




|
STUDENT DIGITAL NEWSLETTER ALAGAPPA INSTITUTIONS |

|
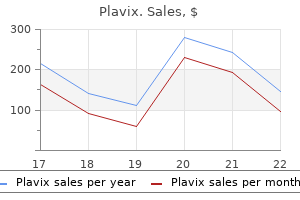
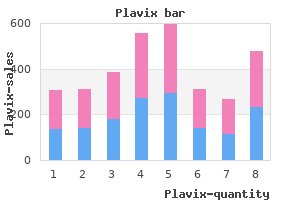
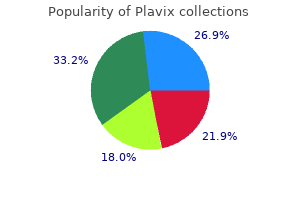
"Purchase plavix 75 mg amex, blood pressure chart too low".
A. Connor, MD
Program Director, Meharry Medical College School of Medicine
In children recovering after surgery for posterior fossa tumours blood pressure medication makes me pee buy 75mg plavix fast delivery, a syndrome of mutism and other behavioural problems in the early postoperative days is sometimes seen blood pressure 5040 order plavix 75 mg amex. This is sometimes referred to as cerebellar mutism heart attack usher mp3 cheap 75mg plavix with amex, or the syndrome of cerebellar mutism and subsequent dysarthria heart attack fever buy discount plavix 75 mg on-line, and sometimes as the posterior fossa syndrome. There is thus uncertainty as to the extent this acute syndrome is related specifically to cerebellar effects, or to problems elsewhere within the posterior fossa. It was labelled the posterior fossa syndrome in a study of 142 children following resection of posterior fossa tumours (Pollack 1997); 12 children, of whom seven had a medulloblastoma, developed transient mutism and in each case the tumour involved the cerebellar vermis. In general mutism developed 14 days postoperatively and typically was associated with neurobehavioural abnormalities including emotional lability, reduced initiation of movement and poor oral intake. Because this neurobehavioural syndrome was generally associated with bilateral pontine oedema, the authors suggested that any of a number of sites within the posterior fossa might have been affected and therefore labelled it posterior fossa syndrome. Similarly, in a study of over 250 children with posterior fossa tumours who underwent surgical resection, 20 cases (8%) of posterior fossa syndrome were identified (Doxey et al. The most frequent postoperative findings included mutism, lasting on average about 10 weeks, as well as more permanent neurological sequelae such as ataxia and hemiparesis. On the other hand, a similar constellation of symptoms, centred on acquired mutism lasting between 1 day and 5 months, was observed in 12 of 42 children following surgery to tumours localised to the cerebellum (Catsman-Berrevoets et al. Again, children with medulloblastoma, often involving the cerebellar midline/vermis, were at greatest risk, as were those with tumours greater than 5 cm in Cerebral Tumours 297 diameter. More recently, a study of patients seen in a psychiatric liaison service has highlighted changes in mood and behaviour (Turkel et al. The changes were regarded as similar but more acute to those seen in the cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. The effects just described are found after the child has presented with neurological symptoms. However, occasionally, posterior fossa tumours appear to lead to early and pronounced changes of behaviour. Cairns (1950) reported three children with astrocytomas of the pons in whom the initial symptoms included irritability, fretfulness, cruelty and obstinacy. In two of these, symptoms were sufficiently pronounced to constitute a complete change of character, and in all three they antedated the appearance of headache or the development of physical signs. Some mental sequelae can be understood as reactions to the neurological disability. However, in other cases mental symptoms can be traced to direct effects of the tumour on brainstem pathways or to raised intracranial pressure. Shepherd and Wadia (1956) reported six patients with acoustic neuromas in whom chronic hydrocephalus produced confusion, impaired memory, change of personality and lack of insight. Woodcock (1967) found mental changes including personality deterioration, impairment of memory and intellect, confusion, depression, euphoria and neurotic traits in 7 of 30 cases and concluded that these were attributable to vascular disturbances consequent on brainstem distortion. Psychotic symptoms have been reported in a surprising number of cases, chiefly depressive or paranoid psychoses occurring in clear consciousness (Dobrokhotova & Faller 1969; Scott 1970). Manic or mixed states have been described in three adults with acoustic neuroma (Kalayam et al. Visual hallucinations may occur with subtentorial tumours, presumably via pressure effects transmitted through the tentorium to the adjacent occipital cortex (see above). In the meantime preliminary investigations will need to include a full medical examination, including a neurological examination, and chest radiography to exclude metastatic disease. Neurological examination may need to be augmented by quantitative evaluation of visual fields using a combination of Goldman kinetic perimetry and Humphries static perimetry, particularly if there is suspicion of a tumour in the vicinity of the pituitary. Audiometry may be a useful screening test for the diagnosis of cerebellopontine angle tumours, for example 98% of patients with vestibular schwannoma have sensorineural hearing loss on pure tone audiometry. Haematological, biochemical and immunological tests should form part of the basic diagnostic armamentarium. Endocrinological evaluation to assess the functioning of the hypothalamicpituitary axis before and after treatment is important in the management of tumours in this region as well as in brain tumour patients treated with radiotherapy, as these patients frequently develop hormonal deficits. Evoked potentials, such as brainstem auditory-evoked potentials and visual-evoked potentials, have a role in the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological function during surgical resection of tumours.
