


|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
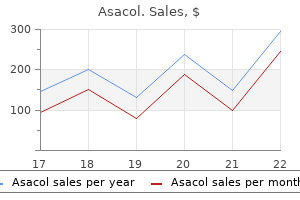
"800 mg asacol free shipping, symptoms xanax".
M. Giacomo, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine
Researchers may choose to measure an index rather than the population abundance symptoms quivering lips buy asacol 400mg low cost, especially if it is more efficient or cost-effective to do so (Conroy medications routes buy 400 mg asacol, 1996) medicine under tongue buy asacol 400 mg lowest price. The reliability and usefulness of a population abundance index are based on how closely the index and the true abundance are correlated treatment genital herpes purchase 800mg asacol mastercard, which is often difficult to measure. In many cases, true population abundance cannot be measured to quantify its relationship with an index (often, this is why the index is being used in the first place). In these cases, abundance indices can be used as a measure of "relative abundance" for comparison among populations and for tracking population changes over time, as long as special attention is given to standardizing the measurements taken. Indices commonly used to assess bat population abundance include capture rates, direct observations. This section describes three population abundance indices that show the most promise for use during disease sampling fieldwork: capture rates, density measurements, and guano deposition. Although measuring the relationship between an index and the true population abundance is beyond the scope of disease studies, these indices may serve as measures of relative abundance that can be used for comparison over a long-term disease sampling programme. Capture rate In a study that involves capturing bats, the number of bats captured per unit of effort/time can index the abundance of the population being sampled (for a more detailed description see Kunz et al. This capture index assumes that changes in capture rates reflect proportional changes in the abundance of the population being sampled (Conroy, 1996), and is usually expressed as the number of bats caught per net-hour, per night, per mist net night, or per net metre per night. The reliability of a capture index depends on standardized capture methods appropriate to the species being captured (Hodgkison et al. Bat density Bat density (in roosts or during foraging activity) can be measured through visual or acoustic observation, providing an index to abundance. Assuming uniform density, measurements of bat density in a known area can be used to estimate population abundance over a larger area (Conroy, 1996). This technique can also be especially helpful in assessing population abundance for species that roost solitarily or in small groups, and it may be incorporated into other ongoing fieldwork (Kunz et al. Away from the roost, if researchers have the time to count the bats detected within a known area, the density of bat activity can also be a useful index to relative abundance (Hayes, 1999; Hayes, Ober and Sherwin, 2009), offering a point of comparison for subsequent sampling sessions. This technique is improved with bat species identification training and access to night-vision equipment and/or ultrasonic detectors (Parsons and Jones, 2000; Walsh and Catto, 2004). For frugivorous bats, the use of faeces as an index to population abundance remains unexplored. Faecal deposition rates of Old World fruit bats have not been studied, but fruit bat droppings can be collected under a roost and enumerated (Stier and Mildenstein, 2005), suggesting that this may provide a useful surrogate to the direct assessment of population abundance (Figure 3. Monitoring programmes can use population abundance data to track changes over time in the size, roost site occupation, seasonal movement patterns, distribution and connectivity of bat populations. However, the use and application of population abundance assessments depend entirely on the quality of the data and how they were acquired. Fruit bat biology suggests that each faecal sample collected under the roost in the morning represents one bat individual Source: Stier and Mildenstein, 2005 were collected. It is therefore important that the survey design reflects the study goals, that the methodology is standardized and repeatable, and that the sources of variability in the data are well understood. The following should be considered when designing and implementing bat population assessments. Define the research goals Population abundance assessment is usually conducted for a specific reason. The first step of a population survey is establishing research and management goals and identifying the role that a population abundance estimate will have in reaching those goals (Hayes, Ober and Sherwin, 2009). Having a clear understanding of the reason for the population survey will guide assessors in choosing the appropriate assessment method, planning the assessment and evaluating the results. Be prepared Whether the goal is a one-time measure of population size to determine the sampling effort required or the establishment of a population abundance baseline for comparison with future assessments, it is critical that surveyors are well prepared for abundance estimation. Surveyors should be trained in population abundance assessment techniques and know the assumptions implicit to the methods they are using. Potential sampling errors can often be mitigated if the sources of error are identified at the fieldwork planning stage. Standardize methods For any survey technique, it is critical that assessors describe their methods clearly and standardize them across assessments for comparison among replicates and/or with future assessments. For example, many bat species exhibit synchronized seasonal birth pulses (Kunz and Pierson, 1994).
