




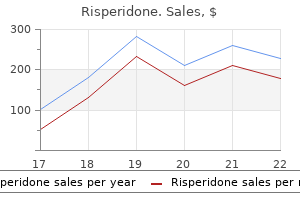
|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
"Buy 3mg risperidone with visa, treatment lower back pain".
C. Saturas, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, Marist College
At the porta hepatis the structures are the portal vein medications by class buy cheap risperidone 2mg on line, bile ducts and hepatic artery medications via ng tube buy generic risperidone 2 mg online. The hepatic veins (right medications janumet buy 4 mg risperidone with amex, middle and left) enter separately into the inferior vena cava (see previously) symptoms 7 days pregnant purchase risperidone 2 mg without a prescription. A, D Liver injuries are rare because of its anatomical position under the diaphragm where it is protected by the lower thoracic cage. Blunt trauma is often associated with damage to neighbouring structures, such as the spleen, kidneys and mesentery. Stab and gunshot wounds causing penetrating injuries are associated with chest trauma. If unstable, the patient needs to be taken to theatre forthwith without wasting time on a scan. The stable patient who has no hollow viscus damage, but continues to bleed from the liver, might well benefit from an interventional radiologist who could perform a hepatic angiogram with a view to doing embolisation. A, B, D, E A penetrating injury, such as a lower right chest and abdominal stab wound, requiring large amounts of blood replacement will need urgent exploration. The patient should be transferred to the operating theatre whilst active resuscitation is underway. In the management of these patients, there should be close liaison with the blood transfusion department, as these patients will not only require large amounts of blood but also fresh frozen plasma and cryoprecipitate. These patients are prone to develop irreversible coagulopathies due to lack of fibrinogen and clotting factors. Standard intraoperative coagulation studies are inadequate and factors are given empirically. The initial definitive treatment is endoscopic sclerotherapy or banding, the latter having a lesser incidence of oesophageal ulceration. Long-term beta-blocker therapy with endoscopic sclerotherapy or banding is the main treatment for portal hypertension. In such an extreme situation oesophageal tamponade by the use of a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube (Figure 65. F Amoebic liver abscess Having returned from a stay in the Indian subcontinent, this patient has amoebic dysentery with an amoebic abscess. Aspiration helps in the penetration of metronidazole and so reduces the morbidity when carried out with drug treatment in a large abscess. Surgical treatment is reserved for rupture into the pleural, peritoneal, or pericardial cavities. Resuscitation, drainage and appropriate lavage with vigorous medical treatment are the key principles in management (see Chapter 6, Surgery in the tropics). She needs to be resuscitated with intravenous fluids and given antibiotics to combat the sepsis and vitamin K to prevent excessive bleeding from the increase in prothrombin time. The hepatic venous outflow obstruction causes a congested liver, impaired liver function, portal hypertension, ascites and oesophageal varices. Confirmation is by hepatic venography via the transjugular route, which might allow a biopsy. Patients who present acutely in fulminant liver failure or with established cirrhosis and portal hypertension should be considered for liver transplantation. If and when the disease is limited to one lobe of the liver, lobectomy might be carried out (see Chapter 67, the gallbladder and bile ducts). Focal nodular hyperplasia contains hepatocytes and Kupffer cells, which are very few in tumours. Thus a sulphur colloid scan, which is taken up by Kupffer cells, would be diagnostic and differentiate it from metastasis.