Sensory memory-Visual (iconic) and auditory (echoic) stimuli briefly stored in memory; fades very quickly unless attention is paid to the information heart attack upset stomach purchase plavix 75mg. Sensory neuron-A neuron that transmits information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system prehypertension uptodate cheap 75 mg plavix overnight delivery. Serial position effect-The tendency to better remember items presented at the beginning or end of a list; related to the primacy and recency effects arteria musculophrenica purchase 75 mg plavix visa. Shaping-In operant conditioning arrhythmia recognition poster plavix 75 mg on line, the process of conditioning a complicated behavior by rewarding successive approximations of the behavior. Signal detection theory-A theory of perception in which internal (psychological) and external (environmental) context both play a role in the perception of stimuli. Similarity-An aspect of interpersonal attraction based on being alike in attitudes, intelligence, education, height, age, religion, appearance, or socioeconomic status. Situational (external) attributions-Attributions that relate to features of the surroundings, such as threats, money, social norms, and peer pressure, rather than to features of the individual. Sleep apnea-Sleep disorder in which a person may cease to breathe while sleeping; may be due to obstruction or a central (neurological) cause. Social action-Actions and behaviors that individuals are conscious of and performing because others are around. Social capital-The investment people make in their society in return for economic or collective rewards. Social class-A category of people with a shared socioeconomic background that exhibit similar lifestyles, job opportunities, attitudes, and behaviors. Social cognitive theory-A theory that attitudes are formed through observation of behavior, cognition, and the environment. Social construction model-A theory of emotional expression that assumes there are no biologically wired emotions; rather, they are based on experiences and situational context alone. Social constructionism-A theoretical approach that uncovers the ways in which individuals and groups participate in the formation of their perceived social reality. Social facilitation-The tendency of people to perform at a different level based on the fact that others are around. Social institutions-Well-established, structured patterns of behavior or relationships that are accepted as a fundamental part of a culture. Social mobility-The movement of individuals in the social hierarchy through changes in income, education, or occupation. Social movements-Philosophies that drive large numbers of people to organize to promote or resist social change. Social perception-Understanding the thoughts and motives of other people present in the social world; also referred to as social cognition. Social stratification-Organization of societies into a hierarchical system, usually based on socioeconomic status and social class. Social support-The perception or reality that one is cared for by a social network. Socialization-The process of developing and spreading norms, customs, and beliefs. Somatic nervous system-The voluntary branch of the peripheral nervous system, which consists of sensory and motor neurons used to control bodily movements. Somatosensation-The sense of touch, which contains multiple modalities: pressure, vibration, pain, and temperature. Somnambulism-Sleep disorder in which one carries out actions in his or her sleep; also called sleepwalking. Source amnesia-A memory error by which a person remembers the details of an event but confuses the context by which the details were gained; often causes a person to remember events that happened to someone else as having happened to him- or herself. Spacing effect-The phenomenon of retaining larger amounts of information when the amount of time between sessions of relearning is increased. Spatial inequality-A form of social stratification across territories and their populations that can involve residential, environmental, or global components. Spreading activation-The unconscious activation of closely linked nodes of a semantic network. State-dependent memory-A retrieval cue by which memory is aided when a person is in the same state of emotion or intoxication as when encoding took place.