Course Although there is some evidence that medicine in spanish discount 400 mg asacol, in males treatment xanthelasma buy 800mg asacol fast delivery, intellectual functioning may undergo a decline in late childhood or early adolescence (Dykens et al symptoms bipolar disorder discount 800mg asacol. Treatment Testosterone treatment improves libido and erectile function medications hyperthyroidism order asacol 400mg mastercard, and tends to help with energy and overall outlook (Nielsen et al. Developmental disabilities and mental retardation are treated in the usual fashion. An expansion of this sequence to include from 55 to 200 repeats is known as a premutation, whereas expansions to over 200 triplets constitute 9. Patients with pre-mutations do not develop the fragile X syndrome; however, those with full mutations do. Interestingly, although both female and male parents with a premutation may pass a full mutation to their children, this is far more commonly the case with female parents. The reason for this is that expansion of a pre-mutation to a full mutation occurs readily during oogenesis but only rarely during spermatogenesis. Magnetic resonance imaging studies have revealed hypertrophy of the hippocampus with atrophy of the superior temporal gyrus (Reiss et al. Autopsy studies have demonstrated that, although neuronal cell counts are normal in the cortex, dendritic spines are long and tortuous in shape (Hinton et al. Clinical features the facial dysmorphism is characterized by hypertelorism, a large, bulbous nose with a squared-off nasal root, and micrognathia. Most patients have a degree of velopharyngeal insufficiency, leading to a hypernasal voice. About 50 percent of patients suffer from either borderline intellectual functioning or mental retardation, which is generally of mild degree (Swillen et al. As these patients pass through adolescence into adult years, up to one-third will develop a psychosis phenotypically similar to that seen in schizophrenia (Bassett et al. Mood disturbances may also occur and may be more frequent than psychosis: both manic or hypomanic episodes (Papolos et al. Obsessions and compulsions have also been noted in roughly one-third of teenagers (Gothelf et al. Other clinical features include cardiac defects, hypocalcemia secondary to hypoparathyroidism, and, in a small minority, seizures (Kao et al. Differential diagnosis the full clinical syndrome of mental retardation, with or without autism, and the characteristic facial dysmorphism (with, in males, macro-orchidism) is distinctive. As noted earlier, patients with pre-mutations do not develop the fragile X syndrome. Course the course is chronic; although some die of cardiac complications, most live a normal lifespan. Course Self-mutilation may decrease, or even remit, in early adolescence (Mizuno 1986); most patients, however, die of infection or renal failure in their teenage or early adult years. The hyperuricemia, however, does not explain the mental retardation, movement disorder or self-mutilation. Post-mortem work has demonstrated reduced dopamine content in the caudate (Saito et al. Taken together, these results are consistent with a reduction of dopamine in pre-synaptic neurons and an expected compensatory up-regulation of post-synaptic dopamine receptors. Clinical features the overall clinical picture has been described in several studies (Christie et al. Toward the end of the first year of life, dystonia and choreoathetosis gradually appear, and with time spasticity may also occur. The characteristic self-mutilation typically begins in early childhood, after teeth come in; later onsets, up to the age of 8 years, however, have been reported (Hatanaka et al. Despite being normally sensitive to pain, patients repeatedly bite at their lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, and fingers, to the point where the lips and fingers are literally bitten off in some cases. Hyperuricemia is a constant feature of this disease, and tophaceous gout and gouty nephropathy may appear in adolescence. Differential diagnosis Although patients with other forms of mental retardation may bite themselves, the degree of self-biting rarely ever approaches that seen in the LeschNyhan syndrome. Treatment Allopurinol, by forestalling gouty nephropathy, may prolong life; it has, however, no effect on the central nervous system manifestations. Various medications have been reported in non-blind case reports or studies to be helpful in reducing the biting, including risperidone (Allen and Rice 1996), levodopa (Jankovic et al.
