: Reservations cancelled less than 24 hours in advance will be billed unless someone else signs up. The shop is staffed by one machinist 24 hours/week although there are currently no routine hours of operation. Turn-around-time is dictated by the complexity of the project requested and the current work load in the shop. Work is generally dealt with on a first-come-first served basis, however, the shop staff does strive to meet the requirements of the person requesting the work and occasionally is able to accelerate the completion of a particular project. As exemplified over the last years, the Core has continued to develop diagnostic tools to predict disease and monitor the progress and treatment of disease. Any minor scheduling conflicts will be handled by the Core Director in close collaboration with the affected users. User fees are based on 12-month cost studies conducted and reviewed by University of Colorado. Quantification of 15-F2t-isoprostane in human urine and plasma using highperformance liquid chromatography  atmospheric pressure chemical ionizationtandem mass spectrometry. Analysis of 25 underivatized amino acids in human plasma using ion-pairing reversed-phase liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. However, it must be noted that due to the inherent problem of ion suppression in the electrospray source use of this data for semi-quantitative comparison may be limited. International hands-on and web-based proteomics, metabolomics, genomics, and informatics training program b. This includes the date of service, customer and technician names, type and number of analyses provided, discount or special pricing information, and miscellaneous information. At the end of each month this information is used to create invoices which are emailed/mailed to individual investigators. The facility has been established to offer researchers with small molecule synthesis and drug metabolism expertise. Wempe, PhD a) How is the quality of your measurements evaluated  quality control? University of Colorado Cancer Center Metabolomics Core Contact: Natalie Serkova, PhD, Director Associate Professor, Dept. Natalie Serkova Metabolomics, one of the "omic" sciences in systems biology, is the global assessment and validation of endogenous small-molecule biochemicals (metabolites) within a biologic system. This Core provides an array of assays over a broad range of species (rat, mouse, human, sheep) and tissue types (fat, muscle, liver), for multiple investigators studying the clinical consequences of nutrition-related disorders. Thus, the Metabolic Core of the Nutrition Center achieves an overall cost-savings and provides more important investigator time in their own laboratories for their own experiments. The Core measures activity and phosphorylation state (tyrosine and/or serine) where appropriate. We provide experimental support and technical advice regarding measurement of insulin sensitivity in vivo (insulin clamps) and end organ-based metabolism. This section of the lab includes a general work area, surgery set-up, lamps, Harvard infusion pumps and metabolic chamber. The extent of support provided by core staff will depend largely on the type of extramural support available for the project, with priority given to those projects for which funds for personnel expenses are limited (pilot/exploratory studies, career development awards, etc). Detailed plans for prioritizing samples are based on the source of funding and the type of award, as follows: 1. Members of the research base with non-federal funding for nutrition/obesity projects. Members of the research base with non-federal funding for non nutrition/obesity projects. The mechanisms for monitoring budgetary overlap of current funded projects and the Metabolic Core lab are handled by Dr. Investigators receive assistance in determining the most appropriate assay for a specific research study. In helping each investigator to decide on which assay is best to use, the following issues are addressed: 1) appropriateness of assay to the study, 2) appropriateness of a given assay to the scientific question, and 3) cost. The Mass Spectrometry/Proteomics core is operated by the Program in Biomolecular Structure and the Colorado Cancer Center. Access to appropriate technologies is being provided through collaborative agreements with the Gene Expression Core of the Cancer Center. For high-volume needs (over 96 or multiples of 96 reactions at a time) sequencing is outsourced to a commercial sequencing laboratory. This is accomplished in cooperation with the Biophysics Laboratories, a user facility operated by the Program in Biomolecular Structure at the University of Colorado Denver (directed by R. Instrumentation is available for the structural characterization of proteins and nucleic acids by chemical and thermodynamic methods. This instrument, equipped with three lasers and capable of scanning gels, blots, storage phosphor screens, tissue sections, and multi-well plates is located in the area occupied by the Biomolecular Structure Program and easily accessible to Center members. For instructions on preparing skin samples for histological processing, please see below: Harvesting skin samples for histological analysis 1. Samples for paraffin embedding General: Make sure that the volume of formalin used for fixing the tissue equals >10x the volume of the sample. If you a re us ing ba ck s kin, t ake t he biopsy f rom t he m iddle of t he b ack (on t op of t he s pine) m idway b etween t he h ead a nd t ail. Unless otherwise indicated, the biopsy will be sectioned along the long axis of the rectangle. If sectioned this way, your sections will provide a good view of the interfollicular epidermis as well as the hair follicles. Place your rectangular piece of skin flat on a piece of Whatman filter paper or unlined index card (dermis side down). Ear skin: Remove the entire ear of an adult mouse and trim the biopsy into a rectangle, such that the long axis of the rectangle is perpendicular to the head of the mouse. If possible, the cutting edge should be perpendicular to the skin of the mouse, such that your section will contain the most superficial as well as the most basal part of the tumor. Since the sample will be sectioned from the bottom of the cryomold, your sample should be placed in the cryomold accordingly. The following services are available: Paraffin histology Processing and embedding (per sample) One unstained slide (per slide) H&E staining (per slide) Frozen section histology First unstained slide (per