The precise delineation of vascular anomalies may still require X-ray angiographic techniques heart attack remix generic plavix 75mg otc. For a while a place remained for the technique in a small minority of patients blood pressure medication that starts with m generic 75 mg plavix with amex, chiefly for visualising small basal tumours near the optic or auditory nerves or in the brainstem blood pressure news generic 75 mg plavix with mastercard, and for clarifying obstructions in the aqueductal region pulse blood pressure relationship buy plavix 75 mg low cost. These tests are usually carried out by a clinical neurophysiologist and require some skill in their interpretation. Their main role is in the diagnosis and monitoring of disorders of the peripheral nervous and neuromuscular systems. Useful overviews of their role in clinical practice are provided by Mallik and Weir (2005) and Mills (2005a,b). Interested readers should consult the appropriate neurophysiological texts for more information. Surface electrodes are designed to give information about the whole of a muscle stimulated, providing data for the time taken for the fastest axons to conduct an impulse to the muscle and the size of the response. However, needle recordings are most appropriate when severe muscle wasting has occurred, or when the depth of a muscle under study makes a surface recording impossible (quoted from Mallik & Weir 2005). It can, by determining the distribution of neurogenic abnormalities, differentiate focal nerve, plexus, or radicular pathology; it can also provide supportive evidence of the pathophysiology of peripheral neuropathy, either axonal degeneration or demyelination. Recordings are made with a disposable concentric needle electrode inserted into the muscle. A fine wire in the axis of the needle is insulated from the shaft, the end of the needle being cut at an acute angle. The many hundreds of muscle fibres belonging to one motor unit are distributed widely throughout the cross-section of the muscle, and therefore within the detection region of the needle there may be just four to six fibres of a single motor unit. Analysis of the waveforms and firing Clinical Assessment rates of single motor or multiple motor units can give diagnostic information. Electromyographers are skilled at interpreting both the appearance of muscle activity and the sound of the activity transmitted through a loudspeaker. Neurophysiology offers the most sensitive diagnostic tests for disorders of neuromuscular transmission. Repetitive nerve stimulation shows a decrementing response in myasthenia gravis, the decrement being more pronounced in proximal muscles. In LambertEaton myasthenic syndrome, the compound muscle action potential evoked in hand muscles is small and increases dramatically after exercise. Lezak (1995) reviews the now extensive literature of this simple test and the sometimes elaborate scoring procedures employed. Visual Object and Space Perception Battery Warrington and James (1991) have introduced a nine-test battery for exploring visual perception that can be given in parts or as a whole. Minimal motor response is required from the patient so that any praxic element is eliminated. The first test screens for visual impairment, which might preclude proceeding further. The next four tests show views of letters, animals or objects that have been rendered puzzling in various ways. In Incomplete Letters, the subject has to identify a series of randomly degraded letters. Silhouettes requires the subject to identify animals and inanimate objects depicted as black silhouettes and rotated through various degrees. In Object Decision the subject has to choose which of a group of silhouettes, again rotated, represents a real as opposed to an imaginary object. In Progressive Silhouettes the subject sees two series of silhouettes, each representing a single object, presented at a series of angles that gradually approach normality. In Position Discrimination the subject must decide which of two squares, presented side by side, has the dot exactly in the centre. Number Location consists of two squares one above the other; in the lower display there is a single dot, and the subject must say which number in the square above corresponds to its position. Cube Analysis requires the subject to count the number of cubes depicted in line drawings of three-dimensional displays. This may be valuable in the investigation of conversion disorders and chronic fatigue syndromes. The main safety concern is the need for caution in patients with a cardiac pacemaker.