Inotropic and Chronotropic Characteristics of the Heart the force contraction refers to inotropic state and changes in the heart rate refer to the chronotropic characteristic medications quotes discount 800mg asacol mastercard. Autonomic actions of the nerves are affected by changes in blood temperature symptoms 7 days pregnant cheap 400mg asacol fast delivery, pH hb treatment order asacol 800 mg with mastercard, & the amount of blood returning to the heart medicine you can take during pregnancy buy asacol 400 mg fast delivery. Parasympathetic stimulation · Acetylcholine has a marked negative inotropic effect on myocardium decreasing contractility. Striated muscles contract most rapidly and smooth muscle contraction is long and slow. Both characteristics are sensitive to many drugs, which can alter the effects of nerves 147 Inherent Rhythmicity the heart cells can be divided into "leader-cells" and "follower-cells". All or None Principle the strength of contraction is not dependent on the strength of the stimulus. Although the heart responds with maximum contraction, the maximum varies with the physiological conditions. Refractory Period the cardiac muscle has much longer refractory period than that of nerve or skeletal muscle. The long absolute refractory period of the heart prevents it from going into sustained contraction, or tetanus, and thus ensures that there is an adequate diastolic period during which the heart fills with blood. Effect of Temperature It is up to a certain point the rate and strength of heart beat are increased by a rise in body temperature. This optimum temperature for enzymatic actions in warm-blooded animals is about 400C. Considerable rise in temperature above this destroys enzymes and structural proteins. Cooling slows the heart, decreases the contractile strengths as the chemical reactions are slowed. Heart rate increases about 10 beats per minute for every one- degree rise in Celsius temperature. Cooling slows the pacemaker and severe cooling is used for some surgical operations. Hyperkalemia decreases resting membrane potential, the intensity of the action potential also decreases, which makes the contraction of the heart weaker. Hypokalemia prolongs the relative refractory period; there is increased incidence of bradycardia, and high risk of arrhythmias Hypercalcemia results in increased myocardial contractility. Contractility Myocardial contractility is affected by the following three factors: 1. Atrial fibers form the atrial bundles; bundle connecting the two nodes is the internodal pathway. This delay in conduction creates efficiency of the heart, since the delay allows time for the atria to empty before ventricular depolarization and contraction begins. Bundle of His this is made up of specialized cardiac fibers, the purkinje fibers that originate in the node and form a bundle in the septum separating the two ventricles. The electric currents from the heart pass into the surrounding tissues and spread to the surface of the body. By analyzing the details of these potential fluctuations, the physicians gain valuable insight concerning: the anatomical orientation of the heart Relative sizes of its chambers A variety of disturbances of rhythm of conduction the extent, location, and progress of ischemic damage to the myocardium the effects of altered electrolyte concentrations. This segment represents the time during which all regions of the ventricles are still depolarized and presents the long plateau phase of the cardiac action potential. Normally, the voltages in the three standard bipolar limb leads, as measured from the peak of the R wave to the bottom of the S wave, vary between 0. The cardiac cycle the cardiac cycle is the period from the end of one heart contraction (Systole) and relaxation (diastole) to the end of next systole and diastole. Cardiac contraction is preceded by electrical changes initiated by the pacemaker of the heart, the sino-atrial node. The contraction of the heart generates pressures within the heart that regulates the opening and closing of the valves and consequently directs the blood flow through the heart and the arteries.