A primary calculus is one that develops in sterile urine such as an oxalate calculus symptoms by dpo generic 4mg risperidone with amex. This is usually solitary pretreatment generic 3 mg risperidone overnight delivery, spiky and dark brown in colour as the white calcium oxalate is incorporated with blood pigment sewage treatment risperidone 3mg mastercard. A triple phosphate calculus medications 230 effective 3 mg risperidone, dirty white and chalky, is one that is composed of ammonium, magnesium and calcium and grows in urine infected with urea-splitting organisms. When there is a large intravesical prostate, urine stagnates in the retroprostatic pouch; infection supervenes and silent stones tend to form. Pain in the form of strangury, dysuria, haematuria and sudden cessation of the urinary stream are the presenting features. Young boys pull on the prepuce or penis during micturition screaming with pain, a typical symptom of bladder calculus. B Bladder carcinoma Carcinoma of the bladder is the fourth most common non-dermatological malignancy in men who are affected three times more than women. Smoking is the principal cause although exposure to urothelial carcinogens of a chemical nature might occur as an occupational hazard. Painless, progressive, profuse and periodic haematuria is the classical presentation and physical signs are few except for anaemia. Rarely a large diverticulum might cause ureteric obstruction from peridiverticular inflammation. The diverticulum needs to be excised if there are complications such as stone formation, tumour or persistent infection. Excision is carried out by the open procedure of intra and extravesical diverticulectomy after cannulating the ureter on the affected site to safeguard it from injury or instantly recognise any injury that might occur inadvertently. The snail is the intermediate host for this parasite, which penetrates the human skin, while man, the definitive host, bathes in infected freshwater. The male and female worms, having attained sexual maturity in the liver, leave the hepatic circulation through the portosystemic anastomoses to enter the systemic circulation, where they have an affinity for the vesical venous circulation ultimately entering the urinary bladder. After the incubation period of 4 to 12 weeks patients might develop high evening temperature, sweating and asthma-like attacks. After several months of quiescence, patients develop intermittent, painless, terminal haematuria. Clinical features of weight loss, malaise, evening rise of temperature, dysuria, urinary frequency and painless haematuria might be present. Depending upon the extent of the disease, the patient might require nephro-ureterectomy. In very late cases the end result might be a squamous carcinoma, bladder and bladder neck fibrosis and urethral strictures. Drug treatment in the form of a course of praziquantel is effective in the early stages. The following statements are true except: A the prostate is anatomically divided into a peripheral zone, a central zone and a transitional zone. D In patients with a residual volume of 250 mL or more, bilateral hydronephrosis will result. The following statements are true except: A -adrenergic blocking agents inhibit the contraction of prostatic smooth muscle. The following statements are true except: A the histological type is an adenocarcinoma. On rectal examination, which of the following features does not suggest carcinoma In the assessment of prostate cancer which of the following investigations are necessary Regarding treatment, the following statements are true except: A Radical prostatectomy is only suitable for T1 and T2 disease (early cancer). E the incidence of severe stress incontinence after radical prostatectomy is about 2%.
Posteriorly directed counterpressure over the anterior shoulder may mitigate the sensation of instability 7 medications that can cause incontinence discount risperidone 2mg with visa. Posterior Dislocation Clinically medicine 75 yellow risperidone 3 mg mastercard, a posterior glenohumeral dislocation does not present with striking deformity; moreover treatment as prevention buy risperidone 2 mg visa, the injured upper extremity is typically held in the traditional sling position of shoulder internal rotation and adduction medicine dictionary discount risperidone 3mg online. A careful neurovascular examination is important to rule out axillary nerve injury, although it is much less common than with anterior glenohumeral dislocations. On examination, limited external rotation (often 0 degrees) and limited anterior forward elevation (often 90 degrees) may be appreciated. Atraumatic Dislocation Patients present with a history of recurrent dislocations with spontaneous reduction. Often the patient will report a history of minimal trauma or volitional dislocation, frequently without pain. Sulcus sign: this is dimpling of skin below the acromion with longitudinal traction. Superior and Inferior (Luxatio Erecta) Dislocation this is extremely rare in children, although cases have been reported. Velpeau axillary view: Compliance is frequently an issue in the irritable, injured child in pain. If a standard axillary view cannot be obtained, the patient may be left in a sling and leaned obliquely backward 45 degrees over the cassette. The beam is directed caudally, orthogonal to the cassette, resulting in an axillary view with magnification. Special views (see Chapter 14) West Point axillary view: Taken with the patient prone with the beam-directed cephalad to the axilla 25 degrees from the horizontal and 25 degrees medially. Stryker notch view: the patient is supine with the ipsilateral palm on the crown of head and the elbow pointing straight upward. Computed tomography may be useful in defining humeral head or glenoid impression fractures, loose bodies, and anterior labral bony injuries (bony Bankart lesion). Single- or double-contrast arthrography may be utilized in cases in which the diagnosis may be unclear; it may demonstrate Chapter 43 Pediatric Shoulder 595 pseudosubluxation, or traumatic epiphyseal separation of the proximal humerus, in a neonate with an apparent glenohumeral dislocation. Magnetic resonance imaging may be used to identify rotator cuff, capsular, and glenoid labral (Bankart lesion) pathology. Atraumatic dislocations may demonstrate congenital aplasia or absence of the glenoid on radiographic evaluation. Classification Degree of stability: Chronology: Force: Patient contribution: Direction: Dislocation versus subluxation Congenital Acute versus chronic Locked (fixed) Recurrent Acquired: generally from repeated minor injuries (swimming, gymnastics, weights); labrum often intact; capsular laxity; increased glenohumeral joint volume; subluxation common Atraumatic: usually owing to congenital laxity; no injury; often asymptomatic; self-reducing Traumatic: usually caused by one major injury; the anteroinferior labrum may be detached (Bankart lesion); unidirectional; generally requires assistance for reduction Voluntary versus involuntary Subcoracoid Subglenoid Intrathoracic Treatment Closed reduction should be performed after adequate clinical evaluation and administration of analgesics and or sedation. Steady, continuous traction eventually results in fatigue of the shoulder musculature in spasm and allows reduction of the humeral head. Stimson technique: the patient is placed prone on the stretcher with the affected upper extremity hanging free. Gentle, manual 596 Part V Pediatric Fractures and Dislocations traction or 5 lb of weight is applied to the wrist, with reduction effected over 15 to 20 minutes. Steel maneuver: With the patient supine, the examiner supports the elbow in one hand while supporting the forearm and wrist with the other. Thumb pressure is applied by the physician to push the humeral head into place, followed by adduction and internal rotation of the shoulder as the extremity is placed across the chest. Following reduction, acute anterior dislocations are treated with sling immobilization. Total time in sling is controversial but may be up to 4 weeks, after which an aggressive program of rehabilitation for rotator cuff strengthening is instituted. Posterior dislocations are treated for 4 weeks in a commercial splint or shoulder spica cast with the shoulder in neutral rotation, followed by physical therapy. Recurrent dislocation or associated glenoid rim avulsion fractures (bony Bankart lesion) may necessitate operative management, including reduction and internal fixation of the anterior glenoid margin, repair of a Bankart lesion (anterior labral tear), capsular shift, or capsulorrhaphy. Postoperatively, the child is placed in sling immobilization for 4 to 6 weeks with gradual increases in rangeof-motion and strengthening exercises. Atraumatic dislocations rarely require reduction maneuvers as spontaneous reduction is the rule. Only after an aggressive, supervised rehabilitation program for rotator cuff and deltoid strengthening has been completed should surgical intervention be considered.
Magnetic resonance imaging may aid in assessing spinal cord or root injury as well as the degree of canal compromise medicine 44291 buy discount risperidone 4 mg line. One can expect up to one to two levels of additional root return medicine glossary purchase risperidone 4mg line, although the prognosis for recovery is extremely poor treatment algorithm cheap 3 mg risperidone visa. Spinal Cord Injury: Incomplete Some neurologic function persists caudal to the level of injury after the return of the bulbocavernosus reflex treatment junctional tachycardia generic 2mg risperidone. As a rule, the greater the function distal to the lesion and the faster the recovery, the better is the prognosis. Sacral sparing is represented by perianal sensation, voluntary rectal motor function, and great toe flexor activity; it indicates at least partial continuity of white matter long tracts (corticospinal and spinothalamic) with implied continuity between the cerebral cortex and lower sacral motor neurons. It indicates incomplete cord injury, with the potential for a greater return of cord function following resolution of spinal shock. The prognosis is good, with over 90% of patients regaining bowel and bladder function and ambulatory capacity. Central Cord Syndrome this is most common and is frequently associated with an extension injury to an osteoarthritic spine in a middle-aged person. It presents with flaccid paralysis of the upper extremities (more involved) and spastic paralysis of the lower extremities (less involved), with the presence of sacral sparing. Radiographs frequently demonstrate no fracture or dislocation because the lesion is created by a pincer effect between anterior osteophytes and posterior infolding of the ligamentum flavum. The prognosis is fair, with 50% to 60% of patients regaining motor and sensory function to the lower extremities, although permanent central gray matter destruction results in poor hand function. The prognosis is good if recovery is evident and progressive within 24 hours of injury. Absence of sacral sensation to temperature or pinprick after 24 hours portends a poor outcome, with functional recovery in 10% of patients according to one series. Posterior Cord Syndrome this is rare and involves loss sensation of deep pressure, deep pain, and proprioception with full voluntary power, pain, and temperature sensation. It may be complete or incomplete; the bulbocavernosus reflex may be permanently lost. This may be partial or complete and results in radicular pain, sensory dysfunction, weakness, hyporeflexia, or areflexia. Clinical manifestations include saddle anesthesia, bilateral radicular pain, numbness, weakness, hyporeflexia or areflexia, and loss of voluntary bowel or bladder function. Incomplete: Motor function is preserved below the neurologic level; most key muscles below the neurologic level have a muscle grade 3. For functional scoring, 10 key muscle segments corresponding to innervation by C5, C6, C7, C8, T1, L2, L3, L4, L5, and S1 are each given a functional score of 0 to 5 out of 5. For sensory scoring, both right and left sides are graded for a total of 100 points. For the 28 sensory dermatomes on each side of the body, sensory levels are scored on a zero- to two-point scale, yielding a maximum possible pinprick score of 112 points for a patient with normal sensation. A rigid cervical collar is indicated until the patient is cleared radi- ographically and clinically. A special backboard with a head cutout must be used for children to accommodate their proportionally larger head size and prominent occiput. The patient should be removed from the backboard (by logrolling) as soon as possible to minimize pressure sore formation. Medical Management of Acute Spinal Cord Injury Intravenous methylprednisolone May improve recovery of neurologic injury Is currently considered the "standard of care" for spinal cord injury if it is administered within 8 hours of injury; it improves motor recovery among patients with complete and partial cord injuries Has a loading dose of 30 mg/kg 5. Gastritis is thought to be the result of sympathetic outflow disruption with subsequent unopposed vagal tone resulting in increased gastric activity.