block) Additional unstained slides (per slide) H&E or toludine blue staining (per slide) * Skin Diseases Research Core Center Member Price Regular price $12. To ensure that investigators receive high quality skin sections, each Core user will receive detailed instructions on harvesting and fixing skin/epithelial samples for histology. Reagents will be maintained and stored as specified by the manufacturer and disposed of on expiration. In addition, equipment will be maintained and serviced on a regular basis by a certified technician. Specifically, the tissue processor will be cleaned daily, alcohols will be rotated every 100 blocks, all reagents will be changed every 400 blocks, and preventive maintenance will be performed annually. We maintain a database in which all service requests (and their costs) are entered. Each month, we generate a billing statement for each Core user, which includes all rendered services and their cost. Services are paid for by Interdepartmental Invoices, and the funds are deposited in our service center account. Tissue Procurement Shared Core Service the Tissue Procurement Core provides University of Colorado Cancer Center members and other funded researchers with well-characterized human tumors and materials derived from human tumors for research in human cancer. Peptide and Protein Chemistry Core Contacts: Robert Hodges, PhD Director 303-724-3268 fax: 303-724-3249 12801 E. The Peptide and Protein Chemistry core personnel help users choose and design experiments using appropriate chemistry/instrumentation, to obtain the necessary data, and interpret the results. The mission of the Pharmacology Core is to assist in the prospective design of studies to assess drug exposure in biological systems, to measure drug levels using validated analytical assays, and to analyze, model and interpret the results. We offer members discounted fees for service, which are calculated either per sample or on an hourly basis. For the quantitation of an analyte in a submitted sample, prices depend on whether we have a validated assay for that analyte and the number of samples submitted. For example, if a study includes a total of 200 samples but are shipped to us and expected to be analyzed in groups of 20 for data reporting, the batch size is 20. We provide more product than measurements and most of the evaluation of that is done by the end users since each it specific for the individual lab and project. The longer times are for production of protein via baculovirus and we have purchased new equipment and hired a part time technician recently in order to decrease the waiting time on these projects. The Lab Manager fills out the invoices and the Cancer Center administration does the billing. Cancer Center members have access to proteomics labs on two campuses: · · Anschutz Medical Campus Boulder Campus -. The Facility has access to several analytical technologies thereby allowing investigators to adopt multiple strategies and to independently verify their findings. The Facility also provides training in proteomics analysis and experimental design Facility Fees A charge is applied to all users of the resource to offset, the running costs associated with maintaining this facility. Protocol Development and Quality Control A new imaging technique looks promising for your clinical study. Age, organ type, exposure duration and frequency are just some of the factors that can influence health risks. Statistical training and mentoring opportunities include short courses, lectures and online tutorials. Assistance will be provided through consulting, training, communication and research collaboration. We will employ the most appropriate methods combined with graphical summaries to aid interpretation. Services related to study design for grants get priority, but we try to meet with investigators within a few days of receiving requests. T his c an be i mportant f or t he characterization of translational models of nervous system disorders including stroke, epilepsy, head trauma, neurodegenerative, psychiatric, genetic and developmental disorders. Raol, PhD (Director) is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine. At the same time, the Laboratory allows faculty the freedom from duplicating instrumentation and other resources that are used only peripherally. Restarting the instrument may take several days before it would be ready for analytical use. The Hitachi uses a very small aliquot of the sample (20 microliters for most analysis) and has detection limits in the low parts-per-billion range. Sample prep is time consuming, the instruments must be reconfigured, and either result in poor detection limits. To address these shortcomings, Leeman Labs created their dedicated mercury analyzer.
Therefore all users of the facility are required to submit a short annual report on their research efforts in the core gastritis symptoms how long do they last purchase zantac 150 mg free shipping. This report should summarize the results obtained chronic gastritis no h pylori effective zantac 150 mg, all grants that are dependent on the core facility and any publications arising from use of the facility gastritis symptoms in the morning buy 300mg zantac free shipping. The only instrumental techniques attempted are routine ones or are those for which the user has received relevent instruction gastritis fever 150 mg zantac amex. In all such cases gastritis diet ëóííûé purchase zantac 150mg line, prior advice should be sought with regard to these special samples gastritis diet what to eat for breakfast lunch and dinner generic zantac 150mg on-line, but permission does not absolve any user from responsibility for harm their samples may cause the Center. Alternatively, external standards contained within a capillary can be included in the sample. The effects of sample on performance can be directly inferred from the data from these controls. More complex experiments, turnaround is between 1 - 2 weeks c) Who documents the data provided and signs off on the data? The Financial Aspects of the Core are maintained by the Program in Structural Biology and the University of Colorado Cancer Center and are thoroughly reviewed on an annual basis. Training the Biophysics Core Staff are available to train users on each of the instruments located in the core. Our ex tensive ex perience i ntegrating research with routine c linical p ractice, specimen co llection an d storage, and information technology has enabled us to maximize efficiency and accuracy in all aspect of our biorepository