Data limitations can be challenging for any health application treatment yeast uti buy asacol 800 mg overnight delivery, given the many categories of evidence required medicine 524 buy asacol 400mg overnight delivery, but these data limitations are particularly salient for newborn screening candidate disorders due to the low incidence and the long time frame over which outcomes need to be considered medicine 665 asacol 400mg without prescription. Constructing a decision analytic model and assembling the necessary inputs can be resource intensive and time consuming medicine you can take during pregnancy purchase asacol 400mg with mastercard, which can present an additional challenge when the need for a policy decision is urgent. Lack of data on long-term outcomes the key data challenge for measuring health outcomes is the absence of data on long-term outcomes of newborn screening programs. More data are becoming available for short-term outcomes of newborn screening programs, such as the sensitivity and specificity of screening protocols. As long-term follow-up programs become established, the increasing availability of long-term data for screened conditions can potentially help inform decisions about candidate conditions that share similar characteristics. However, such research efforts are not likely to address the unique challenge of assessing what long-term outcomes would be in the absence of screening. The advantage of a decision analytic modeling approach is that a range of assumptions for outcomes of clinically identified cohorts can be explored in the analysis. Decision analysis represents a promising approach to evaluating newborn screening policy options. The use of decision analytic models can assist decision makers by providing estimates of health benefits and possible risks for varying time horizons and for varying assumptions for test characteristics, treatment benefits, and possible harms. Understanding the ranges of possible outcomes for different input assumptions can be informative to decision makers, given the absence of long-term data for most conditions that are nominated for newborn screening. A decision analysis can consider a range of assumptions for key issues such as a broader spectrum of disease detected by screening or potential harms of treatment. Page 10 Difficulties in defining costs Author Manuscript Author Manuscript Author Manuscript Author Manuscript There are numerous challenges to obtaining a full account of the costs associated with a newborn screening program. However, because state-level newborn screening programs are public programs, the appropriate perspective to use in most cases would be the societal perspective. Some analyses have used the payer perspective; however, given the substantial burden of many of these conditions on family members, alternative perspectives such as the payer perspective could result in substantial underestimation of the burden of illness and associated benefits of averted illness. In these more narrow analytic perspectives, some of the types of costs listed earlier, such as patient or family time costs, would be excluded. Because identification and treatment may have improved over time, the use of historical data for clinically identified cases may be misleading. For the comparator strategy of clinical identification, the appropriate approach for an economic evaluation should assume usual care from the same time period. Treatment patterns are likely to represent a substantial improvement when compared to historical data from prior to the initiation of newborn screening. For example, the two classic examples of newborn screening programs that are cost saving are phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism. Longterm outcomes for patients with late-treated phenylketonuria show that the degree of cognitive impairment on average is less than was assumed in previously published economic evaluations. Choice of the comparator can affect conclusions about the cost-effectiveness of screening. For example, the comparator strategy for universal screening could be either targeted screening or no screening. Targeted screening is generally difficult to use as a comparator because of a lack of information about the effectiveness and costs of targeted versus universal screening. However, considering alternative screening strategies is one advantage of using a decision analytic approach, allowing for the consideration of alternatives for which little data are available. Valuation of health outcomes the valuation of health outcomes using health utilities for newborn screening presents methodological challenges due to a lack of standardization regarding optimal approaches for assigning health utilities to child health outcomes. Page 11 Defining the scope of the analysis Author Manuscript Author Manuscript Author Manuscript Author Manuscript Calculating the cost-effectiveness of screening for a single condition may not be straightforward. If the out-of-range value could be associated with more than one condition, then it may be more appropriate to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of screening for the panel of conditions instead of the single condition being added to the panel and then evaluating the incremental cost-effectiveness of the expanded panel as compared with the original panel. If these findings are reported and followed up on, these must also be included in the costeffectiveness analysis. In the case of newborn screening, this requires the analyst to explicitly and carefully define the scope of the analysis.