The larynx is well developed for phonation in the human and also helps control pressure during the respiratory cycle medications not to take before surgery purchase 2 mg risperidone amex. Clinical presentation includes early lymph node metastases (70%) treatment ringworm discount risperidone 3 mg online, in particular medications routes order risperidone 3mg line, retropharyngeal nodes and cervical lymphadenopathy in levels 2 or 5 medicine 94 cheap risperidone 2 mg on-line. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of a neck node showing undifferentiated carcinoma requires immediate thorough examination of the nasopharynx. Symptoms related to primary disease include nasal discharge, obstruction and epistaxis, which occurs in one-third of patients. Aural symptoms of unilateral deafness as a consequence of Eustachian tube obstruction and secretory otitis media occur in approximately 20% In around 5% of patients, the nasopharynx might look normal or minimally asymmetrical but contains submucosal nasopharyngeal carcinoma. A biopsy of the nasopharynx is essential if there is suspicion of nasopharyngeal malignancy. The primary treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma is radiotherapy, as the majority of the tumours are radiosensitive undifferentiated squamous cell carcinomas. Elective bilateral radiotherapy is given at the skull base and neck in all patients, even when no neck nodes are apparent, as rates of occult metastasis are high. Platinum-based chemotherapy may be given in both the adjuvant and neoadjuvant setting, particularly in high-risk cases. Due to the proximity of vital structures in the immediate vicinity of the nasopharynx, surgery is complex and often impossible. Recurrent neck disease may be an indication for neck dissection, but recurrent disease at the primary site is very challenging surgically. Although there is experience with nasopharyngectomy in the Far East, few centres in Europe or North America have significant experience of these techniques. A, C, D, E Peritonsillar abscess or quinsy describes the formation of pus in the peritonsillar space. Patients experience severe pain and trismus due to inflammation around the pterygoid muscles. Intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics, fluids and analgesia should be commenced; however, transoral incision and drainage of the pus should be carried out under local anaesthesia. The retropharyngeal space is a potential space that lies posterior to the pharynx, bounded anteriorly by the posterior pharyngeal wall and its covering buccopharyngeal fascia and 392 Absolute Relative Sleep apnoea, chronic respiratory tract obstruction, cor ulmonale Suspected tonsillar malignancy Documented recurrent acute tonsillitis Chronic tonsillitis Peritonsillar abscess (quinsy) Tonsillar asymmetry Tonsillitis resulting in febrile convulsions Diphtheria carriers Systemic disease caused by -haemolytic Streptococcus (nephritis, rheumatic fever) posteriorly by the cervical vertebrae. These nodes are more developed in young children, and it is at this age that they are most likely to be involved in inflammatory processes, which, if severe, might affect swallowing and the airway as a result of swelling and suppuration of the retropharyngeal space. A retropharyngeal abscess is associated with infection of the tonsil, oropharynx, or nasopharynx. Signs and symptoms include airway compromise, dysphagia, torticollis, stiff neck and swelling of the midline of the posterior pharyngeal wall. Operative approaches to a retropharyngeal space abscess include peroral or an external approach, and a decision on approach will be based on imaging findings. Chronic retropharyngeal abscess is now rare and most commonly the result of an extension of tuberculosis of the cervical spine, which has spread through the anterior longitudinal ligament to reach the retropharyngeal space (Table 48. Signs and symptoms are similar as for bacterial tonsillitis; however, the tonsils are typically erythematous with a creamy grey exudate and cervical or generalised lymphadenopathy is present. The diagnosis is confirmed by serological testing showing a positive Paul-Bunnell test, an absolute and relative lymphocytosis and presence of atypical monocytes in the peripheral blood. It is thought to be in part due to a hyperactive upper oesophageal sphincter, and is more common in men over 60 years old. Patients might experience regurgitation of undigested food, sometimes hours after a meal, and halitosis.