m anagement. The services provided by the biorepository core consist of assistance in the procurement, storage, processing and distribution of pa tient bi ospecimens for r esearch us. T herefore, qua lity i s opt imized b y 1) proper collection and handling techniques, 2) assuring integrity of the data, and 3) assuring p roper usage o f bi ospecimens. At p oints w here s amples ar e handed ove r t o ot her p ersons, s uch a s t he t ime it i s transferred from clinic to processing l ab, w e h ave s ign-offs for t he p erson w ho h andled t he s ample up t o that poi nt. The da ta o n t he t racking f orm i s e ntered i nto t he bi orepository database b y a biorepository technician and r eceives a finalizing signature b y the core d irector o r co -director i f e verything i s i n or der. If pr oblems a re f ound, personnel that handled the specimen will be contacted for clarification. If t he v alues ar e within the acceptable range, samples are considered adequate and may be released for distribution. The i nvestigator w ill t hen submit to the Medical Director a short (2-3 pages) proposal as to the nature and importance of the study, the need for biorepository samples, and the likelihood for success. Pulls and processing requests must be preapproved (see above) and then may take up to two weeks depending on how much labor is required. A c ost pe r s pecimen a nd/or hour ly charge r ate a pplies f or ou r s ervices (see attached cost sheet). F or on-campus investigators, requests for services must be accompanied b y a s peed t ype. Contacts: University of Colorado Cancer Center Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Shared Core Service Anna E. Services · · · · · Consultation on study design (clinical and basic science, including gene expression arrays and proteomics experiments) Consultation on sample size and power Development of data collection, storage, and quality control procedures (basic science and clinical studies, protocol review and monitoring) Data analysis, including genomic and proteomic data Collaboration on manuscript and oral presentation preparation, and grant proposal development Rather than charging users for services, we ask Cancer Center investigators to write in funding for biostatistics and bioinformatics support on grants and contracts, then to acknowledge the Core in any publications. Please involve us during the design phase to we can help make sure your project is successful. We will help you put together a basic scope of work and general timeline and identify key collaborators to include. This core also performs lymphoblast immortalization for bio-banking and genomic analysis. This core is designed not only to advance ongoing in-vitro studies but to assist investigators without experience in the area with the adoption of in-vitro approaches. In addition, this core provides the technology and assistance to analyze brain tissue with neuroanatomical and cell labeling techniques as well as with approaches of subcellular fractionation and biochemistry. If you are interested in any of the below listed Cell Culture services for your research please contact Dr. This consulting service is designed primarily for those investigators with little or no experience with in-vitro models or neuronal/glial cultures. In addition, the core can grow newly acquired cell lines for investigators and bank them for later use. Species African green monkey Drosophila Hamster Cell Type male kidney Schneider Chinese hamster ovary cervical cancer glioblastoma hepatocell. For experimentation with very limited scope or pilot studies, the Core prepares cultures of rat or mouse cortical explants or dissociated cells. Training also may include the establishment of other neuron populations (those from hippocampus, cerebellum, olfactory bulb, peripheral ganglia and others) or of glial cell types. Sladek is available to advise investigators on the optimal neuroanatomical and -histological techniques to be used for examining the brains of experimental animals and on the interpretation of results. This may involve the application of double-labeling techniques, with the use of permanent dyes and chromagens, such as diaminobenzidine, nickel-enhanced diaminobenzidine, Vector Red, Vector Blue, and others, or fluorescent conjugated markers, such as fluorescein, rhodamine, Cy2, Cy3, Cy5, and AlexaFluors. The adherence tracking devices, except for EncoreAnywhere and Restraxx, are provided to the investigator with technical support, including set-up, data downloading, data verification, and delivery of complete data sets. For example, with standardized questionnaires we develop electronic surveys if possible, with multiple checks for accurate scoring. For example, adherence monitoring involves dispensing and receiving/downloading monitoring devices in real time as Investigators are collecting data from subjects. The focus here is specialized immunologic assays relevant to immunity and inflammation and not clinical diagnostic assays. Other quality control measures include but are not limited to annual calibration and preventative maintenance, safety inspections and upgrading of equipment to meet the highest standards possible. For example, peripheral blood cell separation, bronchoalveolar lavage cell isolation and induced sputum cell isolation and processing are conducted the day that they are available. Once harvested the cells or supernatant may be frozen for future batch processing. However, if faster turnaround is needed, our Core lab is happy to work with the investigator. Their roles include: · Clinical Expertise · Intensive Care/Step-Down Care · Medical /Surgical Care · Pediatric Care · Perinatal Care · Healthy Volunteer Care · · · · Feasibility Assessments for Study Implementation/Protocol Oversight Consultation Services/Study Design and Consent Development Investigator and Study Coordinator Support Data and Sample Collection Note: Specific sites have screening, enrollment, and participation follow up. Specialized Research Services Please note that all four sites are well-networked and your protocol needs may be met for patients enrolled at any of the sites (site availability in parentheses). Each site has operating procedure manuals specific to that institution f) How will you track billing and financial aspects of your core? Billing and the financial aspects of the protocol are tracked by the administrative personnel at each specific site. Studies in this category are generally funded by private companies or corporations. The study agent will be