However blood pressure medication knee pain buy cheap plavix 75 mg on-line, one study comparing survivors of stroke with Cerebrovascular Disorders 485 Box 8 blood pressure supplements order plavix 75mg with mastercard. These symptoms may include loss of energy blood pressure medication green pill buy plavix 75 mg with amex, appetite and libido; altered sleeping pattern; and poor concentration or inability to make decisions · Abnormal appearance of the emotional status may give the appearance of depression prehypertension at 19 generic plavix 75mg otc. A systematic review of studies of depression after stroke found that the estimates of the prevalence of depression vary according to which rating scales have been used (Hackett & Anderson 2005), but that even using clinical assessments. Nevertheless, when the findings across studies were collated the pooled estimates were fairly consistent, indicating that about one-third of patients had significant depressive symptoms, regardless of whether the cases were ascertained from the community, from hospital or from rehabilitation settings. The pooled estimates of the time course of depression were largely based on different cross-sectional studies, each study assessing depression at a different time after stroke; only a small minority of studies had longitudinally assessed depression. Whether the study was early, in the first few weeks and months after stroke, or late, on average the rate of depression did not change. However, even though the rate of depression at each time point remains fairly constant, depression early after stroke has a good chance of remitting over the course of the first year; this is counterbalanced by the finding that other patients become depressed for the first time many months after stroke. Nevertheless, some longitudinal studies show a trend for rates of depression to decline over the first 12 years (Morris et al. Based on the same systematic review of papers, Hackett and Anderson (2005) found that the best predictor of depression was stroke severity, including the extent of physical disability and cognitive impairment. One matter of interest is whether the laterality of the stroke is related to depression. Early studies suggested that left hemisphere infarcts, particularly if located anteriorally, were more likely to produce depression (Robinson & Price 1982; Robinson et al. More recent studies have failed to demonstrate an effect of laterality (Verdelho et al. It seems likely that biological factors will be especially important in the early weeks following the infarct (Nys et al. Clinical wisdom suggests that depression will be strongly determined by aspects of the premorbid personality. Patients of striving and self-sufficient disposition may react more adversely to handicap and those who have experienced anxiety and depressive reactions under previous stress will be at increased risk. Much will also depend on the family setting and relationships with which the patient is surrounded. Quite frequently, at the era of life where most strokes occur, the patient is relatively unsupported: the spouse may have died or be infirm, and children will have moved away. In their systematic review Hackett and Anderson (2005) found that adverse social factors, particularly those related to social isolation, are associated with depression. However, it was less easy to demonstrate, consistently across studies, effects of age, personal history of depression or stroke subtype. Possible reasons for the discrepancies among the different investigations are likely to include differing levels of physical and cognitive impairment, pre-existing brain damage as well as the time elapsed since the stroke occurred. A host of psychosocial variables in the samples studied may be important, including the proportion of patients having religious beliefs, which may protect against the development of depression (Giaquinto et al. On occasion it may be difficult to recognise depression, especially when the development has been insidious. Sometimes it is masked by stoical attitudes, or absorbed into 486 Chapter 8 habitual or automatic patterns of behaviour. Stroke is associated with suicidal thoughts in perhaps 10% of patients (Kishi et al. Depression may lead to lack of cooperation or poor motivation for rehabilitation, and is associated with generally worse outcomes (Williams 2005) and greater use of health care (Jia et al. Depression early after stroke increases mortality over the subsequent years (Morris et al. Indeed depression probably increases the risk of having a stroke in the first place (Williams 2005). Emotionalism after stroke A heightened tendency to cry, often uncontrollably and with little warning, has traditionally been attributed to pseudobulbar palsy resulting from bilateral lesions of the corticobulbar tracts. However, the disorder has broader connotations, and is not uncommon as an embarrassing and disabling aftermath of strokes. The criteria were that the patient should experience an increase in episodes of crying (or more rarely laughing), with little or no warning, and with an inability to control them. All showed crying as the principal problem, but two had episodes of pathological laughter in addition. In most the disorder had set in during the 46 weeks following the stroke, with a tendency to ameliorate over the following year.