stored and prepared for administration by the National 0 Jewish Health Research Pharmacy Service. We follow Nursing Policies and Procedures f) How will you track billing and financial aspects of your core? Training for new procedures or techniques will be provided by the principal investigator. Please see the attached link for more detailed information regarding this subject. This fee is in addition to specimen processing, handling, storage and shipment fees d) Research Office Start Up Fee: the Research Office Start Up fee is a flat fee that covers the costs associated with opening a clinical trial through the University of Colorado. It covers the costs associated with budget and contract preparation, negotiation, finalization and implementation. These units are used when the research procedures cannot be carried out in the outpatient setting or during out-patient clinic hours. Items Invoiced to the Sponsor: Regulatory Affairs Fees $1800 $125 Administrative Category Regulatory Continuing Review a Regulatory Amendment B Frequency Annually Per Amendment A. This fee also includes yearly regulatory maintenance of the study such as safety reporting, adverse event reporting and other protocol related duties. Note: the above regulatory fees are subject to a late charge for payments received later than 60 days of Invoice date, $100 will be applied to the balance for each month payment is not received. University of Colorado Hospital pricing Every protocol that involves the use of University of Colorado facilities is sent to the applicable department for review and pricing. The primary applicant audience includes those having earned a health sciences graduate degree or a health care professional degree. These three fields of clinical science are important areas of study for translational research activities in the evolving health care environment. Graduates of our program are highly qualified and well-trained Clinician Scientists who will be nationally competitive for grant funding and career advancement in the health sciences. She is Associate Professor, Colorado School of Public Health and the College of Nursing and Associate Director, Clinical Science Graduate Program. Please visit our links, indexed at left, to find out more about our research and clinical activities. Clinical Trials Organization Clinical Services the Clinical Trials Organization serves the children and primary care providers of the Rocky Mountain region by translating cutting-edge research into clinical care. Internationally recognized leaders in pediatric health care research are involved in a variety of groundbreaking studies working towards advancements in pediatric health care. The Clinical Trials Organization conducts studies throughout all arenas of pediatric medicine and exists to advance the health and welfare of children through the careful coordination of state-of-the-art pediatric clinical research. There is also a dark room for photolithography, a general optics and development lab, office space, and conference room. Use of the facility should be reserved in advance and the use of any particular item is subject to availability. If equipment is utilized for 1 full day (8 hours), an automatic discount of 20% will be extended to the user. Agreement For ongoing, long-term grants or departmental support requiring a variety of services. For non-affiliated organizations, the hourly rate will be negotiated, depending on scope of work, plus travel costs, if incurred. We are happy to share our expertise with the University community by addressing quick biostatistical questions or providing short consultations at no charge. Certified genetic counselors are on staff to aid in test interpretation and answer your questions. We provide the most up-to-date information on chromosome abnormalities and microarray findings. Our certified cytogenetic technologists analyze and document their findings in a written report. How can disparities in health and health care for vulnerable populations be reduced? Our investigators currently consult to and collaborate with on a variety of investigators and agencies on grant and contract-funded projects. The Program encourages students to engage in collaborative projects and provides shared mentoring that can include faculty from outside the Program. Additional procedures Tissue culture Initiation, maintenance, harvest, and freezing of cell cultures for cytogenetic purposes. Due to sensitivity limitations of our current instrumentation, we need unique sequence probes larger than 2. Yes, we have many contracts with pharmaceutical and biotech companies in the last 8 years. The Cancer Center requires annual cost study, which is submitted and approved by the University officials. The Core generate an invoice and the Cancer Center Administrative Office assists with all financial issues. These awards should be used to generate sufficient preliminary data to enable investigators to acquire external funding in the future. Requests are submitted online and monthly billing is performed through the same portal to preapproved account holders and speed types. Additionally, there is continuous researcher feedback of islet viability and quality. Barbara Davis Center  Page 1 of 7 c) Who documents the data provided and signs off on the data? Internal quality control of assays with standard samples with results within set ranges and Shewhart plots. Barbara Davis Center  Page 2 of 7 c) Who documents the data provided and signs off on the data? Histology Core the core performs standard histopathological analyses based on light microscopy and immunohistochemistry. The quality of our data is measured by using control tissues to ensure that proper staining has occurred. Stains and alcohol solutions are replaced on a regular basis to ensure that stains are of the highest quality. The histology core has a standard operating procedure manual that is stored in the facility. Additionally we have operating manuals on hand for the Leica tissue processor, microtome, and cryotome. Customers place their order via the website and upon submitting their order they are quoted the price. Monthly accounting reports are created the first of the month and are submitted for billing. Lymphocytes are a fundamental requirement for a wide variety of studies addressing the role of T and B cells in pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Bioplex Instrument calibration is done monthly using a kit containing beads to standardize daily signal output and ensure unit-to unit reproducibility of the reader.
Smartphone-based monitors to record heart rhythms and detect when atrial fibrillation occurs gastritis pathophysiology proven zantac 150 mg. A lot of bleeding after a fall or injury or easy bruising or bleeding may mean that your blood is too thin gastritis diet íîâàÿ order zantac 300 mg visa. Excessive bleeding is bleeding that will not stop after you apply pressure to a wound for 10 minutes gastritis diet ìóëüòôèëüìû buy discount zantac 150mg line. The monitor records heart activity around the clock and can detect abnormal heart rhythms gastritis snacks 150 mg zantac, which are recorded and provided to your physician for review in making a diagnosis chronic gastritis sydney classification discount 300 mg zantac mastercard. Heart flutter can’t always be detected separately from other types of supraventricular tachycardia gastritis upper back pain purchase zantac 150mg on line, such as atrial fibrillation, by an electrocardiogram or a heart monitor alone. In such cases, you’ll be asked to wear a heart monitor that records your electrocardiogram continuously. If your child is a newborn, follow safe sleep recommendations to help reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome. Overactive or underactive thyroid gland, caused by too much or too little thyroid hormone in the body. Leaking or narrowed heart valves make the heart work too hard and can lead to heart failure. Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can greatly lower your risk of stroke or damage to other organs caused by blood clots. Your doctor will determine if a blood-thinning medication is appropriate for you, depending on your type of arrhythmia and your risk of blood clots. These types of arrhythmia seem to cause sudden episodes of palpitations that begin and end abruptly. These are dependent on the specific rhythm abnormality and can range from blood tests to lung evaluations and sleep studies to echocardiograms and electrophysiologic testing. These abnormal electrical short circuits occur at a rate much faster than the sinus node rate, producing a heart rate of 100 or more beats per minute. Symptoms of atrial fibrillation may include heart palpitations, lightheadedness, chest tightness, shortness of breath and fainting. If an arrhythmia is life-threatening, such as ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation, your doctor may recommend an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. If the device detects an abnormal heartbeat, it will deliver an electric shock to the heart to restore a normal heart rhythm. Arrhythmia surgery may also be recommended if you need surgery, such as valve surgery or bypass surgery, to correct other forms of heart disease. Electrical cardioversion Patients with persistent arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, may not be able to achieve a normal heart rhythm with drug therapy alone. Electrical cardioversion delivers an electrical shock to your chest wall, which synchronizes the heart and allows the normal rhythm to restart. In times of stress, the body generates cortisol and adrenaline, causing an increased heart rate in addition to other changes in the body. Ingestion of a variety of drugs can also cause the heart to race, including caffeine, alcohol, and over-the-counter cold medications that include chemicals such as phenylephrine and pseudoephedrine. These compounds are metabolized by the body and act like an adrenaline stimulus to the heart. Illegal drugs such as methamphetamine and cocaine can also cause a sinus tachycardia. Rapid heart rates can originate from either the atrium or the ventricle, but rhythms from the ventricle are more often life threatening. Electrophysiology study, is a procedure in which catheters to record the heart’s electrical activity are inserted into the upper leg and guided into the heart. Medications, pacing through the catheters and the recording of the heart’s electrical signals help doctors identify cardiac arrhythmias. A heart pacemaker is implanted to set the heart rate of the bottom chambers to correct the heart arrhythmia. Certain over-the-counter cough and cold medicines and certain prescription drugs may contribute to arrhythmia development. These portable defibrillators, which can deliver an electric shock that may restart heartbeats, are available in an increasing number of places, such as in airplanes, police cars and shopping malls. That means uninterrupted chest compressions at a rate of 100 to 120 a minute until paramedics arrive. Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure. Most melanomas start as new spots Most melanomas come in the form of a new spot on the skin, not changes to an existing mole. Your healthcare provider may advise you to not have caffeine, alcohol, or any other things that may be causing the problem. If your provider thinks that stress is a cause, they may suggest meditation, stress-management classes, an exercise program, or psychotherapy to ease stress. However, fat, cholesterol and calcium can build plaques in the arteries, causing coronary artery disease. If the episode is a recurrent problem, the diagnosis is known, and the rhythm disturbance resolves itself, then a less urgent call to the primary care professional is warranted. Heart blocks involving the ventricle may be asymptomatic and of little consequence except to point to underlying heart or lung disease. They may become lightheaded, weak, have shortness of breath, and describe a feeling of fullness in the throat. Non-surgical ablation, used for many types of arrhythmias, is performed in a special lab called the electrophysiology laboratory. Because other heart disorders can increase your risk of developing arrhythmias, lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising and not smoking may be recommended. Bradycardias, or abnormally slow heartbeats, may be caused by conditions such as sick sinus syndrome, in which the heart’s sinus node does not send electrical impulses through the heart properly. The heart’s electrical pathways may also be blocked by damaged heart muscle, such as after a myocardial infarction. The heart’s upper chambers, or atria, serve as receptacles for blood, while the lower chambers, or ventricles, pump blood in and out of the heart. The heartbeat is created by an electrical impulse originating in the right atrium. A pacemaker increases the heart rate when required and ensures that electrical impulses from the top chamber are transmitted to the bottom chamber. Doctors insert a catheter into the upper leg to reach the heart and record electrical activity. Brugada syndrome is a related genetic condition of a heart’s abnormal electrical system. Symptoms may also include lightheadedness, sensations that the heart is racing, chest tightness and shortness of breath. Atrial tachycardia can’t always be detected separate from other types of supraventricular tachycardia by an electrocardiogram or a heart monitor alone. If the abnormal heart rhythm tends to happen mostly during exercise, the doctor may order an exercise stress test. Often though, it is due to the side effects of medications used to control high blood pressure. Side effects of beta blocker and certain calcium channel blocker drugs include a slowing of the heart rate. This can occur during a heart attack, in which the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply the heart with blood, are blocked. Lack of oxygen can occur when the lungs are unable to extract oxygen from the air. Significant anemia, or low red blood cell count, decreases the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood and may prevent adequate oxygen delivery. Rapid heart rates may be due to "wiring" problems with the electrical pathways in the heart. After arrhythmia has been treated with medication, a surgical procedure, or both, follow-up care helps patients adhere to their post-treatment guidelines and ensure that recovery goes smoothly. Nurse practitioners with specialized training in electrophysiology and arrhythmias are available to provide monitoring and support and answer any questions patients may have. In some instances, abnormal or irregular heart rhythms can cause the heart to stop beating. If you notice your heart beating out of its typical rhythm, you should talk to a doctor. This can feel as if your heart is beating with extra and/or fast heartbeats, or your heart seems to skip a beat. Electronic devices such as implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and pacemakers may be used to help maintain a normal heart rhythm. Getting an implantable or wearable cardioverter defibrillator to prevent sudden cardiac arrest from arrhythmia if you have heart disease. An excess of thyroid hormone can cause the heart to beat faster, and thyroid deficiency can slow your heart rate. It can also occur suddenly as a result of exertion or stress, imbalances in the blood, medicines, or problems with electrical signals in the heart. Typically, an arrhythmia is set off by a trigger, and the irregular heartbeat can continue if there is a problem in the heart. Without the ventricles pumping blood to the body, sudden cardiac arrest and death can occur within a few minutes. In some cases, the complications that can develop with arrhythmia also differ by sex. Ventricular tachycardia is a fast, regular beating of the ventricles that may last for only a few seconds or for much longer. These can make the heart beat faster than it should, or beat with an irregular or disordered rhythm. If you feel a persistent irregular heartbeat, your doctor can help diagnose the type of arrhythmia and monitor your heart. They may refer you to an Electrophysiology lab, where they can test, diagnose and treat arrhythmias. Atrial flutter occurs when rapidly fired signals cause the muscles in the upper chambers of the heart to contract quickly, leading to a very fast and steady heartbeat. Your heart rhythm is normally controlled by a natural pacemaker located in the right atrium. These impulses cause the atria muscles to contract and pump blood into the ventricles. This type of rapid heartbeat is severely abnormal and causes the ventricles to quiver ineffectively. Share your experiences and connect with others who are dealing with the same struggles of living with an arrhythmia. Additionally, some arrhythmias can be treated with simple home exercises called vagal maneuvers to help control heart rate. Some arrhythmias, including heartbeats that are too slow, can be treated with a pacemaker. Beta-blockers work by slowing the heart rate and decreasing the effects of adrenaline on the heart, thereby lowering blood pressure. Place the tips of your index and middle fingers on the inner wrist of your other arm, just below the base of your thumb. Or, place the tips of your index and middle fingers on your lower neck, on either side of your windpipe. Your ongoing care may focus on reducing the chance that you will have another episode or a complication. Ask about heart-healthy lifestyle changes that you can make to keep your arrhythmia from happening again or getting worse. To diagnose arrhythmia, your doctor will ask you about your symptoms, your medical history, and any signs of arrhythmia in your family. This can cause "short circuits" making the heart speed up and beat 150 beats a minute or more. This may occur if the cells of the upper chamber fail to generate an electrical impulse or if the electrical signals to the ventricle are blocked. However, some heart arrhythmias may cause bothersome — sometimes even life-threatening — signs and symptoms. Current patients may reach one of our outstanding arrhythmia nurse specialists during clinic hours at. When choosing a doctor, it’s important to consider the doctor’s clinical training, experience and expertise in a specialized area that matches your health care needs. At Stanford, your doctor plays a lead role in every aspect of your care, from evaluation to treatment and follow-up. Our expertise in interpreting imaging and other test results provides detailed information to help us determine your treatment options. For example, a 2010 working group on screening for sudden cardiac death in the young aimed to help determine whether screening can help prevent deaths from arrhythmia reliably and economically. Keep a record of changes in your pulse rate, and share this information with your doctor. Other increased risks are of embolization and stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death. In Europe and North America, as of 2014, atrial fibrillation affects about 2% to 3% of the population. Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter resulted in 112,000 deaths in 2013, up from 29,000 in 1990. Sudden cardiac death is the cause of about half of deaths due to cardiovascular disease and about 15% of all deaths globally. Freshly oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the top left chamber through four pulmonary veins, one from each major segment of the lungs. Tachyarrhythmias are the result of spontaneous action potentials arise from cardiac muscle cells.
Syndromes

When any of these proteins is impaired gastritis symptoms light headed zantac 300mg without a prescription, the autosomal recessive disorder maple syrup urine disease may result (see Chapter 212) gastritis diet under 1000 generic 150mg zantac fast delivery. Clarification of this pathophysiology led to an understanding of the mechanisms by which lysosomal enzymes are polarized to remain in lysosomes gastritis diet íùã buy 150mg zantac free shipping. These extracellular enzymes were found to lack mannose 6-phosphate residues gastritis vagus nerve buy zantac 150mg low cost, and this observation led to an understanding of the post-translational mechanisms by which enzymes are both directed to the lysosome and recaptured into endosomes by adding phosphorylated mannose to their protein structure gastritis diet àâèòî order 300mg zantac. Inborn errors affecting single enzymes in the degradative pathway for mucopolysaccharides and gangliosides helped define the steps required for the breakdown of these complex macromolecules gastritis red wine 300mg zantac sale. Catabolic reactions include breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by peroxisomal catalase, a traditional protein of the peroxisome; polyamine oxidation; purine breakdown; ethanol oxidation; phytanic acid hydroxylation; and pipecolic acid degradation. A major function of the peroxisome is beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids, those longer than 24 carbons. An understanding of the importance of a number of reactions that occur in the peroxisome has come from identifying patients with either defects in individual biochemical pathways or lack of peroxisomes. The targeting signal for peroxisomal proteins may lie in their carboxyl terminal end, and mutations in the alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase have resulted in mistargeting of this enzyme to mitochondria with consequent familial hyperoxaluria (see Chapter 205). A large number of inborn errors involve proteins that circulate in blood (see class 3 of Table 32-1). Proteins involved in oxygen transport, coagulation, and immunity are detailed in other chapters, but the pathophysiologic mechanisms and genetic approaches of screening, diagnosis, and intervention to prevent an expected outcome make them appropriate to consider here as inborn errors of metabolism. The enzymes involved in post-translational processing of these proteins may also cause these syndromes. Inborn errors of matrix proteins are exemplified by disorders of collagen metabolism. A traditional compilation of pathophysiologic mechanisms producing inherited diseases. Curiel Gene therapy is a relatively new method of therapeutic intervention targeted at the level of cellular gene expression. These nucleic acids may be genes, portions of genes, oligonucleotides, or ribonucleic acid. Gene therapy was initially conceptualized as a method to treat acquired genetic diseases. Replacing or augmenting a defective gene by delivering its wild-type counterpart thus offers a potential means to rectify definitively the pathogenic basis of the disease state. If the logic of genetic intervention thus exists, clearly defined endpoints of the therapy intervention must exist and an alternate, effective therapy for the targeted disease must not exist. After delivery, the introduced gene must be expressed at an appropriate level for the desired effect and for sufficient time for this effect to be achieved. Additionally, the delivery and expression of the therapeutic gene must be safe for the target cell and, by extension, for the individual being treated. From a conceptual standpoint, it must be recognized that these goals are all interrelated and, furthermore, that all of them must be addressed to rationally implement any gene therapy strategy. In practice, gene therapy implementation in human clinical trials has used two distinct strategies to meet the aforementioned criteria. This ex vivo strategy has been applied in those contexts in which the technical capacity exists to readily harvest and manipulate the relevant target cell. Despite these advantages, this method may be limited to very select settings in which target cells can be propagated ex vivo; at present, this is viable for a very limited set of tissue types. The in vivo approach in theory overcomes this limitation of target tissue accessibility. Delivery in vivo, however, is fraught with considerably greater complexities than the ex vivo approach. Thus, the gene transfer vector in the direct-delivery approach must achieve delivery in the context of significant host barriers, including humoral, reticuloendothelial, and immunologic factors. The retrovirus requires proliferative target cells to mediate effective gene transfer. An additional obstacle for retroviruses is the high susceptibility of the virus particle to humoral factors that ablate its gene-transfer capacity. The development of such a vector system would have two very important consequences for potential gene therapy strategies: (1) it Figure 33-1 Methods to modify the adenoviral cellular tropism. Viral tropism is determined by the fiber and its recognition region in the terminus, or "knob" (dotted circle). Immunologic targeting involves the attachment of molecular conjugates incorporating antibodies against the fiber knob and ligands specific for cognate receptors in target cells. Replication-deficient adenoviruses can be genetically complemented in vivo in cells co-infected with a second vector that encodes the deleted replication-enabling molecules. Tissue- or tumor-specific promoters can regulate the expression of these proteins, thus limiting the occurrence of viral replication to the target tissue. Progeny virus leads to infection of neighboring cells, increased local viral inoculum, and augmentation of therapeutic gene expression. Their design overcomes the potential safety hazards associated with viral gene sequences contained in the viral vectors. Despite this systemic stability, delivery is at present non-specific, because the liposomes lack any mechanism to achieve targeting. This goal is the principal logic behind the design of molecular conjugate vectors. Extensive characterization of the virus has made possible the introduction of numerous modifications in its genome and biochemical composition that overcome some of its limitations. Initial strategies to accomplish gene therapy were designed for inherited genetic disorders. Specific strategies to treat a variety of other disorders are being developed, but the central problem of delivering genes to target cells has limited more general use of these methods for inherited genetic disorders. Gene therapy is also rational in the context of acquired genetic disorders and thus has been used to target cancer; the overwhelming number of human gene therapy protocols in trial have been for cancer therapy. Specific strategies include the following: (1) a wild-type tumor suppressor gene for recessive oncogene mutations, (2) inhibitory gene constructs for dysregulated or overexpressed dominant oncogenes, (3) toxin genes selectively delivered to cancer cells to eradicate them, and (4) immunomodulatory genes to increase the immunogenicity of tumors (Table 33-2). Gene transfer may represent a therapeutic strategy applicable to contexts outside of genetic diseases. Novel, chimeric vector systems may be engineered to capitalize on favorable aspects of available gene therapy vectors. Ellen Magenis Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their behavior as they relate to transmission of the genetic material from parent to offspring. The number of chromosomes found in somatic cells is constant and is termed the diploid (2n) number. To maintain this regularity, two types of cell division occur: mitosis, which is the cell division occurring in somatic tissues during growth and repair, and meiosis, which is the specialized form of cell division occurring when gametes form. This process occurs only during the formation of the gametes and results in four daughter cells, each with the haploid number of chromosomes. In males, each primary spermatocyte forms four functional spermatids that develop into sperm, whereas in females, each oocyte forms only one ovum, the remaining products of meiosis being nonfunctional polar bodies. Processes fundamental to meiosis include chromosome pairing, chromosome crossing-over, and chromosome segregation. Because non-dividing chromosomes cannot be analyzed, live dividing cells are required for chromosome analysis. Skin fibroblasts, bone marrow cells, amniotic fluid cells, chorionic villus cells, and tumor cells are also used for special tests. To accomplish this, a drug (Colcemide) that destroys the mitotic spindle is added to the culture medium toward the end of the culture period. The cells are subjected to hypotonic treatment followed by fixation and spreading on microscope slides. These methods provide a means to precisely identify each chromosome and extra or missing chromosomes 144 as well as the exact localization of breakpoints in chromosome rearrangements. Cells are synchronized with the use of a methotrexate (or other) block; the block is released and the cells harvested at the times predicted to "catch" the chromosomes in late prophase or early metaphase, revealing more bands. With this approach, a band level of over 800 per haploid set can be achieved, which allows detection of a number of microdeletion syndromes. Chromosomes are prepared by routine methods and are denatured using formamide and heat. The hybridization site(s) is detected by using fluorochrome-conjugated reagents and fluorescence microscopy. Each individual chromosome pair can be recognized when banding techniques are used, and the chromosomes are numbered from 1 to 22 in descending order of length. In this notation the number of chromosomes is specified first, followed by the listing of the sex chromosomes. An individual autosome is referred to by its number, its short arm by the letter p, and its long arm by the letter q. This indicates a male with a normal number of chromosomes and a reciprocal translocation between the long arm of chromosome 9 and short arm of chromosome 21 with designated breakpoints. These arise from non-disjunction, that is, from the failure of two homologous chromosomes in the first division of meiosis or of two sister chromatids in either mitosis or the second division of meiosis to pass to opposite poles of the cell. If non-disjunction occurs during an early cleavage division of a zygote, then chromosomal mosaicism (two or more cell lines differing in chromosome complement) may result. When a chromosome breaks it can rejoin in its old form (restitution) or it can rejoin with another broken chromosome (reunion). Types of balanced rearrangements include balanced reciprocal translocations, Robertsonian translocations, and inversions. Such unbalanced rearrangements in meiotic cells usually result in changes in the clinical phenotype. Duplication is the addition of a chromosome segment and may be the result of breakage reunion or of replication error (see. The isochromosome shown in Figure 34-2 D has both a deleted short arm and a duplicated long arm, or deletion and duplication. These result from two chromosome breaks with inversion of the intervening segment and can be detected only by altered position of the centromere or by chromosome banding studies that show a changed banding sequence (see. Inversions result in disturbances in chromosome pairing and in the formation of unbalanced as well as balanced gametes. An individual carrying such a rearrangement has a higher frequency of abnormal gametes as the result of a disturbance in chromosome pairing at meiosis. Such rearrangements may be important in the transmission of Down syndrome when one of the chromosomes involved is chromosome 21. If the structural change occurs in the early embryo, mosaicism with some cells normal and some with the structural abnormality may result. It is estimated that at least 50% of all conceptuses are lost in the first 2 to 3 weeks after conception, most due to major chromosome abnormalities. The most common abnormalities, each occurring in about 25% of the chromosomally abnormal cases, are 45,X, missing a sex chromosome, and triploidy with three sets of chromosomes (3n). The remainder include trisomy for any of the autosomes with the exception of chromosome 1, which has been seen only in studies of the early zygote. Triploidy is characterized by cystic degeneration of the placenta, sometimes appearing as a hydatidiform mole, with an accompanying fetus. There is a markedly increased incidence of toxemia of pregnancy, and eclampsia may ensue. The true mole may be confused with triploidy because it also has cystic degeneration of the placenta, the cysts appearing in grapelike clusters. Both sets of chromosomes are paternal in origin, with no maternal contribution, likely the result of fertilization of an empty egg. The 45,X fetuses are markedly edematous and have large cystic masses encircling the neck. They are small for gestational age and generally have characteristic facial features. Most trisomies 13 and 18 are lost before term, and those that survive to term usually live no more than 1 year. About 70% of trisomy 21 conceptions die before term; with modern treatment, many of those individuals doing well after birth may survive to old age. Seven to 10 per cent of stillbirths and neonatal deaths are due to chromosome imbalance; trisomy 18 and trisomy 13 are frequent in this group. To diagnose the abnormal, an appreciation of normal biologic variation is important. Diversity of facial features and body habitus in individuals, families, and ethnic groups must be considered. Minor malformations having no medical significance such as epicanthal folds or low-set ears should be looked for in the physical examination because they may serve as clues to more serious defects and/or help in defining specific syndromes. In females, the sex chromosomes are identical in 146 Figure 34-2 Partial karyotypes illustrating several types of structural chromosome aberrations. In the right-hand chromosome 9 there is an interstitial duplication of a large segment on the long arm, delineated by the arrows on the normal chromosome. One explanation for this recurring characteristic abnormality is centromere misdivision. E, Inversion: balanced chromosome 4 pericentric inversion delineated by arrows, from a normal woman. F, Translocation: balanced reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 14 and 17 from a normal individual. This likely is due to position in the metaphase spread; chromosomes at the periphery are often longer than those at the center. Eyes may be mildly wide spaced and deep set, nose is mildly prominent, mouth is large, teeth widely spaced.
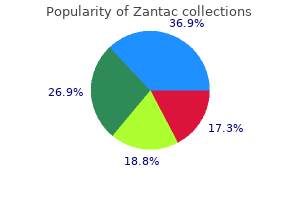
Purchase zantac 150mg free shipping. gastik walata beheth -.